 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Moderate |
| Protein binding | <25% |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.020.429 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
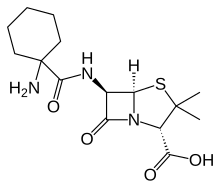
| Formula | C15H23N3O4S |
| Molar mass | 341.43 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Ciclacillin (INN) or cyclacillin (USAN), trade names Cyclapen, Cyclapen-W, Vastcillin, and others, is an aminopenicillin antibiotic. Its spectrum of activity is similar to that of ampicillin, although it is less susceptible to beta-lactamases than ampicillin and has much higher bioavailability. A large randomized, double-blind clinical trial published in 1978 also showed that ciclacillin is associated with significantly fewer and milder adverse effects than ampicillin; later studies seemed to confirm this improved tolerability, at least in children.
Ciclacillin has been superseded by newer antibiotics and is no longer in clinical use, at least in the United States.
Synthesis
In an attempt to form orally active penicillins unrelated to ampicillin, use was made of the fact that certain spiro α-amino acids, such as Cycloleucine, are well absorbed orally and transported like normal amino acids.

Reaction of cyclohexanone with ammonium carbonate and KCN under the conditions of the Bucherer-Bergs reaction led to hydantoin 1. On acid hydrolysis, α-amino acid 2 resulted. Treatment with phosgene both protected the amino group and activated the carboxyl group toward amide formation (as 3) and reaction with 6-aminopenicillanic acid (6-APA) gave cyclacillin (4).
This artifice seems to have worked, since cyclacillin is more active in vivo than its in vitro spectrum suggests.
References
- Warren GH (1976). "Cyclacillin: microbiological and pharmacological properties and use in chemotherapy of infection - a critical appraisal". Chemotherapy. 22 (3–4): 154–182. doi:10.1159/000221924. PMID 773605.
- Gold JA, Hegarty CP, Deitch MW, Walker BR (January 1979). "Double-blind clinical trials of oral cyclacillin and ampicillin". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 15 (1): 55–58. doi:10.1128/aac.15.1.55. PMC 352600. PMID 371540.
- McLinn SE, Goldberg F, Kramer R, Saltstein E, Bomze JP, Deitch MW (October 1982). "Double-blind multicenter comparison of cyclacillin and amoxicillin for the treatment of acute otitis media". The Journal of Pediatrics. 101 (4): 617–621. doi:10.1016/S0022-3476(82)80724-5. PMID 6750067.
- McLinn SE, Kaplan J, West N (1983). "Multicenter comparison of cyclacillin and amoxicillin in the treatment of acute streptococcal pharyngitis". Clinical Therapeutics. 5 (3): 299–304. PMID 6342785.
- Gorbach SL, Bartlett JG, Blacklow NR (2004). Infectious diseases (3rd ed.). Hagerstown, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 186. ISBN 0-7817-3371-5. Retrieved on September 7, 2008 through Google Book Search.
- Alburn HE, Clark RE, Fletcher H, Grant NH (1967). "Synthesis of new broad-spectrum aminoalicyclic penicillins". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 7: 586–589. PMID 5596194.
Further reading
- Scheld WM, Sydnor A, Farr B, Gratz JC, Gwaltney JM (September 1986). "Comparison of cyclacillin and amoxicillin for therapy for acute maxillary sinusitis". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 30 (3): 350–353. doi:10.1128/aac.30.3.350. PMC 180557. PMID 3535660.
This systemic antibiotic-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |