This is the current revision of this page, as edited by Whywhenwhohow (talk | contribs) at 04:47, 27 October 2024 (rank). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 04:47, 27 October 2024 by Whywhenwhohow (talk | contribs) (rank)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Antihypertensive medicationPharmaceutical compound
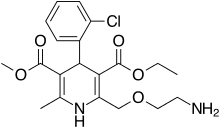 | |
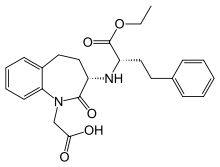 | |
| Combination of | |
|---|---|
| Amlodipine | Calcium channel blocker |
| Benazepril | ACE inhibitor |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Lotrel |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Professional Drug Facts |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Amlodipine/benazepril, sold under the brand name Lotrel among others, is a fixed-dose combination medication used to treat high blood pressure. It is a combination of amlodipine, as the besilate, a calcium channel blocker, and benazepril, an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor. It may be used if a single agent is not sufficient. It is taken by mouth.
Common side effects include cough, dizziness, and swelling. Serious side effects may include angioedema, myocardial infarction, high blood potassium, liver problems, and low blood pressure. Use in pregnancy is not recommended. Amlodipine works by increasing the size of arteries while benazepril works by decreasing renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system activity.
The combination was approved for medical use in the United States in 1995. It is available as a generic medication. In 2022, it was the 170th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 3 million prescriptions.
Medical uses
It is used to treat high blood pressure. It is not a first-line treatment.
References
- ^ "Lotrel- amlodipine besylate and benazepril hydrochloride capsule". DailyMed. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 20 June 2021.
- Cerner Multum. "Amlodipine and benazepril Uses, Side Effects & Warnings". Drugs.com. Retrieved 10 March 2019.
- Bope ET, Kellerman RD (2016). Conn's Current Therapy 2017 E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 124. ISBN 978-0-323-44335-7.
- "The Top 300 of 2022". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 30 August 2024. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- "Amlodipine; Benazepril Drug Usage Statistics, United States, 2013 - 2022". ClinCalc. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- Faulkner MA, Hilleman DE (January 2001). "Amlodipine/benazepril: fixed dose combination therapy for hypertension". Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy. 2 (1): 165–178. doi:10.1517/14656566.2.1.165. PMID 11336577. S2CID 23021242.
This drug article relating to the cardiovascular system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |