 Anhydrous | |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
Vanadium(III) chloride Vanadium trichloride | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.859 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UN number | 2475 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | VCl3 |
| Molar mass | 157.30 g/mol |
| Appearance | violet crystals (anhydrous) green crystals (hexahydrate) |
| Density | 2.8 g/cm (anhydrous) 1.84 g/cm (hexahydrate) |
| Melting point | 350 °C (662 °F; 623 K) (decomposes, anhydrous) |
| Solubility in water | soluble |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | +3030.0·10 cm/mol |
| Structure | |
| Crystal structure | Trigonal, hR24 |
| Space group | R3, No. 148 |
| Lattice constant | a = 6.012 Å, b = 6.012 Å, c = 17.34 Åα = 90°, β = 90°, γ = 120°(anhydrous) |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Heat capacity (C) | 93.2 J mol K |
| Std molar entropy (S298) |
131.0 J mol K |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH298) |
-580.7 kJ/mol |
| Gibbs free energy (ΔfG) | -511.2 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |  
|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H302, H314 |
| Precautionary statements | P260, P264, P270, P280, P301+P312+P330, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340+P310, P305+P351+P338+P310, P363, P405, P501 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Vanadium(III) Chloride |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Vanadium(III) fluoride Vanadium(III) bromide Vanadium(III) iodide |
| Other cations | Titanium(III) chloride Chromium(III) chloride Niobium(III) chloride Tantalum(III) chloride |
| Related compounds | Vanadium(II) chloride Vanadium(IV) chloride |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Vanadium(III) chloride describes the inorganic compound with the formula VCl3 and its hydrates. It forms a purple anhydrous form and a green hexahydrate Cl·2H2O. These hygroscopic salts are common precursors to other vanadium(III) complexes and is used as a mild reducing agent.
Structure and electronic configuration
VCl3 has the common layered BiI3 structure, a motif that features hexagonally closest-packed chloride framework with vanadium ions occupying the octahedral holes. VBr3 and VI3 adopt the same structure, but VF3 features a structure more closely related to ReO3. The Vcation has a d electronic configuration with two unpaired electrons, making the compound paramagnetic. VCl3 is a Mott insulator and undergoes an antiferromagnetic transition at low temperatures.
Solid hexahydrate, Cl·2H2O, has a monoclinic crystal structure and consists of slightly distorted octahedral trans- centers as well as chloride and two molecules of water of crystallization. The hexahydrate phase loses two water of crystallization to form the tetrahydrate if heated to 90 °C in a stream of hydrogen chloride gas.
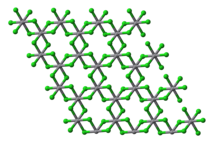 Plan view of a single layer in the crystal structure of vanadium(III) chloride
Plan view of a single layer in the crystal structure of vanadium(III) chloride Layer stacking in the crystal structure of vanadium(III) chloride
Layer stacking in the crystal structure of vanadium(III) chloride Unit cell of hexahydrate, featuring centres
Unit cell of hexahydrate, featuring centres
Uses
Solutions of vanadium(III) chloride in sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid are used as electrolytes in vanadium redox batteries. It is also used as a mild Lewis acid in organic synthesis. One example of such is its use as a catalyst in the cleavage of the acetonide group. Another example of the use of VCl3 as a reducing agent is shown in the determination of nitrate and nitrite concentration in water, where VCl3 reduces nitrate to nitrite. This method is a safer alternative to the cadmium column method.
Preparation
VCl3 is prepared by heating VCl4 at 160–170 °C under a flowing stream of inert gas, which sweeps out the Cl2. The bright red liquid converts to a purple solid.
The vanadium oxides can also be used to produce vanadium(III) chloride. For example, vanadium(III) oxide reacts with thionyl chloride at 200 °C:
- V2O3 + 3 SOCl2 → 2 VCl3 + 3 SO2
The reaction of vanadium(V) oxide and disulfur dichloride also produces vanadium(III) chloride with the release of sulfur dioxide and sulfur.
The hexahydrate can be prepared by evaporation of acidic aqueous solutions of the trichloride.
Reactions
Heating of VCl3 decomposes with volatilization of VCl4, leaving VCl2 above 350 °C. Upon heating under H2 at 675 °C (but less than 700 °C), VCl3 reduces to greenish VCl2.
- 2 VCl3 + H2 → 2 VCl2 + 2 HCl
Comproportionation of vanadium trichloride and vanadium(V) oxides gives vanadium oxydichloride:
- V2O5 + VOCl3 + 3 VCl3 → 6 VOCl2
The heating of the hexahydrate does not give the anhydrous form, instead undergoes partial hydrolysis and forms vanadium oxydichloride at 160 °C. In an inert atmosphere, it forms a trihydrate at 130 °C and at higher temperatures, it forms vanadium oxychloride.
Vanadium trichloride catalyses the pinacol coupling reaction of benzaldehyde (PhCHO) to 1,2-diphenyl-1,2-ethanediol by various reducing metals such as zinc:
- Zn + 2 H2O + 2 PhCHO → (PhCH(OH))2 + Zn(OH)2
Complexes
VCl3 forms colorful adducts and derivatives with a broad scale of ligands. VCl3 dissolves in water to give the aquo complexes. From these solutions, the hexahydrate Cl2H2O crystallizes. In other words, two of the water molecules are not bound to the vanadium, whose structure resembles the corresponding Fe(III) derivative. Removal of the two bound chloride ligands gives the green hexaaquo complex .


With tetrahydrofuran, VCl3 forms the red/pink complex VCl3(THF)3. Vanadium(III) chloride reacts with acetonitrile to give the green adduct VCl3(MeCN)3. When treated with KCN, VCl3 converts to (early metals commonly adopt coordination numbers greater than 6 with compact ligands). Complementarily, larger metals can form complexes with rather bulky ligands. This aspect is illustrated by the isolation of VCl3(NMe3)2, containing two bulky NMe3 ligands. Vanadium(III) chloride is able to form complexes with other adducts, such as pyridine or triphenylphosphine oxide.
Organometallic derivatives
Vanadium(III) chloride as its thf complex is a precursor toV(mesityl)3.
- VCl3(THF)3 + 3 LiC6H2-2,4,6-Me3 → V(C6H2-2,4,6-Me3)3(THF) + 3 LiCl
References
- ^ Sally M. Horner; S. Y. Tyree (1964). "Chloro-Aquo Complexes of Vanadium(III)". Inorganic Chemistry. 3 (8): 1173–1176. doi:10.1021/ic50018a024.
- ^ Yajima Akimasa; Matsuzaki Ryoko; Saeki Yuzo (1979). "The Thermal Decomposition of Vanadium(III) Chloride Oxide and Its Reaction with Oxygen". Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan. 52 (11): 3292–3295. doi:10.1246/bcsj.52.3292.
- ^ Wilhelm Klemm; Ehrhard Krose (1947). "Die Kristallstrukturen von ScCl3, TiCl3 und VCl3" [The Crystal Structures of ScCl3, TiCl3 and VCl3]. Zeitschrift für anorganische Chemie (in German). 253 (3–4): 218–225. doi:10.1002/zaac.19472530313.
- John Rumble (June 18, 2018). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (99 ed.). CRC Press. pp. 5–40. ISBN 978-1-138-56163-2.
- "Vanadium(III) Chloride SDS". American Elements. Retrieved 2018-08-17.
- Holleman, A. F.; Wiberg, E. Inorganic Chemistry Academic Press: San Diego, 2001. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
- ^ Mastrippolito, Dario; Camerano, Luigi; Świątek, Hanna; Šmíd, Břetislav; Klimczuk, Tomasz; Ottaviano, Luca; Profeta, Gianni (2023-07-17). "Polaronic and Mott insulating phase of layered magnetic vanadium trihalide VCl3". Physical Review B. 108 (4): 045126. arXiv:2301.06501. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.108.045126. S2CID 255942777.
- Greenwood, N. N. and Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd Edn.), Oxford:Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 990 ISBN 0-7506-3365-4.
- Starr, C.; Bitter, F.; Kaufmann, A. R. (1940-12-01). "The Magnetic Properties of the Iron Group Anhydrous Chlorides at Low Temperatures. I. Experimental". Physical Review. 58 (11): 977–983. Bibcode:1940PhRv...58..977S. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.58.977.
- ^ Donovan, William F.; Smith, Peter W. (1975). "Crystal and Molecular Structures of Aquahalogenovanadium(III) Complexes. Part I. X-Ray Crystal Structure of trans-Tetrakisaquadibromo-Vanadium(III) Bromide Dihydrate and the Isomorphous Chloro- Compound". Journal of the Chemical Society, Dalton Transactions (10): 894. doi:10.1039/DT9750000894.
- Fiona H. Fry; Brenda Dougan; Nichola McCann; Anthony C. Willis; Christopher J. Ziegler; Nicola E. Brasch (2008). "Synthesis and X-ray structural characterization of tris(l-glycinato)vanadium(III) and trans-tetraquadichlorovanadium(III) chloride". Inorganica Chimica Acta. 361 (8): 2321–2326. doi:10.1016/j.ica.2007.11.025.
- Günter Bauer; Volker Güther; Hans Hess; Andreas Otto; Oskar Roidl; Heinz Roller; Siegfried Sattelberger; Sven Köther-Becker; Thomas Beyer (2017). Vanadium and Vanadium Compounds. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA. p. 16. doi:10.1002/14356007.a27_367.pub2. ISBN 978-3-527-30385-4.
- Gowravaram Sabitha; G.S. Kiran Kumar Reddy; K. Bhaskar Reddy; N. Mallikarjuna Reddy; J.S. Yadav (2005). "Vanadium(III) chloride: A mild and efficient catalyst for the chemoselective deprotection of acetonides". Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical. 238 (1–2): 229–232. doi:10.1016/j.molcata.2005.05.028.
- Bernhard Schnetger; Carola Lehners (2014). "Determination of nitrate plus nitrite in small volume marine water samples using vanadium(III)chloride as a reduction agent". Marine Chemistry. 160: 91–98. Bibcode:2014MarCh.160...91S. doi:10.1016/j.marchem.2014.01.010.
- ^ Georg Brauer (1975). Handbuch der präparativen anorganischen Chemie Volume 3 (in German). the University of Michigan: Enke. p. 1409. ISBN 978-3-432-87823-2.
- Young, Ralph C.; Smith, Maynard E.; Moeller, Therald; Gordon, Paul G.; McCullough, Fred (2007). "Vanadium(III) Chloride". Inorganic Syntheses. pp. 128–130. doi:10.1002/9780470132357.ch43. ISBN 978-0-470-13235-7.
- G. Brauer (1963). "Vanadium Oxydichloride". In G. Brauer (ed.). Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed. NY: Academic Press. p. 1263.
- Ray Colton; J. H. Canterford (1969). Halides of the first row transition metals. Wiley. p. 131. ISBN 978-0-471-16625-2.
- Xu; Hirao, Toshikazu (2005). "Vanadium-Catalyzed Pinacol Coupling Reaction in Water". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 70 (21): 8594–8596. doi:10.1021/jo051213f. PMID 16209617.
- ^ D. Nicholls (1966). "The coordination chemistry of vanadium". Coordination Chemistry Reviews. 1 (3): 379–414. doi:10.1016/S0010-8545(00)80145-9.
- Albert Cotton, F.; Duraj, Stan A.; Powell, Gregory L.; Roth, Wieslaw J. (1986). "Comparative Structural Studies of the First Row Early Transition Metal(III) Chloride Tetrahydrofuran Solvates". Inorganica Chimica Acta. 113: 81. doi:10.1016/S0020-1693(00)86863-2.
- Manzer, L. E. (1982). "31. Tetragtdrfuran Complexes of Selected Early Transition Metals". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 21. pp. 135–140. doi:10.1002/9780470132524.ch31. ISBN 978-0-471-86520-9.
- Vivanco, Marilin; Ruiz, Javier; Floriani, Carlo; Chiesi-Villa, Angiola; Rizzoli, Corrado (1993). "Chemistry of the vanadium-carbon .sigma. Bond. 2. Oxovanadium(IV) and oxovanadium(V) containing metal-to-carbon .sigma. Bonds". Organometallics. 12 (5): 1802–1810. doi:10.1021/om00029a042.
| Vanadium compounds | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vanadium(0) | |||||
| Vanadium(II) | |||||
| Vanadium(III) |
| ||||
| Vanadium(IV) |
| ||||
| Vanadium(V) |
| ||||