| Revision as of 04:01, 26 March 2014 view source116.118.39.68 (talk)No edit summary← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 02:51, 19 December 2024 view source Furnier242 (talk | contribs)198 editsmNo edit summary | ||
| (732 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{ |
{{Short description|German automobile manufacturer}} | ||
| {{About|the automotive brand and manufacturer, Porsche AG|the holding company that is the majority owner of Volkswagen Group|Porsche SE|other uses of Porsche|Porsche (disambiguation)|}} | |||
| {{Expand German|Porsche|date=August 2012}} | |||
| {{pp-vandalism|small=yes}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=October 2012}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=January 2024}} | |||
| {{Infobox company | {{Infobox company | ||
| |name |
| name = Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG | ||
| | native_name = | |||
| |logo = ]<br>] | |||
| | image_caption = Headquarters in Stuttgart | |||
| |caption = | |||
| | trading_name = | |||
| |type = ] (]) | |||
| | logo = Porsche logo.svg | |||
| |traded_as = {{fwb|PAH3}} | |||
| | logo_size = 200 | |||
| |foundation = Stuttgart, Germany (1931) | |||
| | image = Porsche headquarter Stuttgart-Zuffenhausen Werk II.jpg | |||
| |founder = ] | |||
| | image_size = | |||
| |location = ], ], Germany | |||
| | type = ] | |||
| |area_served = Worldwide | |||
| | traded_as = {{FWB|P911|isin=DE000PAG9113}}<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.reuters.com/markets/europe/porsche-shares-fall-below-ipo-pricing-2022-10-03/ |title=Porsche shares fall below IPO pricing |first1=Lucy |last1=Raitano |website=] |date=2022-10-03}}</ref><br/>] component<br/>{{OTC Pink|DRPRY}} | |||
| |key_people = Wolfgang Porsche, ]<br>], ] & ]<br>], New ] & ] of 28 February 2014 | |||
| | ISIN = {{ISIN|sl=n|pl=y|DE000PAG9113}} | |||
| |industry = ] | |||
| | foundation = {{Start date and age|df=yes|1931}} in ], Germany | |||
| |services = Automotive ], engineering services, investment management | |||
| | founder = ] | |||
| |profit for the year = {{increase}} €2.591 billion (2013 annual report) | |||
| | location = Stuttgart, Germany | |||
| |net_income = {{increase}} €2.408 billion (2013 annual report) | |||
| | area_served = Worldwide | |||
| |assets = {{increase}} €31.285 billion (2013 annual report) | |||
| | key_people = ] (chairman)<br>] (])<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.porsche.com/usa/aboutporsche/overview/executiveboard/|title=The Board of Management of Porsche AG - All BOM members - Porsche USA|website=Porsche HOME - Porsche USA}}</ref> | |||
| |equity = {{increase}} €30.470 billion (2013 annual report) | |||
| | industry = ] | |||
| |owner = ] (29%)<br>] (75%)<br>] (10%) | |||
| | products = ]s | |||
| |num_employees = 35 (2013 annual report) | |||
| | production = {{increase}} 321,321 vehicles<ref name=FY2022>{{Cite web|url=https://newsroom.porsche.com/dam/jcr:97e6ac62-edd8-4312-9462-b4fe0c271396/Annual%20and%20Sustainability%20Report%202022%20Porsche%20AG.pdf|title=Annual and Sustainability Report 2022 Porsche AG.pdf | |||
| |parent = | |||
| |date=15 March 2023|website=Porsche Newsroom}}</ref> | |||
| |subsid = ]<br>Porsche Zwischenholding GmbH<br>] | |||
| | production_year = 2022 | |||
| |homepage = <br> | |||
| | services = Automotive ], engineering services, investment management | |||
| |intl = yes | |||
| | revenue = {{increase}} €37.630 billion (2022)<ref name=FY2022/> | |||
| | operating_income = {{increase}} €6.770 billion (2022)<ref name=FY2022/> | |||
| | net_income = {{increase}} €4.957 billion (2022)<ref name=FY2022/> | |||
| | assets = {{decrease}} €47.673 billion (2022)<ref name=FY2022/> | |||
| | equity = {{decrease}} €17.027 billion (2022)<ref name=FY2022/> | |||
| | owners = {{unbulleted list|] (75%)|] (12.5%)|] (2.5%)<ref name=":1"/>}} | |||
| | num_employees = 39,162 (2022)<ref name=FY2022/> | |||
| | parent = | |||
| | subsid = {{unbulleted list|] (81.8%)|Porsche Consulting |] (45%)}} | |||
| | homepage = {{URL|https://www.porsche.com}} | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Porsche Automobil Holding ]''', usually shortened to '''Porsche''' ({{IPA-de|ˈpɔʁʃə|-|De-Porsche.ogg}}<ref>{{cite web |title=How do you say 'Porsche'? |publisher=] |url=http://german.about.com/library/weekly/aa020401b.htm |accessdate=26 June 2009}}</ref>), is a German ] with investments in the ]. | |||
| '''Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG''', usually shortened to '''Porsche''' ({{IPA|de|ˈpɔʁʃə|-|de-Porsche.ogg}}<small>; see ]</small>), is a German automobile manufacturer specializing in luxury, high-performance ]s, ] and ], headquartered in ], ], Germany. The company is owned by ], a controlling stake of which is owned by ]. Porsche's current lineup includes the ], ], ], ], ] and ]. | |||
| Porsche SE is headquartered in ], a city district of ], ] and is owned by the ] families. In July 2012, it was announced that Volkswagen ] was taking over the Porsche automotive company completely, which bears the same name, but is only a subsidiary of Porsche SE.<ref name="AOL Autos">{{cite web |url=http://www.autoblog.com/2012/07/05/volkswagen-finally-really-taking-over-porsche/ |title=Volkswagen finally, really, taking over Porsche |accessdate=5 July 2012 |publisher=AOL Autos |date=5 July 2012}}</ref><ref name="Porsche structure">{{cite web |url=http://www.porsche-se.com/pho/en/porschese/holdingstructure/ |title=Porsche corporate structure |accessdate=13 February 2013}}</ref> In June 2013, Qatar Holdings, through the ], sold its 10% holding back to the founding family, giving them 100% control.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.porsche-se.com/pho/en/press/newsarchive2009/?pool=pho&id=2009-08-14-01 |title=Porsche SE press release 14 August 2009 |publisher=Porsche-se.com |date= |accessdate=1 August 2011}}</ref> Porsche SE currently owns 50.73% of the voting rights in ].<ref name=interim2011>{{cite web |title=Volkswagen Aktiengesellschaft Interim Report January - September 2011 |url=http://www.volkswagenag.com/content/vwcorp/content/en/misc/ir/ir-webcasting.bin.html/downloadfilelist/downloadfile/downloadfile/file/Q3_2011_e.pdf |date=27 October 2011 |work=www.volkswagenag.com |publisher=Volkswagen AG |accessdate=5 November 2011|page=39}}</ref>In December 2013, Porsche Owner 29% of ]. | |||
| The origins of the company date to the 1930s when Czech-German automotive engineer ] founded Porsche<ref name="Auto" /> with ], a keystone figure in the creation of German automotive manufacturer and ] precursor ],<ref>{{Cite web |last=Sherman |first=Don |date=9 August 2018 |title=The Story of Adolf Rosenberger |url=https://www.hagerty.com/media/people/the-story-of-adolf-rosenberger/ |access-date=29 November 2023 |website=Hagerty}}</ref> and ]n businessman ], who was, at the time, also Ferdinand Porsche's son in law. In its early days, it was contracted by the ] to create a vehicle for the masses, which later became the ].<ref name=":3" /> After ], when Ferdinand, a member of both the ] and the ], would be arrested for ]s, his son ], an ] volunteer, began building his own car, which would result in the ]. | |||
| The company was founded in Stuttgart as ''Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche ]'' in 1931 by ] (1875–1951),<ref name="porsche-trad-ferdinand">{{cite web|url=http://www.porsche.com/international/accessoriesandservice/classic/world/tradition/ferdinand/|title=Ferdinand Porsche|work=www.porsche.com|publisher=Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG|accessdate=13 January 2010}} {{Dead link|date=November 2010|bot=H3llBot}}</ref> his son-in-law ] (1894–1952). | |||
| In 2009, Porsche entered an agreement with ] to create an 'integrated working group' by merging the two companies' car manufacturing operations.<ref name="PorscheMerger" /><ref name=":4" /> By 2015, ], the holding company spun off from the original Porsche firm, had a controlling interest in the ], which included Audi and ] as subsidiaries.<ref name=":5" /> | |||
| ==Corporate structure== | |||
| ], ]]] | |||
| Porsche SE is the owner of Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG ('''Porsche AG'''), and in June 2007 became a holding company for its stake in Porsche Zwischenholding GmbH (50.1%) (which in turn holds 100% of Porsche AG) and Volkswagen AG (50.7%).<ref>{{cite news|last=Rauwald |first=Christoph |url=http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748704122904575314062459444270.html |title=Wall Street Journal 18 June 2010 |publisher=Online.wsj.com |date=18 June 2010 |accessdate=1 August 2011}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.porsche-se.com/pho/en/porschese/holdingstructure/ |title=Porsche SE Investor Relations |publisher=Porsche-se.com |date= |accessdate=1 August 2011}}</ref> In August 2009, Porsche SE and ] reached an agreement that the two companies would merge in 2011, to form an "Integrated Automotive Group".<ref name=PorscheMerger>{{cite press release|title=Porsche Supervisory Board agrees on the contracts of implementation|url=http://www.porsche-se.com/pho/en/news/?pool=pho&id=2009-11-20|publisher=Porsche Automobil Holding SE, Stuttgart|date=20 November 2009|accessdate=22 November 2009}}{{dead link|date=February 2014}}</ref><ref name=VWAG_merger>{{cite press release|url=http://www.volkswagenag.com/vwag/vwcorp/info_center/en/news/2009/08/Volkswagen_Aufsichtsrat_stimmt_Grundlagenvereinbarung_fuer.html|title=Volkswagen Supervisory Board approves Comprehensive Agreement for an Integrated Automotive Group with Porsche|publisher=]|date=13 August 2009|accessdate=22 November 2009}}</ref> During December 2009, Porsche SE lost control of Porsche Zwischenholding GmbH, which as a result is now a joint venture between Porsche SE and Volkswagen AG. As of 5 July 2012, Volkswagen is to acquire the 50.1 percent in Porsche's capital that it doesn't already hold from holding company Porsche SE for €4.46 billion plus one Volkswagen share. | |||
| ==History== | |||
| '''Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG''' (which stands for ''Doktor Ingenieur ] Ferdinand Porsche ]''), is responsible for the actual production and manufacture of the Porsche automobile line. The company currently produces ], ] and ] sports cars, the ] and Macan ] and the four-door ]. | |||
| === |
===Origin=== | ||
| ] (1875–1951) founded the company called "Dr. Ing. h. c. F. Porsche ]"<ref name=Auto>{{cite web|author=J. P. Vettraino|title=Porsche at 60: The little sports-car company that could|url=http://www.autoweek.com/article/20081222/FREE/812229989|work=]|date=23 December 2008|access-date=30 January 2009|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090206230009/http://www.autoweek.com/article/20081222/FREE/812229989|archive-date=6 February 2009|url-status=dead}}</ref> with ]<ref>Automobile Quarterly, Volume 18, Issue 4, Automobile Quarterly, 1980</ref> and ] in 1931.<ref>{{cite web |last=Klawitter |first=Nils |title=The Dark Pre-History of the World's Favorite Sports Car |url=http://www.spiegel.de/international/germany/porsche-s-past-the-dark-pre-history-of-the-world-s-favorite-sports-car-a-652371.html |publisher=] |date=1 October 2009}}</ref> The name is short for Ferdinand Porsche's full title in German, Doktor Ingenieur honoris causa {{literal translation|Doctor of Engineering, Honorary Degree}} Ferdinand Porsche.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Girl |first=Pepper |date=2011 |title=Just what do all the initials in Porsche's Corporate Names Mean Anyway? |url=https://flatsixes.com/porsche-culture/porsche-factoids/porsche-corporate-acronyms/ |access-date=28 November 2023 |website=Flatsixes}}</ref> The main offices was at Kronenstraße 24 in the centre of ].<ref name=Historie>{{cite web|title=Historie - Porsche Engineering |url=https://www.porscheengineering.com/peg/de/about/history/ |publisher=Porsche Engineering |access-date=23 February 2016}}</ref> Initially, the company offered motor vehicle development work and consulting,<ref name=Auto/> but did not build any cars under its own name. One of the first assignments the new company received was from the German government to design a car for the people; that is, a '']<nowiki/>swagen''.<ref name=Auto/> This resulted in the ], one of the most successful car designs of all time.<ref name=":3">{{cite web|url=http://www.automotivehalloffame.org/honors/index.php?cmd=view&id=4&type=inductees|title=Béla Barényi (1907–1997)|work=]|access-date=25 March 2009|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091101143217/http://www.automotivehalloffame.org/honors/index.php?cmd=view&id=4&type=inductees|archive-date=1 November 2009}}</ref> Later, the ] would be developed in 1939 using many components from the Beetle.<ref name=Auto/> | |||
| ]'s ]]] | |||
| Other subsidiaries and operating divisions include Porsche Consulting, Porsche Engineering, ], ] (81.1%)<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.mhp.de/Company.10+M5519f187cad.0.html |title=Mieschke Hofmann website |publisher=Mhp.de |date= |accessdate=1 August 2011}}</ref> and ] (25%).<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.bertrandt.com/en/Corporate-history.html |title=Bertrandt website |publisher=Bertrandt.com |date= |accessdate=1 August 2011}}{{dead link|date=February 2014}}</ref> | |||
| ]'' – after the loss of the contract to the Tiger I, Porsche recycled his design into a ].]] | |||
| During ],<ref name=Beetle>{{cite book |last=Burt |first=William |title=Volkswagen Beetle |publisher=MotorBooks/MBI Publishing Company |year=2002 |page=14 |isbn=978-0-7603-1078-6}}</ref> ] production turned to the military version of the Volkswagen Beetle, the ],<ref name=Beetle/> 52,000 produced, and ],<ref name=Beetle/> 15,584 produced.<ref>See ].</ref> Porsche produced several designs for ]s during the war, losing out to ] in both contracts that ultimately led to the ] and the ]. However, not all this work was wasted, as the chassis Porsche designed for the Tiger I was used as the base for the ] ]. Porsche also developed the ] ] in the closing stages of the war, producing two prototypes.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.achtungpanzer.com/panzerkampfwagen-viii-maus-porsche-typ-205-tiger-iip.htm|title=Panzerkampfwagen VIII Maus Porsche Typ 205 / Tiger II(P)|access-date=4 May 2011|work=Achtung Panzer|archive-date=16 March 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180316103737/http://www.achtungpanzer.com/panzerkampfwagen-viii-maus-porsche-typ-205-tiger-iip.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref> Ferdinand Porsche's biographer, Fabian Müller, wrote that Porsche had thousands of people forcibly brought to work at their factories during the war. The workers wore the letter "P" on their clothing at all times. It stood not for "Porsche", but for "Poland".<ref>{{cite web|last=Klawitter|first=Nils|date=1 October 2009|title=Porsche's Past: The Dark Pre-History of the World's Favorite Sports Car|url=https://www.spiegel.de/international/germany/porsche-s-past-the-dark-pre-history-of-the-world-s-favorite-sports-car-a-652371.html|website=www.spiegel.de}}</ref> | |||
| Porsche Engineering Group (PEG) has for many years offered consultancy services to various other car manufacturers. ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and others have consulted Porsche Engineering Group for their cars or engines. The ]<ref>{{Dead link|date=March 2010}}</ref> was partly developed by Porsche in 1984. Porsche Engineering Group also helped ] design the Revolution 60-degree v-twin water-cooled engine and gearbox that is used in their V-Rod motorcycle.<ref>{{cite news|last=McCraw|first=Jim|title=A Harley Takes an Engine From Porsche|url=http://www.nytimes.com/2002/05/26/automobiles/a-harley-takes-an-engine-from-porsche.html|accessdate=4 May 2011|newspaper=New York Times|date=26 May 2002}}</ref> | |||
| At the end of World War II in 1945, the ] at ] fell to the British. Ferdinand lost his position as chairman of the board of management of Volkswagen, and ], a British Army major, was put in charge of the factory. (In Wolfsburg, the Volkswagen company magazine dubbed him "The British Major who saved Volkswagen".)<ref>{{cite book|last=Mantle|first=Jonathan|title=Car wars: fifty years of greed, treachery, and skulduggery in the global marketplace|publisher=]|year=1996|page=216|isbn=978-1-55970-333-8}}</ref> On 15 December of that year, Ferdinand was arrested for war crimes, but not tried. During his 20-month imprisonment, Ferdinand Porsche's son, ], decided to build his own car, because he could not find an existing one that he wanted to buy. He also had to steer the company through some of its most difficult days until his father's release in August 1947.<ref name="Gmünd">{{cite book|last=Meredith|first=Laurence|author2=Mark Hughes|title=Original Porsche 356|publisher=MotorBooks/MBI Publishing Company|year=1995|page=7|isbn=978-1-870979-58-0}}</ref> | |||
| ==History== | |||
| ===Origin=== | |||
| ] founded the company called "Dr. Ing. h. c. F. Porsche GmbH" in 1931,<ref name=Auto>{{cite web|author=J. P. Vettraino|title=Porsche at 60: The little sports-car company that could|url=http://www.autoweek.com/article/20081222/FREE/812229989|work=]|date=23 December 2008|accessdate=30 January 2009}}</ref> with main offices at Kronenstraße 24 in the centre of ]. Initially, the company offered motor vehicle development work and consulting,<ref name=Auto/> but did not build any cars under its own name. One of the first assignments the new company received was from the German government to design a car for the people, that is a "Volkswagen".<ref name=Auto/> This resulted in the ], one of the most successful car designs of all time.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.automotivehalloffame.org/honors/index.php?cmd=view&id=4&type=inductees|title=Béla Barényi (1907–1997)|work=]|accessdate=25 March 2009}}</ref> The ] was developed in 1939 using many components from the Beetle.<ref name=Auto/> | |||
| The first models of what was to become the ] were built in a small sawmill in ], Austria.<ref name="Gmünd"/> The prototype car was shown to German auto dealers, and when pre-orders reached a set threshold, production (with aluminum body) was begun by ], founded by Ferry and ]. Many regard the 356 as the first Porsche simply because it was the first model ''sold'' by the fledgling company. After production of the 356 was taken over by the father's Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche GmbH in Stuttgart in 1950, Porsche commissioned a ]-based company, Reutter Karosserie, which had previously collaborated with the firm on Volkswagen Beetle prototypes, to produce the 356's steel body. In 1952, Porsche constructed an assembly plant (Werk 2) across the street from Reutter Karosserie; the main road in front of Werk 1, the oldest Porsche building, is now known as Porschestrasse.<ref>{{cite book|author=John Lamm|title=Porsche Boxster|publisher=MotorBooks International|url=https://archive.org/details/porscheboxster00lamm|url-access=registration|page=|year=1998|isbn=978-0-7603-0519-5}}</ref> The 356 was road-certified in 1948. | |||
| ]'s ].]] | |||
| ]'', after the loss of the contract to the Tiger I Porsche recycled his design into a ].]] | |||
| During ],<ref name=Beetle>{{cite book|last=Burt|first=William|title=Volkswagen Beetle|publisher=MotorBooks/MBI Publishing Company|year=2002|page=14|isbn=978-0-7603-1078-6}}</ref> ] production turned to the military version of the Volkswagen Beetle, the ],<ref name=Beetle/> 52,000 produced, and ],<ref name=Beetle/> 15,584 produced.<ref>See ].</ref> Porsche produced several designs for ]s during the war, losing out to ] in both contracts that ultimately led to the ] and the ]. However, not all this work was wasted, as the chassis Porsche designed for the Tiger I was used as the base for the ] ]. Porsche also developed the ] ] in the closing stages of the war, producing two prototypes.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.achtungpanzer.com/panzerkampfwagen-viii-maus-porsche-typ-205-tiger-iip.htm|title=Panzerkampfwagen VIII Maus Porsche Typ 205 / Tiger II(P)|accessdate=4 May 2011|work=Achtung Panzer}}</ref> | |||
| At the end of World War II in 1945, the ] at ] fell to the British. Ferdinand lost his position as Chairman of the Board of Management of Volkswagen, and ], a British Army Major, was put in charge of the factory. (In Wolfsburg, the Volkswagen company magazine dubbed him "The British Major who saved Volkswagen."<ref>{{cite book|last=Mantle|first=Jonathan|title=Car wars: fifty years of greed, treachery, and skulduggery in the global marketplace|publisher=]|year=1996|page=216|isbn=978-1-55970-333-8}}</ref>) On 15 December of that year, Ferdinand was arrested for war crimes, but not tried. During his 20-month imprisonment, Ferdinand Porsche's son, ], decided to build his own car, because he could not find an existing one that he wanted to buy. He also had to steer the company through some of its most difficult days until his father's release in August 1947.<ref name="Gmünd">{{cite book|last=Meredith|first=Laurence|coauthors=Mark Hughes|title=Original Porsche 356|publisher=MotorBooks/MBI Publishing Company|year=1995|page=7|isbn=978-1-870979-58-0}}</ref> The first models of what was to become the ] were built in a small sawmill in ], Austria.<ref name="Gmünd"/> The prototype car was shown to German auto dealers, and when pre-orders reached a set threshold, production was begun. Many regard the 356 as the first Porsche simply because it was the first model ''sold'' by the fledgling company. Porsche commissioned a Zuffenhausen-based company, ''Reutter Karosserie'', which had previously collaborated with the firm on Volkswagen Beetle prototypes, to produce the 356's steel body. In 1952, Porsche constructed an assembly plant (Werk 2) across the street from ''Reutter Karosserie''; the main road in front of Werk 1, the oldest Porsche building, is now known as Porschestrasse.<ref>{{cite book|author=John Lamm|title=Porsche Boxster|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=I3vlWXLcwgUC&pg=PA100|page=100|year=1998|isbn=978-0-7603-0519-5}}</ref> The 356 was road certified in 1948. | |||
| ===Company logo=== | ===Company logo=== | ||
| <gallery mode="nolines" widths="80px"> | |||
| ] ] ]]] | |||
| Wappen Volksstaat Württemberg (Farbe).svg|] of ] during the ] | |||
| ]]] | |||
| DEU Stuttgart COA.svg|] | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| Porsche's company logo was based on the ] of former ], which had Stuttgart as its capital (the same arms were used by ] from 1945-1952, while Stuttgart during these years were the capital of adjacent ]). The arms of ] was placed in the middle as an ], since the cars were made in Stuttgart. The heraldic symbols were combined with the texts "Porsche" and "Stuttgart", which shows that it is not a coat of arms since heraldic achievements never spell out the name of the ] nor the armigers home town in the shield. | |||
| Porsche's company logo stems from the ] of ] of 1918–1933, which had ] as its capital. (The ] of ] used the same arms from 1945 to 1952, while Stuttgart during these years operated as the capital of adjacent ].) The arms of Stuttgart appear in the middle of the logo as an ], for the company had its headquarters in Stuttgart. The heraldic symbols, combined with the texts "Porsche" and "Stuttgart", do not form a conventional ], since ]s never spell out the name of the ] nor the armiger's home town in the shield. | |||
| Württemberg-Baden and Württemberg-Hohenzollern became part of the present |
Württemberg-Baden and Württemberg-Hohenzollern both in 1952 became part of the present Bundesland of ] after the political consolidation of ] in 1949, but the old design of the arms of Württemberg lives on in the Porsche logo. On 30 January 1951, not long before the formation of Baden-Württemberg, Ferdinand Porsche died from complications following a stroke. | ||
| ===Developments=== | ===Developments=== | ||
| ] | |||
| ] In post-war Germany, parts were generally in short supply, so the 356 automobile used components from the Volkswagen Beetle, including the engine case from its ], ], and several parts used in the ]. The 356, however, had several evolutionary stages, A, B, and C, while in production, and most Volkswagen sourced parts were replaced by Porsche-made parts. Beginning in 1954 the 356s engines started utilizing engine cases designed specifically for the 356. The sleek bodywork was designed by ] who also had designed the body of the Beetle. Porsche's signature designs have, from the beginning, featured air-cooled rear-engine configurations (like the Beetle), rare for other car manufacturers, but producing automobiles that are very well balanced. | |||
| In post-war Germany, parts were generally in short supply, so the 356 automobile used components from the Volkswagen Beetle, including the engine case from its ], ], and several parts used in the ]. The 356, however, had several evolutionary stages, A, B, and C, while in production, and most Volkswagen-sourced parts were replaced by Porsche-made parts. Beginning in 1954 the 356s engines started utilizing engine cases designed specifically for the 356. The sleek bodywork was designed by ], who also had designed the body of the Beetle. Porsche's signature designs have, from the beginning, featured air-cooled rear-engine configurations (like the Beetle), rare for other car manufacturers, but producing automobiles that are very well balanced. | |||
| In 1964, after a fair amount of success in ] with various models including the ], and with the 356 needing a major re-design, the company launched the ]: another ], ] sports car, this time with a six-cylinder ]. The team to lay out the body shell design was led by Ferry Porsche's eldest son, ] (F. A.). The design phase for the 911 caused internal problems with Erwin Komenda, who led the body design department until then. F. A. Porsche complained Komenda made unauthorized changes to the design. Company leader Ferry Porsche took his son's drawings to neighboring chassis manufacturer Reuter. Reuter's workshop was later acquired by Porsche (so-called Werk 2). Afterward Reuter became a seat manufacturer, today known as ]. | |||
| In 1964, after a fair amount of success in ] with various models including the ], and with the 356 needing a major re-design, the company launched the ]: another ], ] sports car, this time with a six-cylinder ]. The team to lay out the body shell design was led by Ferry Porsche's eldest son, ] (F. A.). The design phase for the 911 caused internal problems with Erwin Komenda, who led the body design department until then. F. A. Porsche complained Komenda made unauthorized changes to the design. Company leader Ferry Porsche took his son's drawings to neighbouring chassis manufacturer Reuter. Reuter's workshop was later acquired by Porsche (so-called Werk 2). Afterward, Reuter became a seat manufacturer, today known as ]. | |||
| ], from the 1960s]] | |||
| ], from the 1960s]] | |||
| The design office gave sequential numbers to every project (See ]), but the designated 901 nomenclature contravened ]'s trademarks on all 'x0x' names, so it was adjusted to 911. Racing models adhered to the "correct" numbering sequence: 904, 906, 908. The 911 has become Porsche's most well-known model – successful on the race-track, in ], and in terms of road car sales. It remains in production; however, after several generations of revision, current-model 911s share only the basic mechanical configuration of a rear-engined, six-cylinder ], and basic styling cues with the original car. A cost-reduced model with the same body, but with a 356-derived four-cylinder engine, was sold as the 912. | |||
| In 1972, the company's legal form was changed from '']'' (KG), or limited partnership, to ] (AG), or public limited company, because Ferry Porsche came to believe the scale of the company outgrew a "family operation", after learning about ]'s "no family members in the company" policy at ]. This led to the establishment of an executive board with members from outside the Porsche family, and a supervisory board consisting largely of family members. With this change, most family members in the operation of the company, including F. A. Porsche and Ferdinand Piëch, departed from the company. | |||
| The design group gave sequential numbers to every project (See ]), but the designated 901 nomenclature contravened ]'s trademarks on all 'x0x' names, so it was adjusted to 911. Racing models adhered to the "correct" numbering sequence: 904, 906, 908. The 911 has become Porsche's most well-known and iconic model – successful on the race-track, in ], and in terms of road car sales. Far more than any other model, the Porsche brand is defined by the 911. It remains in production; however, after several generations of revision, current-model 911s share only the basic mechanical configuration of a rear-engined, six-cylinder ], and basic styling cues with the original car. A cost-reduced model with the same body, but with 356-derived four-cylinder engine, was sold as the 912. | |||
| F. A. Porsche founded his own design company, ], which is renowned for exclusive sunglasses, watches, furniture, and many other luxury articles. Louise's son and Ferry's nephew ], who was responsible for mechanical development of Porsche's production and racing cars (including the very successful ], ] and ] models), formed his own engineering bureau, and developed a ] ] for ]. A short time later he moved to ] (used to be a division, then a subsidiary, of Volkswagen), and pursued his career through the entire company, ultimately becoming the chairman of ]. | |||
| In 1972, the company's legal form was changed from '']'' (KG), or limited partnership, to ] (AG), or public limited company, because Ferry Porsche came to believe the scale of the company outgrew a "family operation", after learning about ]'s "no family members in the company" policy at ]. This led to the establishment of an Executive Board with members from outside the Porsche family, and a Supervisory Board consisting largely of family members. With this change, most family members in the operation of the company including F. A. Porsche and Ferdinand Piëch departed from the company. | |||
| The first chief executive officer (CEO) of Porsche AG was ], who had been working in the company's engine development division. Fuhrmann was responsible for the so-called Fuhrmann-engine, used in the 356 Carrera models as well as the 550 Spyder, having ] instead of a central camshaft with pushrods, as in the Volkswagen-derived serial engines. He planned to cease the 911 during the 1970s and replace it with the ]-] grand sportswagon ]. As we know today, the 911 outlived the 928 by far. Fuhrmann was replaced in the early 1980s by ], an American manager and self-proclaimed 911 aficionado. He was then replaced in 1988 by the former manager of German computer company Nixdorf Computer AG, ], who made some costly miscalculations that led to his dismissal soon after, along with that of the development director, ], who was formerly responsible for BMW's ] model, and was CEO of ] from 2000 to 2013.<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.motorauthority.com/news/1083889_aston-martin-ceo-ulrich-bez-to-step-down-report|title=Aston Martin CEO Ulrich Bez To Step Down: Report|work=Motor Authority|access-date=9 April 2017|language=en|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170410050853/http://www.motorauthority.com/news/1083889_aston-martin-ceo-ulrich-bez-to-step-down-report|archive-date=10 April 2017|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| F. A. Porsche founded his own design company, ], which is renowned for exclusive sunglasses, watches, furniture, and many other luxury articles. Louise's son and Ferry's nephew ], who was responsible for mechanical development of Porsche's production and racing cars (including the very successful ], ] and ] models), formed his own engineering bureau, and developed a ] ] for ]. A short time later he moved to ], and pursued his career through the entire company, ultimately becoming the Chairman of ]. | |||
| ]), introduced in 1989, was the first to be offered with Porsche's ] transmission and four-wheel drive.]] | |||
| The first Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of Porsche AG was Dr. ], who had been working in the company's engine development division. Fuhrmann was responsible for the so-called Fuhrmann-engine, used in the 356 Carrera models as well as the 550 Spyder, having ] instead of a central camshaft with pushrods, as in the Volkswagen-derived serial engines. He planned to cease the 911 during the 1970s, and replace it with the ]-] grand sportswagon ]. As we know today, the 911 outlived the 928 by far. Fuhrmann was replaced in the early 1980s by ], an American manager and self-proclaimed 911 aficionado. He was then replaced in 1988 by the former manager of German computer company Nixdorf Computer AG, ], who made some costly miscalculations that led to his dismissal soon after, along with that of the development director, ], who was formerly responsible for BMW's ] model, and is today the CEO of ]. | |||
| In 1990, Porsche drew up a memorandum of understanding with ] to learn and benefit from Japanese ] methods. In 2004 it was reported that Toyota was assisting Porsche with ].<ref>{{cite web |author=Nexteer Automotive Poland president Rafal Wyszomirski |url=http://www.just-auto.com/news/porsche-asks-for-toyota-hybrid-technology_id71109.aspx |title=Just auto 23 November 2004 |publisher=Just-auto.com |access-date=1 August 2011 |archive-date=27 September 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110927153453/http://www.just-auto.com/news/porsche-asks-for-toyota-hybrid-technology_id71109.aspx |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| Following the dismissal of Bohn, ], a longtime Porsche employee, was appointed as interim CEO. Branitzki served in that position until ] became CEO in 1993. Wiedeking took over the chairmanship of the board at a time when Porsche appeared vulnerable to a takeover by a larger company. During his long tenure, Wiedeking transformed Porsche into a very efficient and profitable company. | |||
| ]), introduced in 1989, was the first to be offered with Porsche's ] transmission.]] | |||
| Ferdinand Porsche's nephew, Ferdinand Piëch, was chairman and CEO of the ] from 1993 to 2002 and is chairman of the Volkswagen AG Supervisory Board since then. With 12.8 percent of the Porsche SE voting shares, he also remains the second-largest individual shareholder of Porsche SE after his cousin, F. A. Porsche, which had 13.6 percent. | |||
| In 1990, Porsche drew up a memorandum of understanding with ] to learn and benefit from Japanese ] methods. In 2004 it was reported that Toyota was assisting Porsche with ].<ref>{{cite web|author=Nexteer Automotive Poland president Rafal Wyszomirski |url=http://www.just-auto.com/news/porsche-asks-for-toyota-hybrid-technology_id71109.aspx |title=Just auto 23 November 2004 |publisher=Just-auto.com |date= |accessdate=1 August 2011}}</ref> | |||
| Porsche's 2002 introduction of the Cayenne also marked the unveiling of a new production facility in ], ], which once accounted for nearly half of Porsche's annual output. In 2004, production of the {{convert|456|kW|PS bhp|0|lk=on}} ] commenced in Leipzig, and at EUR 450,000 ($440,000 in the United States) it was the most expensive production model Porsche ever built. | |||
| Following the dismissal of Bohn, ], a longtime Porsche employee, was appointed as interim CEO. Branitzki served in that position until ] became CEO in 1993. Wiedeking took over the chairmanship of the board at a time when Porsche appeared vulnerable to a takeover by a larger company. During his long tenure, Wiedeking has transformed Porsche into a very efficient and profitable company. | |||
| ] | |||
| Ferdinand Porsche's grandson, Ferdinand Piëch, was chairman and CEO of the ] from 1993 to 2002. Today he is chairman of the Supervisory Board. With 12.8 percent of the Porsche voting shares, he also remains the second largest individual shareholder of Porsche AG after his cousin, F. A. Porsche, (13.6 percent). | |||
| In mid-2006, after years of the Boxster (and later the Cayenne) as the best selling Porsche in North America, the 911 regained its position as Porsche's best-seller in the region. The Cayenne and 911 have cycled as the top-selling model since. In Germany, the 911 outsells the Boxster/Cayman and Cayenne.<ref>{{cite press release|url=http://www.porsche.com/usa/aboutporsche/pressreleases/pag/archive2006/quarter3/|title=Porsche USA press release|date=11 September 2006}}</ref> | |||
| In May 2011, Porsche Cars North America announced plans to spend $80–$100 million, but will receive about $15 million in economic incentives to move their North American headquarters from ], a suburb of ], to ], a new mixed-use development on the site of the old ] adjacent to ].<ref>{{cite news|author=Urvaksh Karkaria |url=http://www.bizjournals.com/atlanta/blog/atlantech/2011/05/porsche-gets-3m-in-incentives.html |title="Porsche HQ relo draws $15M in incentives", Atlanta Business Chronicle, 2011-05-12 |publisher=Bizjournals.com |date= 12 May 2011|access-date=1 August 2011}}</ref> Designed by architectural firm ], the headquarters will include a new office building and test track.<ref>{{cite web|last=Tobin |first=Rachel |url=https://www.ajc.com/business/porsche-north-america-leave-sandy-springs-for-ford-plant/03IwRyDxEPNwqps41mbmNN/ |title=Porsche North America HQ to leave Sandy Springs for ex-Ford plant |publisher=ajc.com |date=11 May 2011 |access-date=1 August 2011}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.atlantaga.gov/media/nr_porsche_051211.aspx |title="Mayor Kasim Reed and Governor Nathan Deal Announce Porsche to Build New U.S. Headquarters in Metropolitan Atlanta", City of Atlanta Online |publisher=Atlantaga.gov |access-date=1 August 2011 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110611040446/http://www.atlantaga.gov/media/nr_porsche_051211.aspx |archive-date=11 June 2011 }}</ref><ref>{{cite news|last=Patton |first=Phil |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2011/11/20/automobiles/porsche-to-build-in-atlanta-and-california.html?_r=1 |title=Porsche to Build in Atlanta and California |newspaper=The New York Times |date=18 November 2011 |access-date=30 November 2011}}</ref> The facility will be known by its new address, One Porsche Drive. | |||
| Porsche's 2002 introduction of the Cayenne also marked the unveiling of a new production facility in ], ], which once accounted for nearly half of Porsche's annual output. In 2004, production of the {{convert|456|kW|PS bhp|0|lk=on}} Carrera GT commenced in Leipzig, and at EUR 450,000 ($440,000 in the United States) it was the most expensive production model Porsche ever built. | |||
| In October 2017, Porsche Cars North America announced the launch of Porsche Passport,<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.porschepassport.com/|title=Porsche Passport|date=14 February 2018|access-date=31 December 2021|archive-date=14 February 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180214144349/http://www.porschepassport.com/|url-status=dead}}</ref> a new sports ]. This new offering allows consumers to access Porsche vehicles through subscribing to the service, rather than owning or leasing a vehicle. The Porsche Passport service was available initially in ],<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://press.porsche.com/news/release.php?id=1050|title=Porsche Launches New Sports Car and SUV Subscription Program|website=press.porsche.com|access-date=7 February 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180208004345/http://press.porsche.com/news/release.php?id=1050|archive-date=8 February 2018|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.bloomberg.com/view/articles/2017-10-20/porsche-s-passport-to-the-new-mobility|title=Porsche's Passport to the New Mobility|date=20 October 2017|work=Bloomberg.com|access-date=7 February 2018|language=en}}</ref> and has become available in many major cities across the US.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Porsche Subscription - Porsche USA |url=https://www.porsche.com/usa/accessoriesandservices/porschedrive/subscription/ |access-date=3 October 2023 |website=Porsche HOME - Porsche USA |language=en-US}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| As of 2005, the extended Porsche and Piëch families controlled all of Porsche AG's voting shares. In early October 2005, the Company announced its acquisition of an 18.53% stake in ] (VW AG), and disclosed intentions to acquire additional VW AG shares in the future. As of June 2006, the Porsche AG stake in VW AG had risen to 25.1%, giving Porsche a blocking minority, whereby Porsche can veto large corporate decisions undertaken by VW AG. | |||
| During the ], in March 2020, Porsche suspended its manufacturing in Europe for two weeks, "By taking this step, the sports car manufacturer is responding to the significant acceleration in the rate of infection caused by the coronavirus and the resultant measures implemented by the relevant authorities."<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.businessinsider.com/coronavirus-porsche-suspends-production-europe-due-to-covid-19-outbreak-2020-3|title=Porsche is suspending production in Europe amid worsening coronavirus outbreak|publisher=]|access-date=18 March 2020}}</ref> | |||
| In mid-2006, after years of the Boxster (and later the Cayenne) as the dominant Porsche in North America, the 911 regained its position as Porsche's backbone in the region. The Cayenne and 911 have cycled as the top-selling model since. In Germany, the 911 clearly outsells the Boxster/Cayman and Cayenne.<ref>{{cite press release|url=http://www.porsche.com/usa/aboutporsche/pressreleases/pag/archive2006/quarter3/|title=Porsche USA press release|date=11 September 2006}}</ref> | |||
| In August 2022, '']'' reported that Porsche has lined up interest in subscription of its ] for a valuation between US$60{{ndash}}85{{nbsp}}billion. It is expected to be listed on ] in September.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2022-08-26/porsche-lines-up-ipo-demand-at-up-to-85-billion-valuation |title=Porsche Attracts IPO Demand at Up to $85 Billion Valuation |date=26 August 2022 |work=] |first1=Eyk |last1=Henning |first2=Jan-Henrik |last2=Foerster |url-access=limited |archive-url=https://archive.today/20220827070238/https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2022-08-26/porsche-lines-up-ipo-demand-at-up-to-85-billion-valuation |archive-date=27 August 2022 |url-status=live | |||
| In May 2011, Porsche Cars North America announced plans to spend $80–$100 million, but will receive about $15 million in economic incentives to move their North American headquarters from ], a suburb of ], to ], a new mixed-use development on the site of the old ] adjacent to ].<ref>{{cite news|author=Atlanta Business Chronicle - by Urvaksh Karkaria |url=http://www.bizjournals.com/atlanta/blog/atlantech/2011/05/porsche-gets-3m-in-incentives.html |title="Porsche HQ relo draws $15M in incentives", Atlanta Business Chronicle, 2011-05-12 |publisher=Bizjournals.com |date= 12 May 2011|accessdate=1 August 2011}}</ref> Designed by architectural firm ], the headquarters will include a new office building and test track.<ref>{{cite web|last=Tobin |first=Rachel |url=http://www.ajc.com/business/porsche-north-america-hq-941520.html |title=Porsche North America HQ to leave Sandy Springs for ex-Ford plant |publisher=ajc.com |date=11 May 2011 |accessdate=1 August 2011}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.atlantaga.gov/media/nr_porsche_051211.aspx |title="Mayor Kasim Reed and Governor Nathan Deal Announce Porsche to Build New U.S. Headquarters in Metropolitan Atlanta", City of Atlanta Online |publisher=Atlantaga.gov |date= |accessdate=1 August 2011}}{{dead link|date=February 2014}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|last=Patton |first=Phil |url=http://www.nytimes.com/2011/11/20/automobiles/porsche-to-build-in-atlanta-and-california.html?_r=1 |title=Porsche to Build in Atlanta and California |publisher=The New York Times |date=18 November 2011 |accessdate=30 November 2011}}</ref> | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| ===Relationship with Volkswagen=== | ===Relationship with Volkswagen=== | ||
| The company has always had a close relationship with, initially, the ] (VW) ], and later, the ] (which also owns ]), because the first ] was designed by ]. The two companies collaborated in 1969 to make the ], whereby the 914-6 had a Porsche engine, and the 914 had a Volkswagen engine, in 1976 with the ]E (USA only) and the ], which used many Audi components, and was built at Audi's ] factory. ]s were also built there,<ref>{{cite web|title=The history of the Neckarsulm plant|url=https://www.audi-mediaservices.com/publish/ms/content/en/public/hintergrundberichte/2011/03/08/der_audi_standort/the_history_of_the.standard.gid-oeffentlichkeit.html|work=Audi MediaServices|publisher=Audi AG|accessdate=4 May 2011}}{{dead link|date=February 2014}}</ref> although they used far fewer Volkswagen components. The Cayenne, introduced in 2002, shares its entire chassis with ] and ], which is built at the ] in ]. In late 2005, Porsche took an 18.65% stake in the Volkswagen Group, further cementing their relationship, and preventing a takeover of Volkswagen Group, which was rumoured at the time. Speculated suitors included ], ], and ]. | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| The company has always had a close relationship with, initially, the ] (VW) ], and later, the ] (which also owns ]), because the first ] was designed by ]. | |||
| On 26 March 2007, Porsche took its holding of Volkswagen AG shares to 30.9%, triggering a takeover bid under ]. Porsche then formally announced in a press statement that it did not intend to take over Volkswagen Group (it would set its offer price at the lowest possible legal value) but intended to move to avoid a competitor taking a large stake, and to stop ]s dismantling Volkswagen Group, which was Porsche's most important partner.<ref>{{cite news|title=Porsche triggers VW takeover bid|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/business/6494593.stm|work=BBC News |date=26 March 2007|accessdate=29 July 2008}}</ref> Porsche's move came after the ] had moved against a German law that protected Volkswagen AG from takeovers. Under the so-called ], any shareholder with more than 20% of the voting rights had veto power over any corporate decision in the annual general meeting – in effect, any shareholder in VW AG cannot exercise more than 20% of the firm's voting rights, regardless of their level of stock holding. (The local state government of ] owns 20.1% of the shares.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/business/7843262.stm|title=Fast bucks: how Porsche made billions|accessdate=22 January 2009|publisher=BBC News |date=22 January 2009|first=Emily|last=Hughes}}</ref>) However, the ] ruled against the law, potentially paving the way for a takeover.<ref>{{cite web|title=VW Law is a write-off|url=http://www.ManagementToday.co.uk/channel/StrategyOperations/news/754256/vw-law-write-off|work=Management Today|date=23 October 2007|accessdate=17 January 2009}} {{Dead link|date=September 2010|bot=H3llBot}}</ref> | |||
| The two companies collaborated in 1969 to make the ], whereby the 914-6 had a Porsche engine, and the 914 had a Volkswagen engine. Further collaboration in 1976 resulted in the ]E (US only) and the ], which used many Audi components, and was built at Audi's ] factory, which had been ]'s. ]s were also built there,<ref>{{cite web|title=The history of the Neckarsulm plant |url=https://www.audi-mediaservices.com/publish/ms/content/en/public/hintergrundberichte/2011/03/08/der_audi_standort/the_history_of_the.standard.gid-oeffentlichkeit.html |work=Audi MediaServices |publisher=Audi AG |access-date=4 May 2011 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111008202612/https://www.audi-mediaservices.com/publish/ms/content/en/public/hintergrundberichte/2011/03/08/der_audi_standort/the_history_of_the.standard.gid-oeffentlichkeit.html |archive-date=8 October 2011 }}</ref> although they used far fewer Volkswagen components. The Cayenne, introduced in 2002, shares its chassis with the ] and the ], which is built at the ] in ], ]. | |||
| On 16 September 2008, Porsche increased its holdings by another 4.89%,<ref>{{cite press release|title=Porsche erhöht seine VW-Beteiligung auf 35,14 Prozent|language={{de icon}}|url=http://www.porsche.com/germany/aboutporsche/pressreleases/?pool=germany&id=2d745b91-8c92-4354-9805-f9aa45bb7c68|publisher=Porsche AG|date=16 September 2008|accessdate=17 January 2009}}</ref> in effect almost taking control of the company, with more than 35% of the voting rights. It again triggered a takeover bid, but this time over Audi. Porsche dismissed the bid as a mere formality, since it was Porsche's intention to keep the corporate structure of the Volkswagen Group. | |||
| There has been some tension and anxiety among the Volkswagen Group workers, who feared that a Porsche takeover might signify a hardened production efficiency control, rejection of demands for payment rises or even personnel cuts.<ref name=IHT>{{cite web|author=Nelson D. Schwartz|title=Porsche maneuvers to take control of Volkswagen|url=http://www.iht.com/articles/2008/09/16/business/vw.php|work=International Herald Tribune|date=16 September 2008|accessdate=17 September 2008}}</ref> ] and his cousin, ], also seemed to be on a collision course.<ref name=IHT/> | |||
| However, on 13 August 2009, Volkswagen AG's Supervisory Board signed the agreement to create an "integrated automotive group" with Porsche, led by Volkswagen AG. Volkswagen would initially take a 49.9 percent stake in Porsche AG by the end of 2009, and it would also see the family shareholders selling the automobile trading business of Porsche Holding Salzburg to Volkswagen AG.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://news.taume.com/World-Business/Business-Finance/Volkswagen-to-take-a-42-0-percent-stake-in-Porsche-AG-11861|title=Volkswagen to take a 42.0 percent stake in Porsche AG|accessdate=22 January 2009|publisher=Taume News|date=14 August 2009}}{{dead link|date=February 2014}}</ref> | |||
| On 5 July 2012, Volkswagen AG announced a deal with Porsche resulting in VW's full ownership of Porsche on 1 August 2012. The deal was classified as a restructuring rather than a takeover due to the transfer of a single share as part of the deal. Volkswagen AG paid Porsche shareholders $5.61 billion for the remaining 50.1% it did not own.<ref name="AOL Autos"/> | |||
| ===Corporate restructuring=== | ===Corporate restructuring=== | ||
| ] | |||
| Through the ] stake acquisition, Porsche reformed the company's structure, with Dr Ing. h. c. F. Porsche AG becoming a ], renamed "Porsche Automobil Holding SE",<ref name="porsche-se-announce-2007">{{cite web|url=http://www.porsche-se.com/filestore.aspx/default.pdf?pool=uk&type=download&id=investorrelations-announcement-pdf&lang=none&filetype=default|title=Announcement on Change of Name, Change of Corporate Form and Change to Stock Exchange Quotation|date=15 November 2007|work=www.porsche-se.com|publisher=Porsche Automobil Holding SE|accessdate=13 January 2010}}</ref> and a new Dr Ing. h. c. F. Porsche AG operating company being formed in 2007.<ref name="new-porsche-ag-2007">{{cite web|url=http://www.porsche.com/international/aboutporsche/pressreleases/archive2007/quarter4/?pool=international-de&id=2007-11-19|title=Supervisory Board of new Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG constituted|date=19 November 2007|work=www.porsche.com|publisher=Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG |accessdate=13 January 2010}}</ref> Thus the operating activities are separated from holding activities of the company.<ref name=SE>{{cite web|title=Porsche Automobile Holding SE|url=http://www.porsche.com/international/aboutporsche/porschese/|work=Porsche official website}}{{dead link|date=September 2011}}</ref> There was an ] (EGM) for Porsche AG shareholders which took place on 26 June 2007, at the Porsche Arena in ], Germany to discuss the change to the company structure. | |||
| ] in front of the factory in which it was assembled, Porsche-Werk Stuttgart (right), and the manufacturer's central dealership, Porsche Zentrum Stuttgart (left)]] | |||
| In late 2009, VW (which also owns Audi) bought the controlling rights to Porsche.<ref>{{cite web|title=Porsche SE|url=http://www.porsche-se.com/pho/en/porschese/|work=Porsche SE official website}}</ref> | |||
| ], Detlev von Platen, ] ...]] | |||
| ] | |||
| Porsche SE was created in June 2007 by renaming the old Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG, and became a holding company for the families' stake in Porsche Zwischenholding GmbH (50.1%) (which in turn held 100% of the old Porsche AG) and Volkswagen AG (50.7%).<ref>{{cite news|last=Rauwald |first=Christoph |url=http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748704122904575314062459444270.html |title=Wall Street Journal 18 June 2010 |publisher=Online.wsj.com |date=18 June 2010 |access-date=1 August 2011}}</ref><ref name=":4">{{cite web |url=http://www.porsche-se.com/pho/en/porschese/holdingstructure/ |title=Porsche SE Investor Relations |publisher=Porsche-se.com |access-date=1 August 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160901065434/http://www.porsche-se.com/pho/en/porschese/holdingstructure/ |archive-date=1 September 2016 |url-status=dead }}</ref> At the same time, the new Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG ('''Porsche AG''') was created for the car manufacturing business. | |||
| In August 2009, Porsche SE and ] reached an agreement that the car manufacturing operations of the two companies would merge in 2011, to form an "Integrated Automotive Group".<ref name="PorscheMerger">{{cite press release|title=Porsche Supervisory Board agrees on the contracts of implementation |url=http://www.porsche-se.com/pho/en/news/?pool=pho&id=2009-11-20 |publisher=Porsche Automobil Holding SE, Stuttgart |date=20 November 2009 |access-date=22 November 2009 }}{{dead link|date=June 2016|bot=medic}}{{cbignore|bot=medic}}</ref><ref name="VWAG_merger">{{cite press release|url=http://www.volkswagenag.com/vwag/vwcorp/info_center/en/news/2009/08/Volkswagen_Aufsichtsrat_stimmt_Grundlagenvereinbarung_fuer.html|title=Volkswagen Supervisory Board approves Comprehensive Agreement for an Integrated Automotive Group with Porsche|publisher=]|date=13 August 2009|access-date=22 November 2009|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110720053631/http://www.volkswagenag.com/vwag/vwcorp/info_center/en/news/2009/08/Volkswagen_Aufsichtsrat_stimmt_Grundlagenvereinbarung_fuer.html|archive-date=20 July 2011}}</ref> The management of Volkswagen AG agreed to 50.76% of Volkswagen AG being owned by Porsche SE in return for Volkswagen AG management taking Porsche SE management positions (in order for Volkswagen management to remain in control), and for Volkswagen AG acquiring ownership of Porsche AG. | |||
| On 3 March 2007, Porsche set the stage for obtaining a plurality stake in the Volkswagen AG. One day later Porsche sought to allay fears it would attempt to force a ] with Volkswagen Group.<ref>{{dead link|date=October 2010}}</ref> By September, Porsche owned a 35.14% plurality stake in Volkswagen AG, effectively giving it control over the company.<ref>{{cite web|last=Neff |first=John |url=http://www.autoblog.com/2008/09/16/porsche-raises-stake-in-vw-again-makes-offer-for-audi/ |title=Porsche raises stake in VW again, makes offer for Audi |publisher=Autoblog.com |date=16 September 2008 |accessdate=3 October 2010}}</ref> Volkswagen Group expected the move, and welcomed Porsche's investment.<ref>{{cite news|title=Porsche Gains Nearly 75% of VW, Tightening Grip|url=http://online.wsj.com/article/SB122506315406770367.html?mod=googlenews_wsj|work=Wall Street Journal|publisher=]|date=27 October 2008|accessdate=26 November 2008 | first=Christoph | last=Rauwald}}</ref> | |||
| As of the end of 2015, the 52.2% control interest in VW AG is the predominant investment by Porsche SE, and Volkswagen AG in turn controls brands and companies such as ], ], ], ], ], ], ], Porsche AG, ], VW Commercial Vehicles, ], ], as well as Volkswagen Financial Services.<ref name=":5">{{cite web|title=Porsche SE Annual Report 2015|url=http://www.porsche-se.com/filestore/download/pho/en/investorrelations-annualreport2015-pdf/default/7c2f7397-11f3-11e6-9225-0019999cd470/Annual-Report-Fiscal-Year-2015.pdf/|page=3|access-date=17 October 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161018211112/http://www.porsche-se.com/filestore/download/pho/en/investorrelations-annualreport2015-pdf/default/7c2f7397-11f3-11e6-9225-0019999cd470/Annual-Report-Fiscal-Year-2015.pdf/|archive-date=18 October 2016|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| In October 2008, Porsche announced its intent to raise its stake in Volkswagen AG to 75% during 2009, and on 7 January 2009, Porsche's holding in VW AG was raised to 50.76%.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.channel4.com/4car/news/news-story.jsp?news_id=18546|title=Porsche holds over half of Volkswagen|publisher=Channel Four Television Corporation|work=4Car / Channel4.com|date=7 January 2009|accessdate=15 December 2009}} {{Dead link|date=September 2010|bot=H3llBot}}</ref> Porsche's move automatically triggered a bid for ], because VW AG already had a controlling position in the Swedish truck-maker.<ref>{{cite news|author=Miles Johnson|title=Porsche's VW move boosts carmakers|url=http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/12f9f23a-dc5b-11dd-b07e-000077b07658.html|work=]|date=7 January 2009|accessdate=29 January 2009}}</ref> As Porsche had no strategic interest in the company, on 19 January, they offered the minimum price in that mandatory takeover bid.<ref>{{cite news|title=Porsche offers minimum price in required Scania bid|url=http://www.bloomberg.com/apps/news?pid=20601100&sid=aAf8xFogBtnY&refer=germany|work=]|date=19 January 2009|accessdate=29 January 2009}}</ref> Porsche SE owned 50.8 percent of Volkswagen Group as of 5 January 2009, and has said it plans to lift the stake to 75 percent before the end of 2009, at that level they could bring VW AG's cash onto Porsche's books.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.bloomberg.com/apps/news?pid=20601100&sid=aSxAgX78NB_s&refer=germany|title=VW Gains as Porsche Refinancing Boosts Expectations|last=Cremer|first=Andreas|date=26 March 2009|work=]|accessdate=27 March 2009}}</ref> | |||
| '''Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG''' (which stands for ''] ] Ferdinand Porsche ]''), as a 100% subsidiary of VW AG, is responsible for the actual production and manufacture of the Porsche automobile line. The company currently produces ],<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.thehindu.com/business/Industry/porsche-brings-limited-edition-911-r-priced-at-around-rs-3-crore/article17361797.ece|title=Porsche brings Limited Edition 911 R priced at around Rs 3 crore|last=PTI|work=The Hindu|access-date=9 March 2017|language=en}}</ref> ] and ] sports cars, the ] and Macan ] and the four-door ]. | |||
| By March 2009, Porsche SE was aiming for its first ever credit ratings from U.S. rating agencies ] and ].<ref>{{cite news|url=http://online.wsj.com/article/BT-CO-20090326-705242.html|title=Porsche Seeking Credit Ratings From S&P, Moody's – Source|last=Arends|first=Hilde|date=26 March 2009|work=Wall Street Journal|agency=]|accessdate=28 March 2009}}{{Dead link|date=March 2010}}</ref> | |||
| Porsche AG has a 29% share in German engineering and design consultancy ]<ref>{{cite web|title=Porsche bolsters engineering and design operations|url=http://www.autocar.co.uk/car-news/industry/porsche-bolsters-engineering-and-design-operations|website=Autocar|access-date=16 September 2014|date=3 July 2014}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Porsche AG raises its stake in Bertrandt AG|url=http://www.porsche.com/usa/aboutporsche/pressreleases/pag/?pool=international-de&id=72526|website=Porsche AG|access-date=16 September 2014|date=3 July 2014}}</ref> and 81.8% of ].<ref>{{cite web|title=Mieschke Hofmann und Partner (MHP) – the process supplier|url=http://www.mhp.com/en/company/|website=MHP|access-date=16 September 2014}}</ref> In 2018, Porsche acquired a 10% minority shareholding stake of the Croatian ] manufacturer ] to form a development partnership.<ref name="Porsche 20 June 2018">{{cite press release |url=https://newsroom.porsche.com/en/company/porsche-rimac-automobili-development-partnership-technology-sports-car-company-zagreb-croatia-electromobility-geneva-motor-show-electric-hypercar-c-two-15697.html |title=Porsche takes a stake in the Croatian technology and sports car company Rimac |publisher=Porsche |date=20 June 2018 |access-date=22 June 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180620181128/https://newsroom.porsche.com/en/company/porsche-rimac-automobili-development-partnership-technology-sports-car-company-zagreb-croatia-electromobility-geneva-motor-show-electric-hypercar-c-two-15697.html |archive-date=20 June 2018 |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.theverge.com/2018/6/20/17482656/porsche-rimac-ev-electric-investment |title=Porsche accelerates EV supercar ambitions with investment in Rimac |first=Vlad |last=Savov |work=The Verge |location=US |date=20 June 2018 |access-date=22 June 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180621014855/https://www.theverge.com/2018/6/20/17482656/porsche-rimac-ev-electric-investment |archive-date=21 June 2018 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| In its efforts to acquire a majority holding in Volkswagen AG, Porsche built up a large debt burden, aggravated by taxes due on very large paper profits from Volkswagen AG options. By July 2009, Porsche was faced with debts exceeding 10 billion euros. The supervisory board of Porsche finally agreed to a number of arrangements whereby the ] would inject a large amount of capital, and Porsche would be ] with Volkswagen Group. On 23 July 2009, ] was appointed CEO, to replace ], who is expected to receive a compensation package of 50 million euros.<ref>{{cite news|first=Daniel|last=Schäfer|title=€50m payoff for ousted Porsche chief|url=http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/ba9dce78-774f-11de-8c68-00144feabdc0,dwp_uuid=aa6fe7da-776c-11de-8c68-00144feabdc0.html|work=Financial Times |publisher=The Financial Times Ltd|date=23 July 2009|accessdate=25 July 2009}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|first=Daniel|last=Schäfer|title=Porsche chief ousted in merger with VW|url=http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/af6e14c6-77eb-11de-9713-00144feabdc0.html|work=Financial Times |publisher=The Financial Times Ltd|date=24 July 2009|accessdate=25 July 2009}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|first=Daniel|last=Schäfer|title=Just another week at the office for Piëch|url=http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/f94c8e7e-787c-11de-bb06-00144feabdc0.html|work=Financial Times |publisher=The Financial Times Ltd|date=24 July 2009|accessdate=25 July 2009}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|first=Daniel|last=Schäfer|title='Wiedeking Is to Blame for the Porsche Disaster'|url=http://www.spiegel.de/international/business/0,1518,638084,00.html|work=Der Spiegel |date=24 July 2009|accessdate=25 July 2009}}</ref> | |||
| === Initial public offering === | |||
| In July 2010, Porsche appointed Volkswagen executive ] to its new CEO position, moving Michael Macht to another executive position within Volkswagen AG. | |||
| In February 2022, Volkswagen AG had announced that it would examine the feasibility of a possible ] of Porsche AG.<ref name=":0">{{Cite web |title=Board of Management and Supervisory Board aim for an IPO of Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG and decide on the next step with the "intention to float" |url=https://www.volkswagenag.com/en/news/2022/09/Ad_Hoc_Porsche_IPO_ITF.html |access-date=19 September 2022 |website=www.volkswagenag.com|date=5 September 2022 }}</ref> The ] of Porsche AG has been divided into 50% ] ] and 50% ordinary shares.<ref name=":0" /><ref name=":1">{{Cite news |date=17 September 2022 |title=Factbox: The structure of the planned Porsche IPO |language=en |work=Reuters |url=https://www.reuters.com/business/autos-transportation/structure-planned-porsche-ipo-2022-09-17/ |access-date=19 September 2022}}</ref> Volkswagen AG will retain 75% of ordinary shares, while ] will acquire 25% of ordinary shares. Volkswagen AG will also retain 75% of preference shares, while 25% of preference shares (12.5% of share capital) will be sold during IPO,<ref name=":0" /> while ] has already committed to buy 4.99% of preference shares, leaving another 20.01% (10% of share capital), to other investors.<ref name=":1" /> As part of the preliminary offering, 113,875 thousand shares were sold at the upper limit of the price range - 82.5 euros. Thus, the value of the company was estimated at 75 billion euros. In the first hours of trading on the ] on 29 September, the share price rose to 84 euros.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.reuters.com/markets/europe/porsche-debut-amid-market-tumult-historic-ipo-2022-09-28/|title=Porsche races higher after landmark $72 bln listing|date=29 September 2022|website=reuters.com}}</ref> | |||
| ===Australian eFuel operations=== | |||
| {{main|Highly Innovative Fuels Australia}} | |||
| In April 2022, Porsche Australia announced they are planning to open an efuel manufacturing facility in the island state of ]. The plant will be the first of its type in the country. The facility is to be named the '''HIF (Highly Innovative Fuels) Tasmania Carbon Neutral eFuel Plant'''. It is slated to open in 2026.<ref>{{citation | url = https://www.whichcar.com.au/news/porsche-to-build-australian-efuels-plant-tasmania-operational-from-2026 | title = Porsche to build Australian efuels plant in Tasmania, operational from mid-2026 | publisher = Motor | date = 8 July 2022}}</ref> | |||
| ==Production and sales== | ==Production and sales== | ||
| The headquarters and main factory are located in Zuffenhausen, a district in ], |
The headquarters and main factory are located in Zuffenhausen, a district in ], where Porsche produces flat-6 and V8 piston engines.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://newsroom.porsche.com/EN/History/The-history-of-engine-construction.html|title=The history of engine construction|website=Porsche Newsroom|date=5 October 2014 }}</ref> Cayenne and Panamera models are manufactured in ], Germany, and parts for the SUV are also assembled in the ] factory in ], Slovakia.<ref name=Reuters>{{cite news|title=Union says VW's Slovak plant eyes output cut|url=https://www.reuters.com/article/rbssConsumerGoodsAndRetailNews/idUSL911061920081009|work=]|date=9 October 2008|access-date=17 January 2009}}</ref> Boxster and Cayman production was outsourced to ] in Finland from 1997 to 2011, and in 2012 production moved to Germany.<ref name="valmet-automotive.com">{{cite web|url=http://www.valmet-automotive.com/automotive/bulletin.nsf/headlinespubliceng/ADB15534224D1B0CC225788400418888|title=Porsche's Finnish success story: 227,890 Boxsters and Caymans|access-date=2 May 2011|year=2011|work=valmet-automotive.com|archive-date=4 October 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111004160636/http://www.valmet-automotive.com/automotive/bulletin.nsf/headlinespubliceng/ADB15534224D1B0CC225788400418888|url-status=dead}}</ref> Since 2011, the area of the Zuffenhausen plant has more than doubled, from {{convert|284000|m2|ha|abbr=on}} to {{convert|614000|m2|ha|abbr=on}}, as a result of purchasing the former Layher, Deltona and Daimler sites, among others.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://newsroom.porsche.com/en/company/investitionen-zuffenhausen-10801.html|title=Zuffenhausen is growing|access-date=11 June 2020|work=Porsche Newsroom|date=6 April 2014 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://newsroom.porsche.com/en/company/porsche-site-zuffenhausen-production-4-0-future-taycan-investment-electro-mobility-16382.html|title=A New Era|access-date=11 June 2020|work=Porsche Newsroom|date=11 October 2018 }}</ref> | ||
| In |
In 2015, Porsche reported selling a total of 218,983 cars, 28,953 (13.22%) as domestic German sales, and 190,030 (86.78%) internationally.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://newsroom.porsche.com/en/annual-report/downloads/en/Porsche_AnnualReport2015.pdf|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160924035900/https://newsroom.porsche.com/en/annual-report/downloads/en/Porsche_AnnualReport2015.pdf|url-status=dead|archive-date=24 September 2016|title=Porsche AG Annual Report 2015|pages=44 (German sales),126 (total sales)|access-date=8 November 2016}}</ref> | ||
| The company has been highly successful in recent times, and indeed claims to have the highest profit per unit sold of any car company in the world.<ref>{{cite web|last=Elliott |first=Hannah |url=http://www.forbesautos.com/reviews/2006/porsche/cayman_s/feature2.html |title=Forbes Autos review of Cayman S |publisher=Forbesautos.com | |
The company has been highly successful in recent times, and indeed claims to have the highest profit per unit sold of any car company in the world.<ref>{{cite web |last=Elliott |first=Hannah |url=http://www.forbesautos.com/reviews/2006/porsche/cayman_s/feature2.html |title=Forbes Autos review of Cayman S |publisher=Forbesautos.com |access-date=3 October 2010 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081210200104/http://www.forbesautos.com/reviews/2006/porsche/cayman_s/feature2.html |archive-date=10 December 2008}}</ref> Table of profits (in millions of euros) and number of cars produced. Figures from 2008/9 onwards were not reported as part of Porsche SE.<ref name="porsche-se1">{{cite web |url=http://www.porsche-se.com/filestore.aspx/default.pdf?pool=pho&type=download&id=financialpressconference+-2011-annualreportshortsiscalyear2010-pdf&lang=en&filetype=default&version=1 |title=Porsche Annual Report Short Fiscal Year 2010 |access-date=1 August 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110927210459/http://www.porsche-se.com/filestore.aspx/default.pdf?pool=pho&type=download&id=financialpressconference+-2011-annualreportshortsiscalyear2010-pdf&lang=en&filetype=default&version=1 |archive-date=27 September 2011 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | ||
| On 11 May 2017, Porsche built the one-millionth 911. An Irish green Carrera S was built for the celebration, and it will be taken on a global tour before becoming a permanent exhibit at the ] in Stuttgart.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://blog.caranddriver.com/one-million-dreams-this-is-the-1000000th-porsche-911/ |title=One Million Dreams: This Is the 1,000,000th Porsche 911 |access-date=3 July 2017 |archive-date=1 August 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170801001523/http://blog.caranddriver.com/one-million-dreams-this-is-the-1000000th-porsche-911/ |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| {| class="wikitable floatright" | |||
| |+Sales by region (2023)<ref>{{Cite web |title=Porsche AG: Shareholders Board Members Managers and Company Profile {{!}} DE000PAG9113 {{!}} MarketScreener |url=https://www.marketscreener.com/quote/stock/PORSCHE-AG-144458103/company/ |access-date=2024-03-22 |website=www.marketscreener.com |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| !Region | |||
| !Sales in billion € | |||
| !share | |||
| |- | |||
| |North America | |||
| |11.7 | |||
| |29.5% | |||
| |- | |||
| |China | |||
| |9.5 | |||
| |23.6% | |||
| |- | |||
| |Europe | |||
| |8.8 | |||
| |21.7% | |||
| |- | |||
| |Germany | |||
| |4.9 | |||
| |12.0% | |||
| |- | |||
| |Rest of the World | |||
| |5.8 | |||
| |14.3% | |||
| |} | |||
| In August 2021, Porsche has confirmed that it will be setting up a production plant in Malaysia, the first country outside of Europe.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://paultan.org/2021/08/30/porsche-confirms-ckd-operations-in-malaysia-from-2022/ |title=Porsche confirms CKD operations in Malaysia from 2022 at Sime Darby plant – first outside of Europe! |date=30 August 2021 |website=paultan.org |access-date=9 February 2022}}</ref> Local assembly will be handled by Porsche Malaysia's partner, Sime Darby, which has been the official distributor of the Stuttgart-based company in Malaysia since 2010. | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 154: | Line 192: | ||
| |31 December 2010||€9.23b||€1.67b<ref name=Porschepress-march2012/>||N/A||97,273 | |31 December 2010||€9.23b||€1.67b<ref name=Porschepress-march2012/>||N/A||97,273 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |31 December 2011<ref name=Porschepress-march2012>{{cite press release |url=http://www.porsche.com/international/aboutporsche/pressreleases/archive2012/quarter1/?pool=international-de&id=2012-03-13 |title=Porsche AG turns in record performance in 2011 |date=13 March 2013 |publisher=Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG | |
|31 December 2011<ref name=Porschepress-march2012>{{cite press release |url=http://www.porsche.com/international/aboutporsche/pressreleases/archive2012/quarter1/?pool=international-de&id=2012-03-13 |title=Porsche AG turns in record performance in 2011 |date=13 March 2013 |publisher=Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG |access-date=1 August 2013}}</ref>||€10.9b||€2.05b||127,793||116,978 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |31 December 2012||€13.9b||€2.44b||151,999||143,096<ref name=Porschepress-march2013>{{cite press release |url=http://www.porsche.com/international/aboutporsche/pressreleases/archive2013/quarter1/?pool=international-de&id=2013-03-15 |title=Best year in the history of Porsche |date=15 March 2013 |publisher=Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG | |
|31 December 2012||€13.9b||€2.44b||151,999||143,096<ref name=Porschepress-march2013>{{cite press release |url=http://www.porsche.com/international/aboutporsche/pressreleases/archive2013/quarter1/?pool=international-de&id=2013-03-15 |title=Best year in the history of Porsche |date=15 March 2013 |publisher=Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG |access-date=1 August 2013}}</ref> | ||
| |- | |||
| |31 December 2013||€14.3b||€2.78b||165,808||162,145<ref name=PorscheAG-AnnualReport2013>{{cite web|url=http://files1.porsche.com/filestore.aspx/Annual-Report-2013.pdf|title=Porsche AG Annual Report 2013|access-date=31 July 2014}}{{dead link|date=February 2018 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |31 December 2014||€17.2b||€3.06b||203,097||187,208<ref name=PorscheAG-AnnualReport2014>{{cite web|url=https://newsroom.porsche.com/download/?id=945c3b38-b038-4fb0-b28f-6904c4a5f461&lang=en|title=Porsche AG Annual Report 2014|access-date=17 October 2016}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |31 December 2015||€21.5b<ref>{{cite web|url=https://newsroom.porsche.com/en/company/porsche-at-a-glance-10897.html|title=Porsche at a glance|publisher=Porsche|work=Porsche Newsroom|access-date=17 October 2016|archive-date=10 May 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170510140914/https://newsroom.porsche.com/en/company/porsche-at-a-glance-10897.html|url-status=dead}}</ref>||€3.382b||234,497||225,121<ref name=PorscheAG-AnnualReport2015>{{cite web|url=https://newsroom.porsche.com/en/annual-report/en.html|title=Porsche AG Annual Report 2015|access-date=17 October 2016|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161019033218/https://newsroom.porsche.com/en/annual-report/en.html|archive-date=19 October 2016}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |31 December 2019<ref name=":2">{{Cite web |title=Brief overview |url=https://newsroom.porsche.com/en/company/annual-sustainability-report-2021/brief-overview.html |access-date=19 September 2022 |website=Porsche Newsroom |date=18 March 2022 |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| |€28.5b | |||
| |€4.05b | |||
| |274,463 | |||
| |280,800 | |||
| |- | |||
| |31 December 2020<ref name=":2" /> | |||
| |€28.7b | |||
| |€4.38b | |||
| |263,236 | |||
| |272,162 | |||
| |- | |||
| |31 December 2021<ref name=":2" /> | |||
| |€33.1b | |||
| |€5.73b | |||
| |300,081 | |||
| |301,915 | |||
| |- | |||
| |31 December 2022<ref name=FY2022/> | |||
| |€37.6b | |||
| |€6.77b | |||
| |321,321 | |||
| |309,884 | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| ===Production |
===Production composition=== | ||
| ] | |||
| Of the 105,162 cars produced in the 2007/8 financial year, 34,303 (32.6%) were 911 models, 22,356 (21.3%) were Boxster and Cayman cars and 48,497 (46.1%) were Cayennes. There were three Panamera and three Carrera GT models also reported.<ref name="porsche-se1"/> The production figures of sports cars was quite similar to the 2001/2 totals when 33,061 Porsche 911 and 21,989 Boxsters were produced. | |||
| Of the 246,375 cars produced in the 2017 financial year, 32,197 were 911 models, 25,114 were Boxster and Cayman cars, 63,913 were Cayennes, 27,942 were Panameras and 97,202 were Macans.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://newsroom.porsche.com/de/geschaefts-nachhaltigkeit-bericht-2017/performance/kurz-uebersicht-zusammenfassung-gj-2017.html |title=Porsche 2017 Year in Review |access-date=11 December 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180730021115/https://newsroom.porsche.com/de/geschaefts-nachhaltigkeit-bericht-2017/performance/kurz-uebersicht-zusammenfassung-gj-2017.html |archive-date=30 July 2018 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| Of the 268,691 cars produced in 2018, 36,236 were 911 models, 23,658 were 718 Boxster and Cayman cars, 79,111 were Cayennes, 35,493 were Panameras, 93,953 were Macans and 240 Taycan pre-series vehicles.<ref name="PorscheAG-Annual Report2018">{{cite web|url=https://newsroom.porsche.com/en/annual-sustainability-report-2018/performance/brief-overview-fy-2018-17172.html|title=Porsche AG Annual & Sustainability Report 2018|access-date=19 January 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190812200320/https://newsroom.porsche.com/en/annual-sustainability-report-2018/performance/brief-overview-fy-2018-17172.html|archive-date=12 August 2019|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| Of the 272,162 cars produced in 2020, 34,328 were 911 models, 21,784 were 718 Boxster and Cayman cars, 92,860 were Cayennes, 20,015 Taycan vehicles.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.best-selling-cars.com/brands/2020-full-year-global-porsche-sales-worldwide/ |title=2020 (Full Year) Global: Porsche Sales Worldwide |website=best-selling-cars.com |date=12 January 2021 |access-date=23 August 2021 }}</ref> | |||
| Of the 321,321 vehicles produced in 2022, 41,947 were 911 models,18,080 were 718 Boxster/Cayman models, 91,117 were Macans, 98,113 were Cayennes, 35,241 were Panameras and 36,823 were Taycan models.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Annual and Sustainability Report 2022 Porsche AG |url=https://newsroom.porsche.com/dam/jcr:97e6ac62-edd8-4312-9462-b4fe0c271396/Annual%20and%20Sustainability%20Report%202022%20Porsche%20AG.pdf |access-date=15 March 2023 |website=Porsche AG}}</ref> | |||
| ====U.S. sales==== | |||
| The base price as of March 2024 are: | |||
| *911: $114,400 | |||
| *718: $68,300 | |||
| *Taycan: $99,400 | |||
| *Panamera: $99,900 | |||
| *Cayenne: $79,200 | |||
| *Macan: $78,800 | |||
| ====North American sales==== | |||
| {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center; text-size:94%;" | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center; text-size:94%;" | ||
| |+Annual sales 2003–2005 | |+Annual US sales 2003–2005 | ||
| ! rowspan="2" style="width:120px;"| |
! rowspan="2" style="width:120px;"|Model | ||
| ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2003<ref>{{cite press release|title=January – March – Porsche Vehicle Sales in North America Exceed 30,000 in 2003|publisher=Porsche AG|date=8 January 2004|url=http://www.porsche.com/usa/aboutporsche/pressreleases/pag/archive2004/quarter1/?pool=international-de&id=press108| |
! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2003<ref>{{cite press release|title=January – March – Porsche Vehicle Sales in North America Exceed 30,000 in 2003|publisher=Porsche AG|date=8 January 2004|url=http://www.porsche.com/usa/aboutporsche/pressreleases/pag/archive2004/quarter1/?pool=international-de&id=press108|access-date=10 February 2009}}</ref> | ||
| ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2004<ref>{{cite press release|title=January – March – Porsche sets North American sales record in 2004|publisher=Porsche AG|date=5 January 2005|url=http://www.porsche.com/usa/aboutporsche/pressreleases/pag/archive2005/quarter1/?pool=international-de&id=press45| |
! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2004<ref>{{cite press release|title=January – March – Porsche sets North American sales record in 2004|publisher=Porsche AG|date=5 January 2005|url=http://www.porsche.com/usa/aboutporsche/pressreleases/pag/archive2005/quarter1/?pool=international-de&id=press45|access-date=10 February 2009}}</ref> | ||
| ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2005<ref>{{cite press release|title=January – March – New record year for Porsche in North America|publisher=Porsche AG|date=4 January 2006|url=http://www.porsche.com/usa/aboutporsche/pressreleases/pag/archive2006/quarter1/?pool=international-de&id=2006-01-04-2| |
! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2005<ref>{{cite press release|title=January – March – New record year for Porsche in North America|publisher=Porsche AG|date=4 January 2006|url=http://www.porsche.com/usa/aboutporsche/pressreleases/pag/archive2006/quarter1/?pool=international-de&id=2006-01-04-2|access-date=17 January 2009}}</ref> | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| !<small> |
!<small>Units</small>!!<small>% of total</small>!!<small>Units</small>!!<small>% of total</small>!!<small>Units</small>!!<small>% of total</small> | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| !] ] | !] ] | ||
| Line 181: | Line 265: | ||
| |13,661 ||45%||19,134 ({{increase}} 40%)||57%||14,524 ({{decrease}} 24%)||43% | |13,661 ||45%||19,134 ({{increase}} 40%)||57%||14,524 ({{decrease}} 24%)||43% | ||
| |- style="background:WhiteSmoke;" | |- style="background:WhiteSmoke;" | ||
| ! |
!Total||colspan=2|30,028 ({{increase}} 33%)||colspan=2|33,289 ({{increase}} 11%)||colspan=2|33,859 ({{increase}} 2%) | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center; text-size:94%;" | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center; text-size:94%;" | ||
| |+Annual sales 2006–2008 | |+Annual US sales 2006–2008 | ||
| ! rowspan="2" style="width:120px;"| |
! rowspan="2" style="width:120px;"|Model | ||
| ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2006<ref>{{cite press release|title=Porsche succeeds 2006 with a new record in North America|publisher=Porsche AG|date=3 January 2007|url=http://www.porsche.com/usa/aboutporsche/pressreleases/pag/?pool=international-de&id=2007-01-03| |
! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2006<ref>{{cite press release|title=Porsche succeeds 2006 with a new record in North America|publisher=Porsche AG|date=3 January 2007|url=http://www.porsche.com/usa/aboutporsche/pressreleases/pag/?pool=international-de&id=2007-01-03|access-date=17 January 2009}}</ref> | ||
| ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2007<ref>{{cite press release|title=January – March – Porsche tops its record-breaking sales figures for North America in 2007|publisher=Porsche AG|date=3 January 2008|url=http://www.porsche.com/usa/aboutporsche/pressreleases/pag/archive2008/quarter1/?pool=international-de&id=2008-01-03| |
! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2007<ref>{{cite press release|title=January – March – Porsche tops its record-breaking sales figures for North America in 2007|publisher=Porsche AG|date=3 January 2008|url=http://www.porsche.com/usa/aboutporsche/pressreleases/pag/archive2008/quarter1/?pool=international-de&id=2008-01-03|access-date=17 January 2009}}</ref> | ||
| ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2008<ref>{{cite press release|title=January – March – Porsche Reports Decrease in North American Customer Deliveries in the 2008 Calendar Year|publisher=Porsche AG|date=5 January 2009|url=http://www.porsche.com/usa/aboutporsche/pressreleases/pag/archive2009/quarter1/?pool=international-de&id=2009-01-05-02| |
! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2008<ref>{{cite press release|title=January – March – Porsche Reports Decrease in North American Customer Deliveries in the 2008 Calendar Year|publisher=Porsche AG|date=5 January 2009|url=http://www.porsche.com/usa/aboutporsche/pressreleases/pag/archive2009/quarter1/?pool=international-de&id=2009-01-05-02|access-date=20 August 2009}}</ref> | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| !<small> |
!<small>Units</small>!!<small>% of total</small>!!<small>Units</small>!!<small>% of total</small>!!<small>Units</small>!!<small>% of total</small> | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| !] ] | !] ] | ||
| Line 205: | Line 289: | ||
| |11,141 ({{decrease}} 23%)||31%||13,370 ({{increase}} 20%)||36%||12,898 ({{decrease}} 4%)||46% | |11,141 ({{decrease}} 23%)||31%||13,370 ({{increase}} 20%)||36%||12,898 ({{decrease}} 4%)||46% | ||
| |- style="background:WhiteSmoke;" | |- style="background:WhiteSmoke;" | ||
| ! |
!Total||colspan=2|36,095 ({{increase}} 7%)||colspan=2|36,680 ({{increase}} 2%)||colspan=2|27,717 ({{decrease}} 24%) | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center; text-size:94%;" | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center; text-size:94%;" | ||
| |+Annual sales 2009–2011 | |+Annual US sales 2009–2011 | ||
| ! rowspan="2" style="width:120px;"| |
! rowspan="2" style="width:120px;"|Model | ||
| ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2009<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.theautochannel.com/news/2010/01/05/460581.html |title=Porsche Reports December Sales |publisher=Theautochannel.com | |
! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2009<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.theautochannel.com/news/2010/01/05/460581.html |title=Porsche Reports December Sales |publisher=Theautochannel.com |access-date=12 June 2011}}</ref> | ||
| ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2010<ref>{{cite web|url=http://press.porsche.com/news/release.php?id=602 |title=Porsche Press Release |publisher=Press.porsche.com |date=4 January 2011 | |
! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2010<ref>{{cite web |url=http://press.porsche.com/news/release.php?id=602 |title=Porsche Press Release |publisher=Press.porsche.com |date=4 January 2011 |access-date=12 June 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120522142240/http://press.porsche.com/news/release.php?id=602 |archive-date=22 May 2012 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | ||
| ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2011<ref>{{cite web|url=http://press.porsche.com/news/release.php?id=688 |title=Porsche Press Release |publisher=Press.porsche.com |date=2 January 2012 }}</ref> | ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2011<ref>{{cite web |url=http://press.porsche.com/news/release.php?id=688 |title=Porsche Press Release |publisher=Press.porsche.com |date=2 January 2012 |access-date=6 September 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130514130310/http://press.porsche.com/news/release.php?id=688 |archive-date=14 May 2013 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| !<small> |
!<small>Units</small>!!<small>% of total</small>!!<small>Units</small>!!<small>% of total</small>!!<small>Units</small>!!<small>% of total</small> | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| !] ] | !] ] | ||
| |6,839 ({{decrease}} 17.8%)||35.00%||5,735 ({{decrease}} 16 |
|6,839 ({{decrease}} 17.8%)||35.00%||5,735 ({{decrease}} 16%)||23%||6,016 ({{increase}} 5%)||21% | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| !]&] | !] | ||
| |3,875 ({{decrease}} 39.4%)||19.00%||3,499 ({{decrease}} 9 |
|3,875 ({{decrease}} 39.4%)||19.00%||3,499 ({{decrease}} 9%)||14%||3,150 ({{decrease}} 9%)||11% | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| !] | !] | ||
| |1,247 ||6.33%||7,741 ({{increase}} |
|1,247 ||6.33%||7,741 ({{increase}}520%)||31%||6,879 ({{decrease}}11%)||24% | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| !] | !] | ||
| |7,735 ({{decrease}} |
|7,735 ({{decrease}}31%)||39%||8,343 ({{increase}}8%)||33%||12,978 ({{increase}}55%)||45% | ||
| |- style="background:WhiteSmoke;" | |- style="background:WhiteSmoke;" | ||
| ! |
!Total||colspan=2|19,696 ({{decrease}}24%) ||colspan=2|25,320 ({{increase}}28%)||colspan=2|29,023 ({{increase}}15%) | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center; text-size:94%;" | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center; text-size:94%;" | ||
| |+Annual sales 2012–2014 | |+Annual US sales 2012–2014 | ||
| ! rowspan="2" style="width:120px;"| |
! rowspan="2" style="width:120px;"|Model | ||
| ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2012<ref>{{cite web|url=http://press.porsche.com/news/release.php?id=756 |title=Porsche Reports Best-Ever Sales in 2012; 21 Percent Increase Over 2011 |publisher=Press.porsche.com |date=2013- |
! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2012<ref>{{cite web |url=http://press.porsche.com/news/release.php?id=756 |title=Porsche Reports Best-Ever Sales in 2012; 21 Percent Increase Over 2011 |publisher=Press.porsche.com |date=14 January 2013 |access-date=27 February 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140206230329/http://press.porsche.com/news/release.php?id=756 |archive-date=6 February 2014 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | ||
| ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2013<ref>{{cite web|url=http://press.porsche.com/news/release.php?id=837 |title=Porsche Reports Record Sales in 2013; 21 percent increase over 2012 |publisher=Press.porsche.com |date= | |
! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2013<ref>{{cite web |url=http://press.porsche.com/news/release.php?id=837 |title=Porsche Reports Record Sales in 2013; 21 percent increase over 2012 |publisher=Press.porsche.com |access-date=27 February 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140117011757/http://press.porsche.com/news/release.php?id=837 |archive-date=17 January 2014 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | ||
| ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2014<ref>{{cite web |url=http://press.porsche.com/news/release.php?id=896 |title=U.S. Porsche Dealers Sell 47,007 Vehicles in 2014 |publisher=Press.porsche.com |access-date=31 October 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161031214721/http://press.porsche.com/news/release.php?id=896 |archive-date=31 October 2016 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2014 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| !<small> |
!<small>Units</small>!!<small>% of total</small>!!<small>Units</small>!!<small>% of total</small>!!<small>Units</small>!!<small>% of total</small> | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| !] | !] | ||
| |8,528 || 24 |
|8,528 || 24%|| 10,442 ||24.67% ||10,529 ||22% | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| !] & ] | !] | ||
| |3,356 || |
|3,356 || 10%|| 7,953 ||18.79% ||7,292 ||15% | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| !] | !] | ||
| |7,614 || |
|7,614 || 22%|| 5,421 ||13% ||5,740 ||12% | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| !] | !] | ||
| |15,545 || 44.36%|| 18,507 || || || |
|15,545 || 44.36%|| 18,507 ||44% ||16,205 ||34,47% | ||
| |- | |||
| !] | |||
| |n.a. ||n.a. || n.a. ||n.a. ||7,241 ||15% | |||
| |- style="background:WhiteSmoke;" | |||
| !Total||colspan=2| 35,043 ({{increase}}21%) ||colspan=2| 42,323 ({{increase}}21%) ||colspan=2|47,007 ({{increase}}11%) | |||
| |} | |||
| {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center; text-size:94%;" | |||
| |+Annual US sales 2015–2017 | |||
| ! rowspan="2" style="width:120px;"|Model | |||
| ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2015<ref>{{cite web |url=http://press.porsche.com/news/release.php?id=971 |title=Porsche Sets Record Year in 2015 with 51,756 Vehicles Delivered in the United States |publisher=Press.porsche.com |date=5 January 2016 |access-date=31 October 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161104140536/http://press.porsche.com/news/release.php?id=971 |archive-date=4 November 2016 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2016<ref>{{cite web |url=http://press.porsche.com/news/release.php?id=1010 |title=Porsche Sets Record in 2016 with 54,280 Vehicles Delivered in the U.S |publisher=Press.porsche.com |date=4 January 2017 |access-date=5 June 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170518154319/http://press.porsche.com/news/release.php?id=1010 |archive-date=18 May 2017 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2017<ref>{{cite web |url=https://presse.porsche.de/prod/presse_pag/PressResources.nsf/Content?ReadForm&languageversionid=812758 |website=presse.porsche.de |publisher=Porsche |title=Porsche Sets U.S. Sales Record in 2017 with 55,420 Vehicles Delivered, Up 2.1 Percent |access-date=16 May 2020}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| !<small>Units</small>!!<small>% of total</small>!!<small>Units</small>!!<small>% of total</small>!!<small>Units</small>!!<small>% of total</small> | |||
| |- | |||
| !] | |||
| | 9,898 || 19.12% || 8,901 || 16.40% || 8,970 || 16.19% | |||
| |- | |||
| !] | |||
| | 6,663 || 12.87% || 6,260 || 11.53% || 5,087 || 9.18% | |||
| |- | |||
| !] | |||
| | 4,986 || 9.63% || 4,403 || 8.11% || 6,731 || 12.15% | |||
| |- | |||
| !] | |||
| | 16,473 || 31.83%|| 15,383 || 28.34% || 13,203 || 23.83% | |||
| |- | |||
| !] | |||
| | 13,533 || 26.15% || 19,332 || 35.62% || 21,429 || 38.67% | |||
| |- style="background:WhiteSmoke;" | |||
| !Total||colspan=2| 51,756 ({{increase}}10%) ||colspan=2| 54,280 ({{increase}}5%) ||colspan=2| 55,420 ({{increase}}2%) | |||
| |} | |||
| {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center; text-size:94%;" | |||
| |+Annual US sales 2018–2020 | |||
| ! rowspan="2" style="width:120px;"|Model | |||
| ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2018<ref>{{cite web |url=https://presse.porsche.de/prod/presse_pag/PressResources.nsf/Content?ReadForm&languageversionid=938866 |website=presse.porsche.de |publisher=Porsche |title=Porsche Sets U.S. Retail Sales Record in 2018 |access-date=16 May 2020}}</ref> | |||
| ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2019<ref>{{cite web |url=https://presse.porsche.de/prod/presse_pag/PressResources.nsf/Content?ReadForm&languageversionid=1055611&hl=unternehmen-presseinformation |website=presse.porsche.de |publisher=Porsche |title=Porsche Posts Record U.S. Retail Sales in 2019 |access-date=16 May 2020}}</ref> | |||
| ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2020<ref>{{cite press release |url=https://newsroom.porsche.com/en_US/2021/company/porsche-cars-north-america-retail-sales-fourth-quarter-year-end-2020-23328.html |title=Porsche Reports U.S. Retail Sales for 2020 |publisher=Porsche Cars North America |date=5 January 2021 |access-date=23 August 2021 }}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| !<small>Units</small>!!<small>% of total</small>!!<small>Units</small>!!<small>% of total</small>!!<small>Units</small>!!<small>% of total</small> | |||
| |- | |||
| !] | |||
| | 9,647 || 17% || 9,265 || 15% || 8,840 ({{decrease}}4.6%)|| 15% | |||
| |- | |||
| !] | |||
| | 5,276 || 9% || 3,880 || 6% || 3,447 ({{decrease}}11%)|| 6% | |||
| |- | |||
| !] | |||
| | n.a. || n.a. || 130 || 0.2% || 4,414 || 8% | |||
| |- | |||
| !] | |||
| | 8,042 || 14% || 6,625 || 11% || 3,870 ({{decrease}}42%)|| 7% | |||
| |- | |||
| !] | |||
| | 10,733 || 19% || 19,001 || 31% || 18,092 ({{decrease}}5%)|| 32% | |||
| |- | |||
| !] | |||
| | 23,504 || 41% || 22,667 || 37% || 18,631 ({{decrease}}18%)|| 33% | |||
| |- style="background:WhiteSmoke;" | |||
| !Total||colspan=2| 57,202 ({{increase}}3%) ||colspan=2| 61,568 ({{increase}}7%) ||colspan=2| 57,294 ({{decrease}}7.5%) | |||
| |} | |||
| {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center; text-size:94%;" | |||
| |+Annual US sales 2021–2023 | |||
| ! rowspan="2" style="width:120px;"|Model | |||
| ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2021<ref>{{cite press release |url=https://newsroom.porsche.com/en_US/2022/company/porsche-cars-north-america-retail-sales-fourth-quarter-year-end-2021-26964.html |title=Porsche reports U.S. retail sales for Q4 and full-year 2021 |publisher=Porsche |date=1 April 2022 |access-date=9 February 2022}}</ref> | |||
| ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2022 | |||
| ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2023<ref>{{cite press release|url=https://newsroom.porsche.com/en_US/2023/company/porsche-cars-north-america-retail-sales-third-quarter-34061.html|title=Porsche reports U.S. retail sales|publisher=Porsche Cars North America |date=October 2023|access-date=12 July 2023}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| !<small>Units</small>!!<small>% of total</small>!!<small>Units</small>!!<small>% of total</small>!!<small>Units</small>!!<small>% of total</small> | |||
| |- | |||
| !] | |||
| |10,042 ({{increase}}14%)||14%||10,204 ({{increase}}2%)||15%||11,692 ({{increase}}15%)||16% | |||
| |- | |||
| !] | |||
| |4,292 ({{increase}}25%)|| 6% ||3,484 ({{decrease}}19%)||5%||4,526 ({{increase}}30%)||6% | |||
| |- | |||
| !] | |||
| |9,419 ({{increase}} 113%)|| 13% ||7,271 ({{decrease}}23%)||10%||7,570 ({{increase}}4%)||10% | |||
| |- | |||
| !] | |||
| |4,257 ({{increase}}10%)|| 6% ||4,224 ({{decrease}}1%)||6%||4,205 (-)||6% | |||
| |- | |||
| !] | |||
| |17,299 ({{decrease}}4%)|| 25% ||21,194 ({{increase}}23%)||30%||20,475 ({{decrease}}3%)||27% | |||
| |- | |||
| !] | |||
| |24,716 ({{increase}}33%)|| 35% ||23,688 ({{decrease}}4%)||34%||26,947 ({{increase}}14%)||36% | |||
| |- style="background:WhiteSmoke;" | |||
| !Total||colspan=2| 70,005 ({{increase}}22%)||colspan=2|70,065 ({{increase}}1/2%)||75,415 ({{increase}}8%) | |||
| |} | |||
| {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center; text-size:94%;" | |||
| |+Annual US sales 2023–2025 | |||
| ! rowspan="2" style="width:120px;"|Model | |||
| ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|YTD Q3 | |||
| ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2025 | |||
| ! colspan="2" style="width:160px;"|2026 | |||
| |- | |||
| !<small>Units</small>!!<small>% of total</small>!!<small>Units</small>!!<small>% of total</small>!!<small>Units</small>!!<small>% of total</small> | |||
| |- | |||
| !] | |||
| |10,841 ({{increase}}25%)||20%|| | |||
| |- | |||
| !] | |||
| |3,821 ({{increase}}8%)||7%|| | |||
| |- | |||
| !] | |||
| |3,394 ({{decrease}}35%)||6%|| | |||
| |- | |||
| !] | |||
| |2,527 ({{decrease}}20%)||5%|| | |||
| |- | |||
| !] | |||
| |15,507 ({{increase}}4%)||29%|| | |||
| |- | |||
| !] | |||
| |17,993 ({{decrease }}14%)||33%|| | |||
| |- style="background:WhiteSmoke;" | |- style="background:WhiteSmoke;" | ||
| ! |
!Total||colspan=2|54,083 ({{decrease}}4%) | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| ==Models== | ==Models== | ||
| {{See also|Category:Porsche vehicles|Porsche type numbers}} | {{See also|List of Porsche vehicles|Category:Porsche vehicles|Porsche type numbers}} | ||
| The current Porsche ] includes sports cars from the ] ] to their most famous product, the ]. The ] is a ] otherwise similar to the Boxster. The ] is Porsche's mid-size luxury ] (SUV). A high performance luxury ], the ], was launched in 2009. | The current Porsche ] includes sports cars from the ] ] to their most famous product, the ]. The ] is a ] otherwise similar to the Boxster. The ] is Porsche's mid-size luxury ] (SUV). A high performance luxury ], the ], was launched in 2009. | ||
| Line 264: | Line 468: | ||
| ===Consumer models=== | ===Consumer models=== | ||
| {{div col|colwidth=25em}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ]]] | |||
| ]]] | |||
| {{div col|cols=3}} | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *''']''' 4-seat ], ] and ] | *''']''' 4-seat ], ] and ] | ||
| **] | |||
| **] | |||
| **] | |||
| **] | |||
| **] | |||
| **] | |||
| **] | |||
| **''']''' | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| Line 277: | Line 485: | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] 4-seat ] | *] 4-seat ] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *''']''' | |||
| *''']''' 2-seat ] | *''']''' 2-seat ] | ||
| **] | |||
| **] | |||
| **] | |||
| **''']''' | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *''']''' 2-seat coupe | *''']''' 2-seat coupe | ||
| * |
**] | ||
| **] | |||
| *''']''' ] ] | |||
| *''']''' |
**''']''' | ||
| *''']''' Mid-size ] | |||
| *''']''' Compact ] | |||
| *''']''' 4- or "4+1"-seat ] and ] ] | |||
| *''']''' 4- or "4+1"-seat ] and shooting-brake estate ] | |||
| {{div col end}} | {{div col end}} | ||
| <gallery mode="nolines" widths="220"> | |||
| File:2018 Porsche 718 Cayman S S-A 2.5 Front.jpg|Porsche Cayman | |||
| File:2018 Porsche 718 Boxster S S-A 2.5 Front.jpg|Porsche Boxster | |||
| File:Porsche 972 IMG 9526.jpg|Porsche Panamera | |||
| File:Porsche Cayenne, IAA 2017 (1Y7A2256).jpg|Porsche Cayenne | |||
| File:2025 Porsche Macan Turbo (United States) front view.jpg| Porsche Macan | |||
| File:2019 Porsche 911 Carrera S S-A 3.0 Front.jpg|Porsche 911 | |||
| File:Porsche Taycan Turbo S IMG 3471.jpg|Porsche Taycan | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| ===Racing models=== | ===Racing models=== | ||
| {{div col| |
{{div col|colwidth=22em}} | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| Line 308: | Line 527: | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| Line 317: | Line 537: | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *Porsche 99X Electric | |||
| *Porsche-March 89P | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] (never raced) | *] (never raced) | ||
| Line 325: | Line 547: | ||
| ===Prototypes and concept cars=== | ===Prototypes and concept cars=== | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| {{div col| |
{{div col|colwidth=22em}} | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| Line 331: | Line 553: | ||
| *] (911 prototype) | *] (911 prototype) | ||
| *] (flat-6 914) | *] (flat-6 914) | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] prototype | ||
| *] | |||
| *]<ref>{{cite web |title=Porsche 969/965 Story, Prototypes and Styling Exercises |url=https://oppositelock.kinja.com/porsche-969-965-story-prototypes-and-styling-exercises-1459215522 |website=Oppositelock |access-date=13 October 2020 |language=en-us |archive-date=14 October 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201014145531/https://oppositelock.kinja.com/porsche-969-965-story-prototypes-and-styling-exercises-1459215522 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] concept | *] concept | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] concept | |||
| *] | |||
| {{div col end}} | {{div col end}} | ||
| ===Tractors=== | ===Tractors=== | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| {{div col| |
{{div col|colwidth=22em}} | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| Line 358: | Line 583: | ||
| ===Hybrid and electric vehicles=== | ===Hybrid and electric vehicles=== | ||
| {{For|details on a Porsche 911-based all-electric car|ERuf Model A}} | {{For|details on a Porsche 911-based all-electric car|ERuf Model A}} | ||
| In 2010, Porsche launched the ] and announced the ], and launched the ] sports car in 2014, which also features a hybrid system. Also a plug-in hybrid model called the ] was released in October 2013 in the United States<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.hybridcars.com/porsche-panamera-s-e-hybrid-now-available-in-the-us/|title=Porsche Panamera S E-Hybrid Now Available in the US|author=Philippe Crowe |publisher=HybridCars.com|date=5 September 2013|access-date=5 September 2013}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://wardsauto.com/vehicle-test-drives/sales-boost-expected-refreshed-panamera|title=Sales Boost Expected for Refreshed Panamera|author=Tom Murphy|work=Wards Auto|date=7 October 2013|access-date=25 October 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131029214455/http://wardsauto.com/vehicle-test-drives/sales-boost-expected-refreshed-panamera|archive-date=29 October 2013|url-status=dead}}</ref> and during the fourth quarter of 2013 in several European countries. | |||
| In 2010 Porsche launched the Cayenne S Hybrid and announced the Panamera Hybrid and launched the ] hypercar in 2014, which also features a hybrid system. The Panamera Hybrid has been released as a plug-in hybrid called the Panamera S E-Hybrid. | |||
| Porsche Intelligent Performance has also released an electric ] called the Boxster E and a hybrid version of a GT3 called the GT3 R Hybrid. These vehicles can be viewed on the website: www.porsche.com/microsite/intelligent-performance/international.aspx It had been previously thought that Porsche planned to offer an electric version of the ] but this has not yet been formally announced.<ref>{{cite web|author=Christoph Hammerschmidt|url=http://www.automotivedesign-europe.com/showArticle.jhtml?articleID=211200115&cid=NL_ADLeu|title=| Automotive DesignLine Europe|publisher=AutomotiveDesign-Europe.com|date=13 October 2008|accessdate=30 May 2009}}</ref> | |||
| Porsche developed a prototype electric ] called the Boxster E in 2011<ref>{{cite web|title=Porsche Publicly Debuts its Electric Boxster E, But It's Not For Sale|url=http://blog.caranddriver.com/porsche-publicly-debuts-its-electric-boxster-e-but-its-not-for-sale/|website=Car and Driver|access-date=16 September 2014|date=24 May 2011|archive-date=9 August 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140809233722/http://blog.caranddriver.com/porsche-publicly-debuts-its-electric-boxster-e-but-its-not-for-sale/|url-status=dead}}</ref> and a hybrid version of the 911 called the GT3 R Hybrid, developed with ] in 2010.<ref>{{cite web|title=PORSCHE 911 GT3R HYBRID|url=http://www.williamsf1.com/AdvancedEngineering/Case-Studies/Porsche-911-GT3R-Hybrid/|website=Williams Grand Prix Engineering Limited|access-date=16 September 2014|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140922110146/http://www.williamsf1.com/AdvancedEngineering/Case-Studies/Porsche-911-GT3R-Hybrid/|archive-date=22 September 2014}}</ref> | |||
| In July 2014, Porsche announced the launch by the end of 2014 of the ] a ], which will displace the Cayenne S Hybrid from the lineup. The S E-Hybrid will be the first plug-in hybrid in the premium ] segment and will allow Porsche to become the first automaker with three production plug-in hybrid models.<ref name=CayennePHEV>{{cite web|url=http://www.greencarcongress.com/2014/07/20140724-cayenne.html|title=Porsche introducing new plug-in Cayenne S E-Hybrid SUV; third plug-in from Porsche|author=Porsche Press Release|publisher=Green Car Congress|date=24 July 2014|access-date=27 July 2014}}</ref> | |||
| In July 2017, Porsche installed its first 350 kW, 800V charging station, which the upcoming ] will use. As of 2017, the Porsche charging station is the fastest electric vehicle charging station in the world, being able to charge a Porsche Mission E up to 80% within 15 minutes. Porsche is also currently working with other manufacturers to make Porsche charging stations compatible with other electric vehicles.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://electrek.co/2017/07/14/porsche-350-kw-ev-charging-station/|title=Porsche installs first ultra-fast 350 kW EV charging station|last=Lambert|first=Fred|date=14 July 2017|work=Electrek|access-date=16 July 2017|language=en-US}}</ref> | |||
| In August 2018, Porsche announced that the formerly named ] electric car would be named "''Taycan''" meaning 'leaping horse'.<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.theweek.co.uk/electric-cars/93814/porsche-taycan-2019-news|title=Porsche Taycan 2019: price, interior specs and release|work=The Week UK|access-date=1 October 2018|language=en|archive-date=1 October 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181001104147/http://www.theweek.co.uk/electric-cars/93814/porsche-taycan-2019-news|url-status=dead}}</ref> The prototype electric car was expected to be revealed in 2019 after its completion.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://electrek.co/2018/07/30/porsche-taycan-all-electric-powertrain-details/|title=Porsche reveals and explains the Taycan all-electric powertrain in detail|date=30 July 2018|work=Electrek|access-date=1 October 2018|language=en-US}}</ref> Porsche Taycan went on sale in 2020. | |||
| ===Aircraft engines=== | ===Aircraft engines=== | ||
| ]]] | |||
| See ]. | See ]. | ||
| === Electric Bicycles === | |||
| In 2021, Porsche released an electric Mountain Bike in partnership with ], with features such as an integrated cockpit designed by ] and drive unit, drivetrain and electronic shifting designed by ].<ref>{{Cite news |last=Spratt |first=Ed |date=Feb 23, 2023 |title=Porsche Launches an eMTB Featuring Magura's Integrated Cockpit & Inverted Fork |url=https://www.pinkbike.com/news/porsche-takes-complete-ownership-of-greyp.html |access-date=Nov 8, 2024 |work=Pink Bike}}</ref> Porsche followed this by completely buying eBike motor and battery company Fazua in 2022<ref>{{Cite news |last=Spratt |first=Ed |date=Jun 8, 2022 |title=Porsche Takes Complete Ownership of Fazua |url=https://www.pinkbike.com/news/porsche-takes-complete-ownership-of-fazua.html |access-date=Nov 8, 2024 |work=Pink Bike}}</ref> and sports bikes company Greyp Bikes, sister company of ], in 2023. Greyp Bikes was renamed to Porsche eBike Performance GmbH.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Spratt |first=Ed |date=Feb 23, 2023 |title=Porsche Takes Complete Ownership of Greyp |url=https://www.pinkbike.com/news/porsche-takes-complete-ownership-of-greyp.html |access-date=Nov 8, 2024 |work=Pink Bike}}</ref> | |||
| ==Motorsport== | ==Motorsport== | ||
| {{Main|Porsche in motorsport}} | {{Main|Porsche in motorsport}} | ||
| ] blue and green "''psychedelic''" livery on a 1970 917K. This car raced at ] in 1970.]] | ] blue and green "''psychedelic''" livery on a 1970 917K. This car raced at ] in 1970.]] | ||
| Porsche |
Porsche has a record 19 outright wins at the ].<ref>{{cite news|last1=Staff|title=Porsche survives to take overall win at 2017 24 Hours of Le Mans|url=http://autoweek.com/article/24-hours-le-mans/porsche-survives-take-overall-win-2017-24-hour-le-mans-reliability-issues|access-date=19 June 2017|work=AutoWeek|publisher=Crain Communications|date=18 June 2017}}</ref> Porsche is currently the world's largest race car manufacturer. In 2006, Porsche built 195 race cars for various international motor sports events. In 2007, Porsche was expected to construct no fewer than 275 dedicated race cars (7 RS Spyder LMP2 prototypes, 37 GT2 spec 911 GT3-RSRs, and 231 911 GT3 Cup vehicles).<ref>{{cite web|author=Gary Watkins|title=Warehouse Shopping – Inside Porsche's Motorsport Center|url=http://www.autoweek.com/apps/pbcs.dll/article?AID=/20070307/FREE/70305013/1001|work=]|date=7 March 2007|access-date=17 January 2009|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111108020927/http://www.autoweek.com/apps/pbcs.dll/article?AID=%2F20070307%2FFREE%2F70305013%2F1001|archive-date=8 November 2011|url-status=dead}}</ref> | ||
| ==Pronunciation |
==Pronunciation== | ||
| In keeping with the family name of founder ], the company's name is pronounced {{IPA |
In keeping with the family name of founder ], the company's name is pronounced {{IPA|de|ˈpɔʁʃə|}} in German, which corresponds to {{IPAc-en|ˈ|p|ɔːr|ʃ|ə|audio=en-uk-Porsche.ogg}} {{respell|POR|shə}} in English,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://german.about.com/library/weekly/aa020401b.htm|title=Porsche and Neanderthal: pronouncing German words in English|publisher=German.about.com|date=15 September 2008|access-date=29 April 2009|archive-date=12 January 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110112144535/http://german.about.com/library/weekly/aa020401b.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref> ] with the feminine name '']''. However, in English it is often mispronounced as a single syllable {{IPAc-en|p|ɔːr|ʃ|audio=en-us-Porsche.ogg}} {{respell|PORSH}}—without a final {{IPAslink|ə}}. In ], word-final {{angbr|e}} is not ] but is instead an ] ]. <!-- Hear it on --> | ||
| ==Reputation== | ==Reputation== | ||
| In a survey conducted by the ] in New York, Porsche was awarded the title of "the most prestigious automobile brand". Five hundred households with a gross annual income of at least $200,000 and a net worth of at least $720,000 participated.<ref>{{cite web|title=Porsche enjoys unsurpassed prestige in US|publisher=Porsche AG press release|url=http://www.porsche.com/usa/aboutporsche/pressreleases/pag/?pool=international-de&id=2006-05-05|access-date=6 April 2008|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080418015724/http://www.porsche.com/usa/aboutporsche/pressreleases/pag/?pool=international-de&id=2006-05-05|archive-date=18 April 2008|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| ] ] GT2 RS]] | |||
| In a May 2006 survey, Porsche was awarded the title of the most prestigious automobile brand by ], New York; it questioned more than 500 households with a gross annual income of at least $200,000 and a net worth of at least $720,000.<ref>{{cite web|title=Porsche enjoys unsurpassed prestige in US|publisher=Porsche AG press release|url=http://www.porsche.com/usa/aboutporsche/pressreleases/pag/?pool=international-de&id=2006-05-05|accessdate=6 April 2008}}</ref> | |||
| Porsche |
Porsche won the ] Initial Quality Study (IQS) in 2006, 2009, 2010, and 2014.<ref>{{cite web |title=Magna Steyr Assembly Plant in Graz, Austria, Receives Top Vehicle Quality Award in Europe |url=http://www.jdpower.com/corporate/news/releases/pdf/2006082b.pdf |work=] |date=7 June 2006 |access-date=31 July 2008 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080530022645/http://www.jdpower.com/corporate/news/releases/pdf/2006082b.pdf |archive-date=30 May 2008 }}</ref> | ||
| ===SUV reception=== | ===SUV reception=== | ||
| Porsche's 2003 SUV, the Cayenne, received generally favorable commentary.<ref name=CNBC>{{cite web|url=https://www.cnbc.com/2009/03/19/peering-into-porsches-future.html|title=Peering into Porsche's Future|last=DeBord|first=Matthew|date=19 March 2009|work=]|access-date=20 March 2009}}</ref><ref name="Frankel">{{cite news|url=http://www.timesonline.co.uk/tol/driving/new_car_reviews/article823701.ece|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081204061507/http://www.timesonline.co.uk/tol/driving/new_car_reviews/article823701.ece|url-status=dead|archive-date=4 December 2008|title=Porsche Cayenne|last=Frankel|first=Andrew|date=17 November 2002|work=The Sunday Times|access-date=20 March 2009|location=London}}</ref> | |||
| In 2015, US News ranked the Macan as the best luxury compact SUV in its class.<ref>{{cite web|title=Porsche Macan Review|url=http://usnews.rankingsandreviews.com/cars-trucks/Porsche_Macan/}}</ref> | |||
| ==Reliability== | |||
| A Canadian study in 2011 revealed that 97.4 percent of Porsches from the last 25 years are still on the road.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.autoguide.com/auto-news/2011/03/porsche-911-named-most-reliable-sports-car-by-j-d-power.html|title=Porsche 911 Named Most Reliable Sports Car By J.D. Power|work=autoguide.com|date=21 March 2011 }}</ref> | |||
| In 2014, the ] and ] made the '']'' list for most reliable vehicles on the road.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.forbes.com/sites/hannahelliott/2012/12/07/the-2014-porsche-cayman-is-better-than-you-think-heres-why/|title=The 2014 Porsche Cayman is Better Than You Think. Here's Why.|first=Hannah|last=Elliott|website=Forbes}}</ref> | |||
| Porsche's 911 has been officially named by the ] (Technischer Überwachungsverein; Technical Inspection Association) as Germany's most reliable car.<ref>{{cite web|title=It's Official: Toyota Prius and Porsche 911 Are Germany's Most Reliable Cars|url=http://www.thetruthaboutcars.com/2011/12/it%E2%80%99s-official-toyota-prius-and-porsche-911-are-germany%E2%80%99s-most-reliable-cars/|date=8 December 2011}}</ref> | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| {{Portal|Baden-Württemberg|Companies|Cars}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{Portal bar|Companies}} | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| ===Notes=== | |||
| {{Reflist|30em}} | |||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| ===Bibliography=== | |||
| <!-- last updated January 2023 --> | |||
| {{refbegin}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Frankenberg |first1=Richard von |author1-link=Richard von Frankenberg |title=Porsche: the Man and his Cars |date=1973 |orig-year=1961 |publisher=G.T. Foulis & Co. |location=Henley-on-Thames, Oxfordshire, UK |isbn=0854290907 |edition=revised}} <!-- template --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Leffingwell |first1=Randy |last2=Ingram |first2=Cameron |last3=Furman |first3=Michael |title=Porsche Unexpected: Discoveries in Collecting |date=2014 |publisher=Coachbuilt Press |location=Philadelphia, PA, USA |isbn=9780988273337}} | |||
| * {{Ludvigsen-EwE-1}} | |||
| * {{Ludvigsen-EwE-2 |author-mask=7}} | |||
| * {{Ludvigsen-EwE-3 |author-mask=7}} | |||
| * {{Ludvigsen-EwE-4 |author-mask=7}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Seiff |first1=Ingo |title=Porsche: Portrait of a Legend |date=1989 |publisher=Macdonald Orbis |location=London |isbn=0356150623}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Smith |first1=Luke |title=The Story of Porsche: A Tribute to the Legendary Manufacturer |date=2022 |publisher=Welbeck Publishing Group |location=London |isbn=9781802792911}} | |||
| * {{Wood-GMG}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{Commons category}} | {{Commons category}} | ||
| * {{official website}} | |||
| * – the top-tier parent company | |||
| * |
* – the top-tier parent company | ||
| * – Service by the Porsche Communication for journalists and the online community. | |||
| * | * | ||
| * | * | ||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| ;Video clips | |||
| * | |||
| {{Porsche}} | {{Porsche vehicles}} | ||
| {{Porsche early timeline}} | |||
| {{Porsche modern timeline}} | |||
| {{Volkswagen Group brands}} | {{Volkswagen Group brands}} | ||
| {{Automotive industry in Germany}} | {{Automotive industry in Germany}} | ||
| {{DAX companies}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 02:51, 19 December 2024
German automobile manufacturer This article is about the automotive brand and manufacturer, Porsche AG. For the holding company that is the majority owner of Volkswagen Group, see Porsche SE. For other uses of Porsche, see Porsche (disambiguation).
 | |
 Headquarters in Stuttgart Headquarters in Stuttgart | |
| Company type | Public |
|---|---|
| Traded as | FWB: P911 DAX component OTC Pink: DRPRY |
| ISIN | DE000PAG9113 |
| Industry | Automotive |
| Founded | 1931; 93 years ago (1931) in Stuttgart, Germany |
| Founder | Ferdinand Porsche |
| Headquarters | Stuttgart, Germany |
| Area served | Worldwide |
| Key people | Wolfgang Porsche (chairman) Oliver Blume (CEO) |
| Products | Automobiles |
| Production output | |
| Services | Automotive financial services, engineering services, investment management |
| Revenue | |
| Operating income | |
| Net income | |
| Total assets | |
| Total equity | |
| Owners |
|
| Number of employees | 39,162 (2022) |
| Subsidiaries |
|
| Website | www |
Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG, usually shortened to Porsche (German pronunciation: [ˈpɔʁʃə] ; see below), is a German automobile manufacturer specializing in luxury, high-performance sports cars, SUVs and sedans, headquartered in Stuttgart, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The company is owned by Volkswagen AG, a controlling stake of which is owned by Porsche Automobil Holding SE. Porsche's current lineup includes the 718, 911, Panamera, Macan, Cayenne and Taycan.
The origins of the company date to the 1930s when Czech-German automotive engineer Ferdinand Porsche founded Porsche with Adolf Rosenberger, a keystone figure in the creation of German automotive manufacturer and Audi precursor Auto Union, and Austrian businessman Anton Piëch, who was, at the time, also Ferdinand Porsche's son in law. In its early days, it was contracted by the German government to create a vehicle for the masses, which later became the Volkswagen Beetle. After World War II, when Ferdinand, a member of both the Nazi Party and the SS, would be arrested for war crimes, his son Ferry Porsche, an SS volunteer, began building his own car, which would result in the Porsche 356.
In 2009, Porsche entered an agreement with Volkswagen to create an 'integrated working group' by merging the two companies' car manufacturing operations. By 2015, Porsche SE, the holding company spun off from the original Porsche firm, had a controlling interest in the Volkswagen Group, which included Audi and Lamborghini as subsidiaries.
History
Origin
Ferdinand Porsche (1875–1951) founded the company called "Dr. Ing. h. c. F. Porsche GmbH" with Adolf Rosenberger and Anton Piëch in 1931. The name is short for Ferdinand Porsche's full title in German, Doktor Ingenieur honoris causa lit. 'Doctor of Engineering, Honorary Degree' Ferdinand Porsche. The main offices was at Kronenstraße 24 in the centre of Stuttgart. Initially, the company offered motor vehicle development work and consulting, but did not build any cars under its own name. One of the first assignments the new company received was from the German government to design a car for the people; that is, a Volkswagen. This resulted in the Volkswagen Beetle, one of the most successful car designs of all time. Later, the Porsche 64 would be developed in 1939 using many components from the Beetle.


During World War II, Volkswagen production turned to the military version of the Volkswagen Beetle, the Kübelwagen, 52,000 produced, and Schwimmwagen, 15,584 produced. Porsche produced several designs for heavy tanks during the war, losing out to Henschel & Son in both contracts that ultimately led to the Tiger I and the Tiger II. However, not all this work was wasted, as the chassis Porsche designed for the Tiger I was used as the base for the Elefant tank destroyer. Porsche also developed the Maus super-heavy tank in the closing stages of the war, producing two prototypes. Ferdinand Porsche's biographer, Fabian Müller, wrote that Porsche had thousands of people forcibly brought to work at their factories during the war. The workers wore the letter "P" on their clothing at all times. It stood not for "Porsche", but for "Poland".
At the end of World War II in 1945, the Volkswagen factory at KdF-Stadt fell to the British. Ferdinand lost his position as chairman of the board of management of Volkswagen, and Ivan Hirst, a British Army major, was put in charge of the factory. (In Wolfsburg, the Volkswagen company magazine dubbed him "The British Major who saved Volkswagen".) On 15 December of that year, Ferdinand was arrested for war crimes, but not tried. During his 20-month imprisonment, Ferdinand Porsche's son, Ferry Porsche, decided to build his own car, because he could not find an existing one that he wanted to buy. He also had to steer the company through some of its most difficult days until his father's release in August 1947.
The first models of what was to become the 356 were built in a small sawmill in Gmünd, Austria. The prototype car was shown to German auto dealers, and when pre-orders reached a set threshold, production (with aluminum body) was begun by Porsche Konstruktionen GesmbH, founded by Ferry and Louise. Many regard the 356 as the first Porsche simply because it was the first model sold by the fledgling company. After production of the 356 was taken over by the father's Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche GmbH in Stuttgart in 1950, Porsche commissioned a Zuffenhausen-based company, Reutter Karosserie, which had previously collaborated with the firm on Volkswagen Beetle prototypes, to produce the 356's steel body. In 1952, Porsche constructed an assembly plant (Werk 2) across the street from Reutter Karosserie; the main road in front of Werk 1, the oldest Porsche building, is now known as Porschestrasse. The 356 was road-certified in 1948.
Company logo
-
 Coat of arms of Württemberg during the Weimar-era
Coat of arms of Württemberg during the Weimar-era
-
 Coat of arms of Stuttgart
Coat of arms of Stuttgart
Porsche's company logo stems from the coat of arms of the Free People's State of Württemberg of Weimar Germany of 1918–1933, which had Stuttgart as its capital. (The Bundesland of Württemberg-Hohenzollern used the same arms from 1945 to 1952, while Stuttgart during these years operated as the capital of adjacent Württemberg-Baden.) The arms of Stuttgart appear in the middle of the logo as an inescutcheon, for the company had its headquarters in Stuttgart. The heraldic symbols, combined with the texts "Porsche" and "Stuttgart", do not form a conventional coat of arms, since heraldic achievements never spell out the name of the armiger nor the armiger's home town in the shield.
Württemberg-Baden and Württemberg-Hohenzollern both in 1952 became part of the present Bundesland of Baden-Württemberg after the political consolidation of West Germany in 1949, but the old design of the arms of Württemberg lives on in the Porsche logo. On 30 January 1951, not long before the formation of Baden-Württemberg, Ferdinand Porsche died from complications following a stroke.
Developments

In post-war Germany, parts were generally in short supply, so the 356 automobile used components from the Volkswagen Beetle, including the engine case from its internal combustion engine, transmission, and several parts used in the suspension. The 356, however, had several evolutionary stages, A, B, and C, while in production, and most Volkswagen-sourced parts were replaced by Porsche-made parts. Beginning in 1954 the 356s engines started utilizing engine cases designed specifically for the 356. The sleek bodywork was designed by Erwin Komenda, who also had designed the body of the Beetle. Porsche's signature designs have, from the beginning, featured air-cooled rear-engine configurations (like the Beetle), rare for other car manufacturers, but producing automobiles that are very well balanced.
In 1964, after a fair amount of success in motor-racing with various models including the 550 Spyder, and with the 356 needing a major re-design, the company launched the Porsche 911: another air-cooled, rear-engined sports car, this time with a six-cylinder "boxer" engine. The team to lay out the body shell design was led by Ferry Porsche's eldest son, Ferdinand Alexander Porsche (F. A.). The design phase for the 911 caused internal problems with Erwin Komenda, who led the body design department until then. F. A. Porsche complained Komenda made unauthorized changes to the design. Company leader Ferry Porsche took his son's drawings to neighbouring chassis manufacturer Reuter. Reuter's workshop was later acquired by Porsche (so-called Werk 2). Afterward, Reuter became a seat manufacturer, today known as Keiper-Recaro.

The design office gave sequential numbers to every project (See Porsche type numbers), but the designated 901 nomenclature contravened Peugeot's trademarks on all 'x0x' names, so it was adjusted to 911. Racing models adhered to the "correct" numbering sequence: 904, 906, 908. The 911 has become Porsche's most well-known model – successful on the race-track, in rallies, and in terms of road car sales. It remains in production; however, after several generations of revision, current-model 911s share only the basic mechanical configuration of a rear-engined, six-cylinder coupé, and basic styling cues with the original car. A cost-reduced model with the same body, but with a 356-derived four-cylinder engine, was sold as the 912.
In 1972, the company's legal form was changed from Kommanditgesellschaft (KG), or limited partnership, to Aktiengesellschaft (AG), or public limited company, because Ferry Porsche came to believe the scale of the company outgrew a "family operation", after learning about Soichiro Honda's "no family members in the company" policy at Honda. This led to the establishment of an executive board with members from outside the Porsche family, and a supervisory board consisting largely of family members. With this change, most family members in the operation of the company, including F. A. Porsche and Ferdinand Piëch, departed from the company.
F. A. Porsche founded his own design company, Porsche Design, which is renowned for exclusive sunglasses, watches, furniture, and many other luxury articles. Louise's son and Ferry's nephew Ferdinand Piëch, who was responsible for mechanical development of Porsche's production and racing cars (including the very successful 911, 908 and 917 models), formed his own engineering bureau, and developed a five-cylinder-inline diesel engine for Mercedes-Benz. A short time later he moved to Audi (used to be a division, then a subsidiary, of Volkswagen), and pursued his career through the entire company, ultimately becoming the chairman of Volkswagen Group.
The first chief executive officer (CEO) of Porsche AG was Ernst Fuhrmann, who had been working in the company's engine development division. Fuhrmann was responsible for the so-called Fuhrmann-engine, used in the 356 Carrera models as well as the 550 Spyder, having four overhead camshafts instead of a central camshaft with pushrods, as in the Volkswagen-derived serial engines. He planned to cease the 911 during the 1970s and replace it with the V8-front engined grand sportswagon 928. As we know today, the 911 outlived the 928 by far. Fuhrmann was replaced in the early 1980s by Peter W. Schutz, an American manager and self-proclaimed 911 aficionado. He was then replaced in 1988 by the former manager of German computer company Nixdorf Computer AG, Arno Bohn, who made some costly miscalculations that led to his dismissal soon after, along with that of the development director, Dr. Ulrich Bez, who was formerly responsible for BMW's Z1 model, and was CEO of Aston Martin from 2000 to 2013.

In 1990, Porsche drew up a memorandum of understanding with Toyota to learn and benefit from Japanese lean manufacturing methods. In 2004 it was reported that Toyota was assisting Porsche with hybrid technology.
Following the dismissal of Bohn, Heinz Branitzki, a longtime Porsche employee, was appointed as interim CEO. Branitzki served in that position until Wendelin Wiedeking became CEO in 1993. Wiedeking took over the chairmanship of the board at a time when Porsche appeared vulnerable to a takeover by a larger company. During his long tenure, Wiedeking transformed Porsche into a very efficient and profitable company.
Ferdinand Porsche's nephew, Ferdinand Piëch, was chairman and CEO of the Volkswagen Group from 1993 to 2002 and is chairman of the Volkswagen AG Supervisory Board since then. With 12.8 percent of the Porsche SE voting shares, he also remains the second-largest individual shareholder of Porsche SE after his cousin, F. A. Porsche, which had 13.6 percent.
Porsche's 2002 introduction of the Cayenne also marked the unveiling of a new production facility in Leipzig, Saxony, which once accounted for nearly half of Porsche's annual output. In 2004, production of the 456 kilowatts (620 PS; 612 bhp) Carrera GT commenced in Leipzig, and at EUR 450,000 ($440,000 in the United States) it was the most expensive production model Porsche ever built.

In mid-2006, after years of the Boxster (and later the Cayenne) as the best selling Porsche in North America, the 911 regained its position as Porsche's best-seller in the region. The Cayenne and 911 have cycled as the top-selling model since. In Germany, the 911 outsells the Boxster/Cayman and Cayenne.
In May 2011, Porsche Cars North America announced plans to spend $80–$100 million, but will receive about $15 million in economic incentives to move their North American headquarters from Sandy Springs, a suburb of Atlanta, to Aerotropolis, Atlanta, a new mixed-use development on the site of the old Ford Hapeville plant adjacent to Atlanta's airport. Designed by architectural firm HOK, the headquarters will include a new office building and test track. The facility will be known by its new address, One Porsche Drive.
In October 2017, Porsche Cars North America announced the launch of Porsche Passport, a new sports car and SUV subscription program. This new offering allows consumers to access Porsche vehicles through subscribing to the service, rather than owning or leasing a vehicle. The Porsche Passport service was available initially in Atlanta, and has become available in many major cities across the US.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, in March 2020, Porsche suspended its manufacturing in Europe for two weeks, "By taking this step, the sports car manufacturer is responding to the significant acceleration in the rate of infection caused by the coronavirus and the resultant measures implemented by the relevant authorities."
In August 2022, Bloomberg News reported that Porsche has lined up interest in subscription of its initial public offering for a valuation between US$60–85 billion. It is expected to be listed on Frankfurt Stock Exchange in September.
Relationship with Volkswagen

The company has always had a close relationship with, initially, the Volkswagen (VW) marque, and later, the Volkswagen Group (which also owns Audi AG), because the first Volkswagen Beetle was designed by Ferdinand Porsche.
The two companies collaborated in 1969 to make the VW-Porsche 914 and 914-6, whereby the 914-6 had a Porsche engine, and the 914 had a Volkswagen engine. Further collaboration in 1976 resulted in the Porsche 912E (US only) and the Porsche 924, which used many Audi components, and was built at Audi's Neckarsulm factory, which had been NSU's. Porsche 944s were also built there, although they used far fewer Volkswagen components. The Cayenne, introduced in 2002, shares its chassis with the Volkswagen Touareg and the Audi Q7, which is built at the Volkswagen Group factory in Bratislava, Slovakia.
Corporate restructuring




Porsche SE was created in June 2007 by renaming the old Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG, and became a holding company for the families' stake in Porsche Zwischenholding GmbH (50.1%) (which in turn held 100% of the old Porsche AG) and Volkswagen AG (50.7%). At the same time, the new Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG (Porsche AG) was created for the car manufacturing business.
In August 2009, Porsche SE and Volkswagen AG reached an agreement that the car manufacturing operations of the two companies would merge in 2011, to form an "Integrated Automotive Group". The management of Volkswagen AG agreed to 50.76% of Volkswagen AG being owned by Porsche SE in return for Volkswagen AG management taking Porsche SE management positions (in order for Volkswagen management to remain in control), and for Volkswagen AG acquiring ownership of Porsche AG.
As of the end of 2015, the 52.2% control interest in VW AG is the predominant investment by Porsche SE, and Volkswagen AG in turn controls brands and companies such as Volkswagen, Audi, SEAT, Škoda, Bentley, Bugatti, Lamborghini, Porsche AG, Ducati, VW Commercial Vehicles, Scania, MAN, as well as Volkswagen Financial Services.
Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG (which stands for Doktor Ingenieur honoris causa Ferdinand Porsche Aktiengesellschaft), as a 100% subsidiary of VW AG, is responsible for the actual production and manufacture of the Porsche automobile line. The company currently produces Porsche 911, Boxster and Cayman sports cars, the Cayenne and Macan sport utility vehicles and the four-door Panamera.
Porsche AG has a 29% share in German engineering and design consultancy Bertrandt AG and 81.8% of Mieschke Hofmann und Partner. In 2018, Porsche acquired a 10% minority shareholding stake of the Croatian electric sportscar manufacturer Rimac Automobili to form a development partnership.
Initial public offering
In February 2022, Volkswagen AG had announced that it would examine the feasibility of a possible IPO of Porsche AG. The share capital of Porsche AG has been divided into 50% non-voting preference shares and 50% ordinary shares. Volkswagen AG will retain 75% of ordinary shares, while Porsche SE will acquire 25% of ordinary shares. Volkswagen AG will also retain 75% of preference shares, while 25% of preference shares (12.5% of share capital) will be sold during IPO, while Qatar Investment Authority has already committed to buy 4.99% of preference shares, leaving another 20.01% (10% of share capital), to other investors. As part of the preliminary offering, 113,875 thousand shares were sold at the upper limit of the price range - 82.5 euros. Thus, the value of the company was estimated at 75 billion euros. In the first hours of trading on the Frankfurt stock exchange on 29 September, the share price rose to 84 euros.
Australian eFuel operations
Main article: Highly Innovative Fuels AustraliaIn April 2022, Porsche Australia announced they are planning to open an efuel manufacturing facility in the island state of Tasmania. The plant will be the first of its type in the country. The facility is to be named the HIF (Highly Innovative Fuels) Tasmania Carbon Neutral eFuel Plant. It is slated to open in 2026.
Production and sales
The headquarters and main factory are located in Zuffenhausen, a district in Stuttgart, where Porsche produces flat-6 and V8 piston engines. Cayenne and Panamera models are manufactured in Leipzig, Germany, and parts for the SUV are also assembled in the Volkswagen Touareg factory in Bratislava, Slovakia. Boxster and Cayman production was outsourced to Valmet Automotive in Finland from 1997 to 2011, and in 2012 production moved to Germany. Since 2011, the area of the Zuffenhausen plant has more than doubled, from 284,000 m (28.4 ha) to 614,000 m (61.4 ha), as a result of purchasing the former Layher, Deltona and Daimler sites, among others.
In 2015, Porsche reported selling a total of 218,983 cars, 28,953 (13.22%) as domestic German sales, and 190,030 (86.78%) internationally.
The company has been highly successful in recent times, and indeed claims to have the highest profit per unit sold of any car company in the world. Table of profits (in millions of euros) and number of cars produced. Figures from 2008/9 onwards were not reported as part of Porsche SE.
On 11 May 2017, Porsche built the one-millionth 911. An Irish green Carrera S was built for the celebration, and it will be taken on a global tour before becoming a permanent exhibit at the Porsche Museum in Stuttgart.
| Region | Sales in billion € | share |
|---|---|---|
| North America | 11.7 | 29.5% |
| China | 9.5 | 23.6% |
| Europe | 8.8 | 21.7% |
| Germany | 4.9 | 12.0% |
| Rest of the World | 5.8 | 14.3% |
In August 2021, Porsche has confirmed that it will be setting up a production plant in Malaysia, the first country outside of Europe. Local assembly will be handled by Porsche Malaysia's partner, Sime Darby, which has been the official distributor of the Stuttgart-based company in Malaysia since 2010.
| Year ending | Revenue | Pre-tax profit | Production | Sales |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31 July 2002 | €4,857m | €829m | 55,050 | 54,234 |
| 31 July 2003 | €5,583m | €933m | 73,284 | 66,803 |
| 31 July 2004 | €6,148m | €1,137m | 81,531 | 76,827 |
| 31 July 2005 | €6,574m | €1,238m | 90,954 | 88,379 |
| 31 July 2006 | €7,273m | €2,110m | 102,602 | 96,794 |
| 31 July 2007 | €7,368m | €5,857m | 101,844 | 97,515 |
| 31 July 2008 | €7,466m | €8,569m | 105,162 | 98,652 |
| 31 July 2009 | €?m | €-2,559m | 76,739 | 75,238 |
| 31 July 2010 | €7.79b | N/A | 89,123 | 81,850 |
| 31 December 2010 | €9.23b | €1.67b | N/A | 97,273 |
| 31 December 2011 | €10.9b | €2.05b | 127,793 | 116,978 |
| 31 December 2012 | €13.9b | €2.44b | 151,999 | 143,096 |
| 31 December 2013 | €14.3b | €2.78b | 165,808 | 162,145 |
| 31 December 2014 | €17.2b | €3.06b | 203,097 | 187,208 |
| 31 December 2015 | €21.5b | €3.382b | 234,497 | 225,121 |
| 31 December 2019 | €28.5b | €4.05b | 274,463 | 280,800 |
| 31 December 2020 | €28.7b | €4.38b | 263,236 | 272,162 |
| 31 December 2021 | €33.1b | €5.73b | 300,081 | 301,915 |
| 31 December 2022 | €37.6b | €6.77b | 321,321 | 309,884 |
Production composition
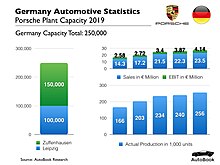
Of the 246,375 cars produced in the 2017 financial year, 32,197 were 911 models, 25,114 were Boxster and Cayman cars, 63,913 were Cayennes, 27,942 were Panameras and 97,202 were Macans.
Of the 268,691 cars produced in 2018, 36,236 were 911 models, 23,658 were 718 Boxster and Cayman cars, 79,111 were Cayennes, 35,493 were Panameras, 93,953 were Macans and 240 Taycan pre-series vehicles.
Of the 272,162 cars produced in 2020, 34,328 were 911 models, 21,784 were 718 Boxster and Cayman cars, 92,860 were Cayennes, 20,015 Taycan vehicles.
Of the 321,321 vehicles produced in 2022, 41,947 were 911 models,18,080 were 718 Boxster/Cayman models, 91,117 were Macans, 98,113 were Cayennes, 35,241 were Panameras and 36,823 were Taycan models.
U.S. sales
The base price as of March 2024 are:
- 911: $114,400
- 718: $68,300
- Taycan: $99,400
- Panamera: $99,900
- Cayenne: $79,200
- Macan: $78,800
| Model | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Units | % of total | Units | % of total | Units | % of total | |
| 911 (996) | 9,935 ( |
33% | 10,227 ( |
31% | 10,653 ( |
31% |
| Boxster | 6,432 ( |
21% | 3,728 ( |
11% | 8,327 ( |
25% |
| Cayenne | 13,661 | 45% | 19,134 ( |
57% | 14,524 ( |
43% |
| Total | 30,028 ( |
33,289 ( |
33,859 ( | |||
| Model | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Units | % of total | Units | % of total | Units | % of total | |
| 911 (997) | 12,702 ( |
35% | 13,153 ( |
36% | 8,324 ( |
30% |
| Boxster | 4,850 ( |
14% | 3,904 ( |
11% | 2,982 ( |
11% |
| Cayman | 7,313 | 20% | 6,249 ( |
17% | 3,513 ( |
13% |
| Cayenne | 11,141 ( |
31% | 13,370 ( |
36% | 12,898 ( |
46% |
| Total | 36,095 ( |
36,680 ( |
27,717 ( | |||
| Model | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Units | % of total | Units | % of total | Units | % of total | |
| 911 (997) | 6,839 ( |
35.00% | 5,735 ( |
23% | 6,016 ( |
21% |
| Boxster/Cayman | 3,875 ( |
19.00% | 3,499 ( |
14% | 3,150 ( |
11% |
| Panamera | 1,247 | 6.33% | 7,741 ( |
31% | 6,879 ( |
24% |
| Cayenne | 7,735 ( |
39% | 8,343 ( |
33% | 12,978 ( |
45% |
| Total | 19,696 ( |
25,320 ( |
29,023 ( | |||
| Model | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Units | % of total | Units | % of total | Units | % of total | |
| 911 | 8,528 | 24% | 10,442 | 24.67% | 10,529 | 22% |
| Boxster/Cayman | 3,356 | 10% | 7,953 | 18.79% | 7,292 | 15% |
| Panamera | 7,614 | 22% | 5,421 | 13% | 5,740 | 12% |
| Cayenne | 15,545 | 44.36% | 18,507 | 44% | 16,205 | 34,47% |
| Macan | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | 7,241 | 15% |
| Total | 35,043 ( |
42,323 ( |
47,007 ( | |||
| Model | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Units | % of total | Units | % of total | Units | % of total | |
| 911 | 9,898 | 19.12% | 8,901 | 16.40% | 8,970 | 16.19% |
| 718 Boxster/Cayman | 6,663 | 12.87% | 6,260 | 11.53% | 5,087 | 9.18% |
| Panamera | 4,986 | 9.63% | 4,403 | 8.11% | 6,731 | 12.15% |
| Cayenne | 16,473 | 31.83% | 15,383 | 28.34% | 13,203 | 23.83% |
| Macan | 13,533 | 26.15% | 19,332 | 35.62% | 21,429 | 38.67% |
| Total | 51,756 ( |
54,280 ( |
55,420 ( | |||
| Model | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Units | % of total | Units | % of total | Units | % of total | |
| 911 | 9,647 | 17% | 9,265 | 15% | 8,840 ( |
15% |
| 718 | 5,276 | 9% | 3,880 | 6% | 3,447 ( |
6% |
| Taycan | n.a. | n.a. | 130 | 0.2% | 4,414 | 8% |
| Panamera | 8,042 | 14% | 6,625 | 11% | 3,870 ( |
7% |
| Cayenne | 10,733 | 19% | 19,001 | 31% | 18,092 ( |
32% |
| Macan | 23,504 | 41% | 22,667 | 37% | 18,631 ( |
33% |
| Total | 57,202 ( |
61,568 ( |
57,294 ( | |||
| Model | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Units | % of total | Units | % of total | Units | % of total | |
| 911 | 10,042 ( |
14% | 10,204 ( |
15% | 11,692 ( |
16% |
| 718 | 4,292 ( |
6% | 3,484 ( |
5% | 4,526 ( |
6% |
| Taycan | 9,419 ( |
13% | 7,271 ( |
10% | 7,570 ( |
10% |
| Panamera | 4,257 ( |
6% | 4,224 ( |
6% | 4,205 (-) | 6% |
| Cayenne | 17,299 ( |
25% | 21,194 ( |
30% | 20,475 ( |
27% |
| Macan | 24,716 ( |
35% | 23,688 ( |
34% | 26,947 ( |
36% |
| Total | 70,005 ( |
70,065 ( |
75,415 ( | |||
| Model | YTD Q3 | 2025 | 2026 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Units | % of total | Units | % of total | Units | % of total | |
| 911 | 10,841 ( |
20% | ||||
| 718 | 3,821 ( |
7% | ||||
| Taycan | 3,394 ( |
6% | ||||
| Panamera | 2,527 ( |
5% | ||||
| Cayenne | 15,507 ( |
29% | ||||
| Macan | 17,993 ( |
33% | ||||
| Total | 54,083 ( | |||||
Models
See also: List of Porsche vehicles, Category:Porsche vehicles, and Porsche type numbersThe current Porsche model range includes sports cars from the Boxster roadster to their most famous product, the 911. The Cayman is a coupé otherwise similar to the Boxster. The Cayenne is Porsche's mid-size luxury sport utility vehicle (SUV). A high performance luxury saloon/sedan, the Panamera, was launched in 2009.
- Note: models in bold are current models
Consumer models
- 356
- 911 4-seat coupe, targa and cabriolet
- 911 GT1 Straßenversion
- 912
- 914
- 918 Spyder
- 924
- 928 4-seat grand tourer
- 944
- 959
- 968
- Boxster 2-seat roadster
- Carrera GT
- Cayman 2-seat coupe
- Cayenne Mid-size crossover SUV
- Macan Compact crossover SUV
- Panamera 4- or "4+1"-seat liftback and shooting-brake estate
- Taycan 4- or "4+1"-seat sedan and shooting-brake estate EV
-
 Porsche Cayman
Porsche Cayman
-
 Porsche Boxster
Porsche Boxster
-
 Porsche Panamera
Porsche Panamera
-
 Porsche Cayenne
Porsche Cayenne
-
 Porsche Macan
Porsche Macan
-
 Porsche 911
Porsche 911
-
 Porsche Taycan
Porsche Taycan
Racing models
- 64
- 360 Cisitalia
- 550 Spyder
- 718
- 787
- 804
- 904
- 906
- 907
- 908
- 909 Bergspyder
- 910
- 911 GT1
- 917
- 919 hybrid
- 934
- 934/5
- 935
- 936
- 956
- 961
- 962
- 963
- Porsche 99X Electric
- Porsche-March 89P
- WSC-95 / LMP1-98
- LMP2000 (never raced)
- RS Spyder (9R6)
Prototypes and concept cars

- Porsche 114
- Porsche 356/1
- Porsche 695 (911 prototype)
- Porsche 901 (911 prototype)
- Porsche 916 (flat-6 914)
- Porsche 942
- Porsche 959 prototype
- 918 RSR
- Porsche 965
- Porsche 969
- Porsche 989
- Porsche Boxster concept
- Porsche C88
- Porsche Panamericana
- Porsche Boxster E
- Porsche Panamera Sport Turismo concept
- Porsche Mission E
Tractors

- Porsche Type 110
- Porsche AP Series
- Porsche Junior (14 hp)
- Porsche Standard (25 hp)
- Porsche Super (38 hp)
- Porsche Master (50 hp)
- Porsche 312
- Porsche 108F
- Porsche R22
Hybrid and electric vehicles
For details on a Porsche 911-based all-electric car, see ERuf Model A.In 2010, Porsche launched the Cayenne S Hybrid and announced the Panamera S Hybrid, and launched the Porsche 918 sports car in 2014, which also features a hybrid system. Also a plug-in hybrid model called the Panamera S E-Hybrid was released in October 2013 in the United States and during the fourth quarter of 2013 in several European countries.
Porsche developed a prototype electric Porsche Boxster called the Boxster E in 2011 and a hybrid version of the 911 called the GT3 R Hybrid, developed with Williams Grand Prix Engineering in 2010.
In July 2014, Porsche announced the launch by the end of 2014 of the Porsche Cayenne S E-Hybrid a plug-in hybrid, which will displace the Cayenne S Hybrid from the lineup. The S E-Hybrid will be the first plug-in hybrid in the premium SUV segment and will allow Porsche to become the first automaker with three production plug-in hybrid models.
In July 2017, Porsche installed its first 350 kW, 800V charging station, which the upcoming Porsche Mission E will use. As of 2017, the Porsche charging station is the fastest electric vehicle charging station in the world, being able to charge a Porsche Mission E up to 80% within 15 minutes. Porsche is also currently working with other manufacturers to make Porsche charging stations compatible with other electric vehicles.
In August 2018, Porsche announced that the formerly named Mission E electric car would be named "Taycan" meaning 'leaping horse'. The prototype electric car was expected to be revealed in 2019 after its completion. Porsche Taycan went on sale in 2020.
Aircraft engines

See Porsche PFM 3200.
Electric Bicycles
In 2021, Porsche released an electric Mountain Bike in partnership with Rotwilde, with features such as an integrated cockpit designed by Magura GmbH and drive unit, drivetrain and electronic shifting designed by Shimano. Porsche followed this by completely buying eBike motor and battery company Fazua in 2022 and sports bikes company Greyp Bikes, sister company of Rimac Automobili, in 2023. Greyp Bikes was renamed to Porsche eBike Performance GmbH.
Motorsport
Main article: Porsche in motorsport
Porsche has a record 19 outright wins at the 24 Hours of Le Mans. Porsche is currently the world's largest race car manufacturer. In 2006, Porsche built 195 race cars for various international motor sports events. In 2007, Porsche was expected to construct no fewer than 275 dedicated race cars (7 RS Spyder LMP2 prototypes, 37 GT2 spec 911 GT3-RSRs, and 231 911 GT3 Cup vehicles).
Pronunciation
In keeping with the family name of founder Ferdinand Porsche, the company's name is pronounced [ˈpɔʁʃə] in German, which corresponds to /ˈpɔːrʃə/ POR-shə in English, homophonous with the feminine name Portia. However, in English it is often mispronounced as a single syllable /pɔːrʃ/ PORSH—without a final /ə/. In German orthography, word-final ⟨e⟩ is not silent but is instead an unstressed schwa.
Reputation
In a survey conducted by the Luxury Institute in New York, Porsche was awarded the title of "the most prestigious automobile brand". Five hundred households with a gross annual income of at least $200,000 and a net worth of at least $720,000 participated.
Porsche won the J.D. Power and Associates Initial Quality Study (IQS) in 2006, 2009, 2010, and 2014.
SUV reception
Porsche's 2003 SUV, the Cayenne, received generally favorable commentary.
In 2015, US News ranked the Macan as the best luxury compact SUV in its class.
Reliability
A Canadian study in 2011 revealed that 97.4 percent of Porsches from the last 25 years are still on the road.
In 2014, the Cayman and Boxster made the Consumer Reports list for most reliable vehicles on the road.
Porsche's 911 has been officially named by the TÜV (Technischer Überwachungsverein; Technical Inspection Association) as Germany's most reliable car.
See also
- CTS Fahrzeug-Dachsysteme
- List of automobile manufacturers of Germany
- List of Porsche engines
- Akira Nakai
- Porsche Club of America
- Porsche VIN specification
References
Notes
- Raitano, Lucy (3 October 2022). "Porsche shares fall below IPO pricing". Reuters.
- "The Board of Management of Porsche AG - All BOM members - Porsche USA". Porsche HOME - Porsche USA.
- ^ "Annual and Sustainability Report 2022 Porsche AG.pdf" (PDF). Porsche Newsroom. 15 March 2023.
- ^ "Factbox: The structure of the planned Porsche IPO". Reuters. 17 September 2022. Retrieved 19 September 2022.
- ^ J. P. Vettraino (23 December 2008). "Porsche at 60: The little sports-car company that could". Autoweek. Archived from the original on 6 February 2009. Retrieved 30 January 2009.
- Sherman, Don (9 August 2018). "The Story of Adolf Rosenberger". Hagerty. Retrieved 29 November 2023.
- ^ "Béla Barényi (1907–1997)". Automotive Hall of Fame. Archived from the original on 1 November 2009. Retrieved 25 March 2009.
- ^ "Porsche Supervisory Board agrees on the contracts of implementation" (Press release). Porsche Automobil Holding SE, Stuttgart. 20 November 2009. Retrieved 22 November 2009.
- ^ "Porsche SE Investor Relations". Porsche-se.com. Archived from the original on 1 September 2016. Retrieved 1 August 2011.
- ^ "Porsche SE Annual Report 2015". p. 3. Archived from the original on 18 October 2016. Retrieved 17 October 2016.
- Automobile Quarterly, Volume 18, Issue 4, Automobile Quarterly, 1980
- Klawitter, Nils (1 October 2009). "The Dark Pre-History of the World's Favorite Sports Car". Der Spiegel.
- Girl, Pepper (2011). "Just what do all the initials in Porsche's Corporate Names Mean Anyway?". Flatsixes. Retrieved 28 November 2023.
- "Historie - Porsche Engineering". Porsche Engineering. Retrieved 23 February 2016.
- ^ Burt, William (2002). Volkswagen Beetle. MotorBooks/MBI Publishing Company. p. 14. ISBN 978-0-7603-1078-6.
- See Volkswagen Schwimmwagen#Development.
- "Panzerkampfwagen VIII Maus Porsche Typ 205 / Tiger II(P)". Achtung Panzer. Archived from the original on 16 March 2018. Retrieved 4 May 2011.
- Klawitter, Nils (1 October 2009). "Porsche's Past: The Dark Pre-History of the World's Favorite Sports Car". www.spiegel.de.
- Mantle, Jonathan (1996). Car wars: fifty years of greed, treachery, and skulduggery in the global marketplace. Arcade Publishing. p. 216. ISBN 978-1-55970-333-8.
- ^ Meredith, Laurence; Mark Hughes (1995). Original Porsche 356. MotorBooks/MBI Publishing Company. p. 7. ISBN 978-1-870979-58-0.
- John Lamm (1998). Porsche Boxster. MotorBooks International. p. 100. ISBN 978-0-7603-0519-5.
- "Aston Martin CEO Ulrich Bez To Step Down: Report". Motor Authority. Archived from the original on 10 April 2017. Retrieved 9 April 2017.
- Nexteer Automotive Poland president Rafal Wyszomirski. "Just auto 23 November 2004". Just-auto.com. Archived from the original on 27 September 2011. Retrieved 1 August 2011.
- "Porsche USA press release" (Press release). 11 September 2006.
- Urvaksh Karkaria (12 May 2011). ""Porsche HQ relo draws $15M in incentives", Atlanta Business Chronicle, 2011-05-12". Bizjournals.com. Retrieved 1 August 2011.
- Tobin, Rachel (11 May 2011). "Porsche North America HQ to leave Sandy Springs for ex-Ford plant". ajc.com. Retrieved 1 August 2011.
- ""Mayor Kasim Reed and Governor Nathan Deal Announce Porsche to Build New U.S. Headquarters in Metropolitan Atlanta", City of Atlanta Online". Atlantaga.gov. Archived from the original on 11 June 2011. Retrieved 1 August 2011.
- Patton, Phil (18 November 2011). "Porsche to Build in Atlanta and California". The New York Times. Retrieved 30 November 2011.
- "Porsche Passport". 14 February 2018. Archived from the original on 14 February 2018. Retrieved 31 December 2021.
- "Porsche Launches New Sports Car and SUV Subscription Program". press.porsche.com. Archived from the original on 8 February 2018. Retrieved 7 February 2018.
- "Porsche's Passport to the New Mobility". Bloomberg.com. 20 October 2017. Retrieved 7 February 2018.
- "Porsche Subscription - Porsche USA". Porsche HOME - Porsche USA. Retrieved 3 October 2023.
- "Porsche is suspending production in Europe amid worsening coronavirus outbreak". Business Insider. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- Henning, Eyk; Foerster, Jan-Henrik (26 August 2022). "Porsche Attracts IPO Demand at Up to $85 Billion Valuation". Bloomberg News. Archived from the original on 27 August 2022.
- "The history of the Neckarsulm plant". Audi MediaServices. Audi AG. Archived from the original on 8 October 2011. Retrieved 4 May 2011.
- Rauwald, Christoph (18 June 2010). "Wall Street Journal 18 June 2010". Online.wsj.com. Retrieved 1 August 2011.
- "Volkswagen Supervisory Board approves Comprehensive Agreement for an Integrated Automotive Group with Porsche" (Press release). Volkswagen Aktiengesellschaft. 13 August 2009. Archived from the original on 20 July 2011. Retrieved 22 November 2009.
- PTI. "Porsche brings Limited Edition 911 R priced at around Rs 3 crore". The Hindu. Retrieved 9 March 2017.
- "Porsche bolsters engineering and design operations". Autocar. 3 July 2014. Retrieved 16 September 2014.
- "Porsche AG raises its stake in Bertrandt AG". Porsche AG. 3 July 2014. Retrieved 16 September 2014.
- "Mieschke Hofmann und Partner (MHP) – the process supplier". MHP. Retrieved 16 September 2014.
- "Porsche takes a stake in the Croatian technology and sports car company Rimac" (Press release). Porsche. 20 June 2018. Archived from the original on 20 June 2018. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
- Savov, Vlad (20 June 2018). "Porsche accelerates EV supercar ambitions with investment in Rimac". The Verge. US. Archived from the original on 21 June 2018. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
- ^ "Board of Management and Supervisory Board aim for an IPO of Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG and decide on the next step with the "intention to float"". www.volkswagenag.com. 5 September 2022. Retrieved 19 September 2022.
- "Porsche races higher after landmark $72 bln listing". reuters.com. 29 September 2022.
- Porsche to build Australian efuels plant in Tasmania, operational from mid-2026, Motor, 8 July 2022
- "The history of engine construction". Porsche Newsroom. 5 October 2014.
- "Union says VW's Slovak plant eyes output cut". Reuters. 9 October 2008. Retrieved 17 January 2009.
- "Porsche's Finnish success story: 227,890 Boxsters and Caymans". valmet-automotive.com. 2011. Archived from the original on 4 October 2011. Retrieved 2 May 2011.
- "Zuffenhausen is growing". Porsche Newsroom. 6 April 2014. Retrieved 11 June 2020.
- "A New Era". Porsche Newsroom. 11 October 2018. Retrieved 11 June 2020.
- "Porsche AG Annual Report 2015" (PDF). pp. 44 (German sales), 126 (total sales). Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 September 2016. Retrieved 8 November 2016.
- Elliott, Hannah. "Forbes Autos review of Cayman S". Forbesautos.com. Archived from the original on 10 December 2008. Retrieved 3 October 2010.
- "Porsche Annual Report Short Fiscal Year 2010" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 September 2011. Retrieved 1 August 2011.
- "One Million Dreams: This Is the 1,000,000th Porsche 911". Archived from the original on 1 August 2017. Retrieved 3 July 2017.
- "Porsche AG: Shareholders Board Members Managers and Company Profile | DE000PAG9113 | MarketScreener". www.marketscreener.com. Retrieved 22 March 2024.
- "Porsche confirms CKD operations in Malaysia from 2022 at Sime Darby plant – first outside of Europe!". paultan.org. 30 August 2021. Retrieved 9 February 2022.
- ^ "Porsche AG turns in record performance in 2011" (Press release). Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG. 13 March 2013. Retrieved 1 August 2013.
- "Best year in the history of Porsche" (Press release). Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG. 15 March 2013. Retrieved 1 August 2013.
- "Porsche AG Annual Report 2013" (PDF). Retrieved 31 July 2014.
- "Porsche AG Annual Report 2014". Retrieved 17 October 2016.
- "Porsche at a glance". Porsche Newsroom. Porsche. Archived from the original on 10 May 2017. Retrieved 17 October 2016.
- "Porsche AG Annual Report 2015". Archived from the original on 19 October 2016. Retrieved 17 October 2016.
- ^ "Brief overview". Porsche Newsroom. 18 March 2022. Retrieved 19 September 2022.
- "Porsche 2017 Year in Review". Archived from the original on 30 July 2018. Retrieved 11 December 2018.
- "Porsche AG Annual & Sustainability Report 2018". Archived from the original on 12 August 2019. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- "2020 (Full Year) Global: Porsche Sales Worldwide". best-selling-cars.com. 12 January 2021. Retrieved 23 August 2021.
- "Annual and Sustainability Report 2022 Porsche AG" (PDF). Porsche AG. Retrieved 15 March 2023.
- "January – March – Porsche Vehicle Sales in North America Exceed 30,000 in 2003" (Press release). Porsche AG. 8 January 2004. Retrieved 10 February 2009.
- "January – March – Porsche sets North American sales record in 2004" (Press release). Porsche AG. 5 January 2005. Retrieved 10 February 2009.
- "January – March – New record year for Porsche in North America" (Press release). Porsche AG. 4 January 2006. Retrieved 17 January 2009.
- "Porsche succeeds 2006 with a new record in North America" (Press release). Porsche AG. 3 January 2007. Retrieved 17 January 2009.
- "January – March – Porsche tops its record-breaking sales figures for North America in 2007" (Press release). Porsche AG. 3 January 2008. Retrieved 17 January 2009.
- "January – March – Porsche Reports Decrease in North American Customer Deliveries in the 2008 Calendar Year" (Press release). Porsche AG. 5 January 2009. Retrieved 20 August 2009.
- "Porsche Reports December Sales". Theautochannel.com. Retrieved 12 June 2011.
- "Porsche Press Release". Press.porsche.com. 4 January 2011. Archived from the original on 22 May 2012. Retrieved 12 June 2011.
- "Porsche Press Release". Press.porsche.com. 2 January 2012. Archived from the original on 14 May 2013. Retrieved 6 September 2012.
- "Porsche Reports Best-Ever Sales in 2012; 21 Percent Increase Over 2011". Press.porsche.com. 14 January 2013. Archived from the original on 6 February 2014. Retrieved 27 February 2014.
- "Porsche Reports Record Sales in 2013; 21 percent increase over 2012". Press.porsche.com. Archived from the original on 17 January 2014. Retrieved 27 February 2014.
- "U.S. Porsche Dealers Sell 47,007 Vehicles in 2014". Press.porsche.com. Archived from the original on 31 October 2016. Retrieved 31 October 2016.
- "Porsche Sets Record Year in 2015 with 51,756 Vehicles Delivered in the United States". Press.porsche.com. 5 January 2016. Archived from the original on 4 November 2016. Retrieved 31 October 2016.
- "Porsche Sets Record in 2016 with 54,280 Vehicles Delivered in the U.S". Press.porsche.com. 4 January 2017. Archived from the original on 18 May 2017. Retrieved 5 June 2017.
- "Porsche Sets U.S. Sales Record in 2017 with 55,420 Vehicles Delivered, Up 2.1 Percent". presse.porsche.de. Porsche. Retrieved 16 May 2020.
- "Porsche Sets U.S. Retail Sales Record in 2018". presse.porsche.de. Porsche. Retrieved 16 May 2020.
- "Porsche Posts Record U.S. Retail Sales in 2019". presse.porsche.de. Porsche. Retrieved 16 May 2020.
- "Porsche Reports U.S. Retail Sales for 2020" (Press release). Porsche Cars North America. 5 January 2021. Retrieved 23 August 2021.
- "Porsche reports U.S. retail sales for Q4 and full-year 2021" (Press release). Porsche. 1 April 2022. Retrieved 9 February 2022.
- "Porsche reports U.S. retail sales" (Press release). Porsche Cars North America. October 2023. Retrieved 12 July 2023.
- "Porsche 969/965 Story, Prototypes and Styling Exercises". Oppositelock. Archived from the original on 14 October 2020. Retrieved 13 October 2020.
- Philippe Crowe (5 September 2013). "Porsche Panamera S E-Hybrid Now Available in the US". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 5 September 2013.
- Tom Murphy (7 October 2013). "Sales Boost Expected for Refreshed Panamera". Wards Auto. Archived from the original on 29 October 2013. Retrieved 25 October 2013.
- "Porsche Publicly Debuts its Electric Boxster E, But It's Not For Sale". Car and Driver. 24 May 2011. Archived from the original on 9 August 2014. Retrieved 16 September 2014.
- "PORSCHE 911 GT3R HYBRID". Williams Grand Prix Engineering Limited. Archived from the original on 22 September 2014. Retrieved 16 September 2014.
- Porsche Press Release (24 July 2014). "Porsche introducing new plug-in Cayenne S E-Hybrid SUV; third plug-in from Porsche". Green Car Congress. Retrieved 27 July 2014.
- Lambert, Fred (14 July 2017). "Porsche installs first ultra-fast 350 kW EV charging station". Electrek. Retrieved 16 July 2017.
- "Porsche Taycan 2019: price, interior specs and release". The Week UK. Archived from the original on 1 October 2018. Retrieved 1 October 2018.
- "Porsche reveals and explains the Taycan all-electric powertrain in detail". Electrek. 30 July 2018. Retrieved 1 October 2018.
- Spratt, Ed (23 February 2023). "Porsche Launches an eMTB Featuring Magura's Integrated Cockpit & Inverted Fork". Pink Bike. Retrieved 8 November 2024.
- Spratt, Ed (8 June 2022). "Porsche Takes Complete Ownership of Fazua". Pink Bike. Retrieved 8 November 2024.
- Spratt, Ed (23 February 2023). "Porsche Takes Complete Ownership of Greyp". Pink Bike. Retrieved 8 November 2024.
- Staff (18 June 2017). "Porsche survives to take overall win at 2017 24 Hours of Le Mans". AutoWeek. Crain Communications. Retrieved 19 June 2017.
- Gary Watkins (7 March 2007). "Warehouse Shopping – Inside Porsche's Motorsport Center". AutoWeek. Archived from the original on 8 November 2011. Retrieved 17 January 2009.
- "Porsche and Neanderthal: pronouncing German words in English". German.about.com. 15 September 2008. Archived from the original on 12 January 2011. Retrieved 29 April 2009.
- "Porsche enjoys unsurpassed prestige in US". Porsche AG press release. Archived from the original on 18 April 2008. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- "Magna Steyr Assembly Plant in Graz, Austria, Receives Top Vehicle Quality Award in Europe" (PDF). J. D. Power and Associates. 7 June 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 May 2008. Retrieved 31 July 2008.
- DeBord, Matthew (19 March 2009). "Peering into Porsche's Future". CNBC. Retrieved 20 March 2009.
- Frankel, Andrew (17 November 2002). "Porsche Cayenne". The Sunday Times. London. Archived from the original on 4 December 2008. Retrieved 20 March 2009.
- "Porsche Macan Review".
- "Porsche 911 Named Most Reliable Sports Car By J.D. Power". autoguide.com. 21 March 2011.
- Elliott, Hannah. "The 2014 Porsche Cayman is Better Than You Think. Here's Why". Forbes.
- "It's Official: Toyota Prius and Porsche 911 Are Germany's Most Reliable Cars". 8 December 2011.
Bibliography
- Frankenberg, Richard von (1973) . Porsche: the Man and his Cars (revised ed.). Henley-on-Thames, Oxfordshire, UK: G.T. Foulis & Co. ISBN 0854290907.
- Leffingwell, Randy; Ingram, Cameron; Furman, Michael (2014). Porsche Unexpected: Discoveries in Collecting. Philadelphia, PA, USA: Coachbuilt Press. ISBN 9780988273337.
- Ludvigsen, Karl (2019). Porsche: Excellence Was Expected – Book 1: Surpassing Expectations (1948-1971) (All new ed.). Cambridge, MA, USA: Bentley Publishers. ISBN 9780837617701.
- ——————— (2019). Porsche: Excellence Was Expected – Book 2: Hitting the Apex (1967-1989) (All new ed.). Cambridge, MA, USA: Bentley Publishers. ISBN 9780837617718.
- ——————— (2019). Porsche: Excellence Was Expected – Book 3: Comeback (1982-2008) (All new ed.). Cambridge, MA, USA: Bentley Publishers. ISBN 9780837617725.
- ——————— (2019). Porsche: Excellence Was Expected – Book 4: 21st Century (2002-2020) (All new ed.). Cambridge, MA, USA: Bentley Publishers. ISBN 9780837617732.
- Seiff, Ingo (1989). Porsche: Portrait of a Legend. London: Macdonald Orbis. ISBN 0356150623.
- Smith, Luke (2022). The Story of Porsche: A Tribute to the Legendary Manufacturer. London: Welbeck Publishing Group. ISBN 9781802792911.
- Wood, Jonathan, ed. (1985). Great Marques of Germany. London: Octopus Books. ISBN 0706422562.
External links
- Official website

- Porsche Automobil Holding SE – the top-tier parent company
- Porsche Newsroom – Service by the Porsche Communication for journalists and the online community.
- Porsche Engineering
- Porsche Consulting
- Porsche Leipzig
- Cisitalia Museum
- Porsche YouTube channel
| Porsche | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volkswagen Group marques & companies | |||||||
| Cars |
| ||||||
| Tractors | |||||||
| Motorsport |
| ||||||
| Engines and technologies | |||||||
| People |
| ||||||
| See also |
| ||||||
| Porsche road car timeline, 1948–1990s — next » | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| « previous — Porsche road car timeline, 2000–present | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Volkswagen Group | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ownership | |||||||||||||
| Divisions and subsidiaries |
| ||||||||||||
| Shareholdings |
| ||||||||||||
| Products and technologies |
| ||||||||||||
| Discontinued brands | |||||||||||||
| Places | |||||||||||||
| People |
| ||||||||||||
| Motorsport | |||||||||||||
| Other | |||||||||||||
|
- Porsche
- Car brands
- Car manufacturers of Germany
- Vehicle manufacturing companies established in 1931
- Companies based in Stuttgart
- German brands
- Luxury motor vehicle manufacturers
- Sports car manufacturers
- Volkswagen Group
- German companies established in 1931
- Companies formerly in the MDAX
- Companies in the DAX index
- Companies listed on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange
- 2022 initial public offerings