| Superior medullary velum | |
|---|---|
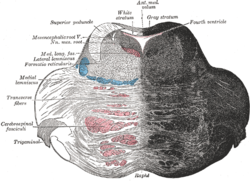 Transverse section of the pons, at its upper part. (Ant. med. velum labeled at center top.) Transverse section of the pons, at its upper part. (Ant. med. velum labeled at center top.) | |
 Anterior view of the cerebellum. (Ant. medullary velum labeled at center top.) Anterior view of the cerebellum. (Ant. medullary velum labeled at center top.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | velum medullare superius |
| NeuroNames | 593 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1300 |
| TA98 | A14.1.05.007 A14.1.05.719 |
| TA2 | 5976 |
| FMA | 74508 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy[edit on Wikidata] | |
The superior medullary velum (anterior medullary velum) is a thin, transparent lamina of white matter which - together with the inferior medullary velum - forms the roof of the fourth ventricle. It extends between the two superior cerebellar peduncles. The lingula of cerebellum covers - and adheres to - its dorsal surface.
Anatomy
Relations
The superior medullary velum extends between the dorsomedial margins of the two superior cerebellar peduncles. On the dorsal surface of its lower half the folia and lingula are prolonged.
It forms, together with the superior cerebellar peduncle, the roof of the upper part of the fourth ventricle; it is narrow above, where it passes beneath the facial colliculi, and broader below, where it is continuous with the white substance of the superior vermis.
A slightly elevated ridge, the frenulum veli, descends upon its upper part from between the inferior colliculi, and on either side of this the trochlear nerve emerges.
Blood supply
Blood is supplied by branches from the superior cerebellar artery.
Additional images
-
 Scheme of roof of fourth ventricle. 1. Posterior medullary velum 2. Choroid plexus 3. Cisterna cerebellomedullaris of subarachnoid cavity 4. Central canal 5. Corpora quadrigemina 6. Cerebral peduncle 7. Anterior medullary velum 8. Ependymal lining of ventricle 9. Cisterna pontis of subarachnoid cavity (Arrow = Flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) through foramen of Magendie)
Scheme of roof of fourth ventricle. 1. Posterior medullary velum 2. Choroid plexus 3. Cisterna cerebellomedullaris of subarachnoid cavity 4. Central canal 5. Corpora quadrigemina 6. Cerebral peduncle 7. Anterior medullary velum 8. Ependymal lining of ventricle 9. Cisterna pontis of subarachnoid cavity (Arrow = Flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) through foramen of Magendie)
-
 Mesal aspect of a brain sectioned in the median sagittal plane.
Mesal aspect of a brain sectioned in the median sagittal plane.
-
 Rhomboid fossa.
Rhomboid fossa.
-
Human brain midsagittal view description
-
Fourth ventricle. Posterioe view.Deep dissection.
See also
References
- ^ Waxman, Stephen G. (2009). Clinical Neuroanatomy (26th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. p. 150. ISBN 978-0-07-160399-7.
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 793 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 793 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Atlas image: n2a8p1 at the University of Michigan Health System
| Anatomy of the cerebellum | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface |
| ||||
| Grey matter |
| ||||
| White matter | |||||
| Anatomy of the pons | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dorsal/ (tegmentum) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Ventral/ (base) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Other grey: Raphe/ reticular | |||||||||||||||
| Ventricular system of the human brain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lateral ventricles |
| ||||||||
| Third ventricle | |||||||||
| Fourth ventricle |
| ||||||||
| Cerebrospinal fluid | |||||||||
| Related | |||||||||
This neuroanatomy article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |