| Revision as of 21:50, 30 October 2014 editDoc James (talk | contribs)Administrators312,255 edits ?← Previous edit | Revision as of 07:45, 4 March 2015 edit undo80.42.29.75 (talk)No edit summaryNext edit → | ||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
| <!-- Society and culture --> | <!-- Society and culture --> | ||
| Cloxacillin was discovered and developed by ].<ref name="Greenwood2008">{{cite book|author=David Greenwood|title=Antimicrobial drugs: chronicle of a twentieth century medical triumph|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=i4_FZHmzjzwC&pg=PA124|accessdate=18 November 2010|year=2008|publisher=Oxford University Press US|isbn=978-0-19-953484-5|pages=124–}}</ref> It is sold under a number of trade names, including '''Cloxapen''', '''Cloxacap''', '''Tegopen''' and '''Orbenin'''. It is on the ], a list of the most important medication needed in a basic ].<ref>{{cite web|title=WHO Model List of EssentialMedicines|url=http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/93142/1/EML_18_eng.pdf?ua=1|work=World Health Organization|accessdate=22 April 2014|date=October 2013}}</ref> | Cloxacillin was discovered and developed by ].<ref name="Greenwood2008">{{cite book|author=David Greenwood|title=Antimicrobial drugs: chronicle of a twentieth century medical triumph|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=i4_FZHmzjzwC&pg=PA124|accessdate=18 November 2010|year=2008|publisher=Oxford University Press US|isbn=978-0-19-953484-5|pages=124–}}</ref> It is sold under a number of trade names, including '''Cloxapen''', '''Cloxacap''', '''Tegopen''' and '''Orbenin'''. It is on the ], a list of the most important medication needed in a basic ].<ref>{{cite web|title=WHO Model List of EssentialMedicines|url=http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/93142/1/EML_18_eng.pdf?ua=1|work=World Health Organization|accessdate=22 April 2014|date=October 2013}}</ref> | ||
| ==Synthesis== | |||
| ] | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| *] | *] | ||
Revision as of 07:45, 4 March 2015
Pharmaceutical compound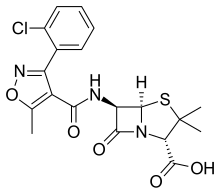 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Cloxapen |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Routes of administration | Oral, IM |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 37 to 90% |
| Protein binding | 95% |
| Elimination half-life | 30 minutes to 1 hour |
| Excretion | Renal and biliary |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.468 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H18ClN3O5S |
| Molar mass | 435.88 g/mol g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Cloxacillin is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. It is semisynthetic and in the same class as penicillin.
Cloxacillin is used against staphylococci that produce beta-lactamase, due to its large R chain, which does not allow the beta-lactamases to bind. This drug has a weaker antibacterial activity than benzylpenicillin, and is devoid of serious toxicity except for allergic reactions.
Cloxacillin was discovered and developed by Beecham. It is sold under a number of trade names, including Cloxapen, Cloxacap, Tegopen and Orbenin. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, a list of the most important medication needed in a basic health system.
Synthesis

See also
References
- David Greenwood (2008). Antimicrobial drugs: chronicle of a twentieth century medical triumph. Oxford University Press US. pp. 124–. ISBN 978-0-19-953484-5. Retrieved 18 November 2010.
- "WHO Model List of EssentialMedicines" (PDF). World Health Organization. October 2013. Retrieved 22 April 2014.
- Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1039/JR9630005838, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1039/JR9630005838instead.
This systemic antibiotic-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |