
In trigonometry, the law of cosines (also known as the cosine formula or cosine rule) relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. For a triangle with sides and opposite respective angles and (see Fig. 1), the law of cosines states:
The law of cosines generalizes the Pythagorean theorem, which holds only for right triangles: if is a right angle then and the law of cosines reduces to
The law of cosines is useful for solving a triangle when all three sides or two sides and their included angle are given.
Use in solving triangles


The theorem is used in solution of triangles, i.e., to find (see Figure 3):
- the third side of a triangle if two sides and the angle between them is known:
- the angles of a triangle if the three sides are known:
- the third side of a triangle if two sides and an angle opposite to one of them is known (this side can also be found by two applications of the law of sines):
These formulas produce high round-off errors in floating point calculations if the triangle is very acute, i.e., if c is small relative to a and b or γ is small compared to 1. It is even possible to obtain a result slightly greater than one for the cosine of an angle.
The third formula shown is the result of solving for a in the quadratic equation a − 2ab cos γ + b − c = 0. This equation can have 2, 1, or 0 positive solutions corresponding to the number of possible triangles given the data. It will have two positive solutions if b sin γ < c < b, only one positive solution if c = b sin γ, and no solution if c < b sin γ. These different cases are also explained by the side-side-angle congruence ambiguity.
History
Book II of Euclid's Elements, compiled c. 300 BC from material up to a century or two older, contains a geometric theorem corresponding to the law of cosines but expressed in the contemporary language of rectangle areas; Hellenistic trigonometry developed later, and sine and cosine per se first appeared centuries afterward in India.
The cases of obtuse triangles and acute triangles (corresponding to the two cases of negative or positive cosine) are treated separately, in Propositions II.12 and II.13:
Proposition 12.
— Euclid's Elements, translation by Thomas L. Heath.
In obtuse-angled triangles the square on the side subtending the obtuse angle is greater than the squares on the sides containing the obtuse angle by twice the rectangle contained by one of the sides about the obtuse angle, namely that on which the perpendicular falls, and the straight line cut off outside by the perpendicular towards the obtuse angle.
Proposition 13 contains an analogous statement for acute triangles. In his (now-lost and only preserved through fragmentary quotations) commentary, Heron of Alexandria provided proofs of the converses of both II.12 and II.13.

Using notation as in Fig. 2, Euclid's statement of proposition II.12 can be represented more concisely (though anachronistically) by the formula
To transform this into the familiar expression for the law of cosines, substitute and
Proposition II.13 was not used in Euclid's time for the solution of triangles, but later it was used that way in the course of solving astronomical problems by al-Bīrūnī (11th century) and Johannes de Muris (14th century). Something equivalent to the spherical law of cosines was used (but not stated in general) by al-Khwārizmī (9th century), al-Battānī (9th century), and Nīlakaṇṭha (15th century).
The 13th century Persian mathematician Naṣīr al-Dīn al-Ṭūsī, in his Kitāb al-Shakl al-qattāʴ (Book on the Complete Quadrilateral, c. 1250), gave a method for finding the third side of a general scalene triangle given two sides and the included angle by dropping a perpendicular from the vertex of one of the unknown angles to the opposite base, reducing the problem to solving a right-angled triangle by the Pythagorean theorem. If written out using modern mathematical notation, the resulting relation can be algebraically manipulated into the modern law of cosines.
About two centuries later, another Persian mathematician, Jamshīd al-Kāshī, who computed the most accurate trigonometric tables of his era, wrote about various methods of solving triangles in his Miftāḥ al-ḥisāb (Key of Arithmetic, 1427), and repeated essentially al-Ṭūsī's method, including more explicit details, as follows:

Another case is when two sides and the angle between them are known and the rest are unknown. We multiply one of the sides by the sine of the angle one time and by the sine of its complement the other time converted and we subtract the second result from the other side if the angle is acute and add it if the angle is obtuse. We then square the result and add to it the square of the first result. We take the square root of the sum to get the remaining side....
— Al-Kāshī's Miftāḥ al-ḥisāb,
translation by Nuh Aydin, Lakhdar Hammoudi, and Ghada Bakbouk
Using modern algebraic notation and conventions this might be written
when is acute or
when is obtuse. (When is obtuse, the modern convention is that is negative and is positive; historically sines and cosines were considered to be line segments with non-negative lengths.) By squaring both sides, expanding the squared binomial, and then applying the Pythagorean trigonometric identity we obtain the familiar law of cosines:
In France, the law of cosines is sometimes referred to as the théorème d'Al-Kashi.
The theorem was first written using algebraic notation by François Viète in the 16th century. At the beginning of the 19th century, modern algebraic notation allowed the law of cosines to be written in its current symbolic form.
Proofs
Using the Pythagorean theorem


Case of an obtuse angle
Euclid proved this theorem by applying the Pythagorean theorem to each of the two right triangles in Fig. 2 (AHB and CHB). Using d to denote the line segment CH and h for the height BH, triangle AHB gives us
and triangle CHB gives
Expanding the first equation gives
Substituting the second equation into this, the following can be obtained:
This is Euclid's Proposition 12 from Book 2 of the Elements. To transform it into the modern form of the law of cosines, note that
Case of an acute angle
Euclid's proof of his Proposition 13 proceeds along the same lines as his proof of Proposition 12: he applies the Pythagorean theorem to both right triangles formed by dropping the perpendicular onto one of the sides enclosing the angle γ and uses the square of a difference to simplify.
Another proof in the acute case

Using more trigonometry, the law of cosines can be deduced by using the Pythagorean theorem only once. In fact, by using the right triangle on the left hand side of Fig. 6 it can be shown that:
using the trigonometric identity
This proof needs a slight modification if b < a cos(γ). In this case, the right triangle to which the Pythagorean theorem is applied moves outside the triangle ABC. The only effect this has on the calculation is that the quantity b − a cos(γ) is replaced by a cos(γ) − b. As this quantity enters the calculation only through its square, the rest of the proof is unaffected. However, this problem only occurs when β is obtuse, and may be avoided by reflecting the triangle about the bisector of γ.
Referring to Fig. 6 it is worth noting that if the angle opposite side a is α then:
This is useful for direct calculation of a second angle when two sides and an included angle are given.
From three altitudes
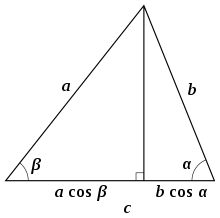
The altitude through vertex C is a segment perpendicular to side c. The distance from the foot of the altitude to vertex A plus the distance from the foot of the altitude to vertex B is equal to the length of side c (see Fig. 5). Each of these distances can be written as one of the other sides multiplied by the cosine of the adjacent angle,
(This is still true if α or β is obtuse, in which case the perpendicular falls outside the triangle.) Multiplying both sides by c yields
The same steps work just as well when treating either of the other sides as the base of the triangle:
Taking the equation for and subtracting the equations for and
This proof is independent of the Pythagorean theorem, insofar as it is based only on the right-triangle definition of cosine and obtains squared side lengths algebraically. Other proofs typically invoke the Pythagorean theorem explicitly, and are more geometric, treating a cos γ as a label for the length of a certain line segment.
Unlike many proofs, this one handles the cases of obtuse and acute angles γ in a unified fashion.
Cartesian coordinates

Consider a triangle with sides of length a, b, c, where θ is the measurement of the angle opposite the side of length c. This triangle can be placed on the Cartesian coordinate system with side a aligned along the x axis and angle θ placed at the origin, by plotting the components of the 3 points of the triangle as shown in Fig. 4:
By the distance formula,
Squaring both sides and simplifying
An advantage of this proof is that it does not require the consideration of separate cases depending on whether the angle γ is acute, right, or obtuse. However, the cases treated separately in Elements II.12–13 and later by al-Ṭūsī, al-Kāshī, and others could themselves be combined by using concepts of signed lengths and areas and a concept of signed cosine, without needing a full Cartesian coordinate system.
Using Ptolemy's theorem

Referring to the diagram, triangle ABC with sides AB = c, BC = a and AC = b is drawn inside its circumcircle as shown. Triangle ABD is constructed congruent to triangle ABC with AD = BC and BD = AC. Perpendiculars from D and C meet base AB at E and F respectively. Then:
Now the law of cosines is rendered by a straightforward application of Ptolemy's theorem to cyclic quadrilateral ABCD:
Plainly if angle B is right, then ABCD is a rectangle and application of Ptolemy's theorem yields the Pythagorean theorem:
By comparing areas


One can also prove the law of cosines by calculating areas. The change of sign as the angle γ becomes obtuse makes a case distinction necessary.
Recall that
- a, b, and c are the areas of the squares with sides a, b, and c, respectively;
- if γ is acute, then ab cos γ is the area of the parallelogram with sides a and b forming an angle of γ′ = π/2 − γ;
- if γ is obtuse, and so cos γ is negative, then −ab cos γ is the area of the parallelogram with sides a and b forming an angle of γ′ = γ − π/2.
Acute case. Figure 7a shows a heptagon cut into smaller pieces (in two different ways) to yield a proof of the law of cosines. The various pieces are
- in pink, the areas a, b on the left and the areas 2ab cos γ and c on the right;
- in blue, the triangle ABC, on the left and on the right;
- in grey, auxiliary triangles, all congruent to ABC, an equal number (namely 2) both on the left and on the right.
The equality of areas on the left and on the right gives
Obtuse case. Figure 7b cuts a hexagon in two different ways into smaller pieces, yielding a proof of the law of cosines in the case that the angle γ is obtuse. We have
- in pink, the areas a, b, and −2ab cos γ on the left and c on the right;
- in blue, the triangle ABC twice, on the left, as well as on the right.
The equality of areas on the left and on the right gives
The rigorous proof will have to include proofs that various shapes are congruent and therefore have equal area. This will use the theory of congruent triangles.
Using circle geometry

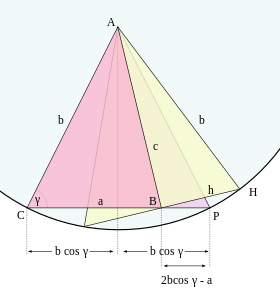

Using the geometry of the circle, it is possible to give a more geometric proof than using the Pythagorean theorem alone. Algebraic manipulations (in particular the binomial theorem) are avoided.
Case of acute angle γ, where a > 2b cos γ. Drop the perpendicular from A onto a = BC, creating a line segment of length b cos γ. Duplicate the right triangle to form the isosceles triangle ACP. Construct the circle with center A and radius b, and its tangent h = BH through B. The tangent h forms a right angle with the radius b (Euclid's Elements: Book 3, Proposition 18; or see here), so the yellow triangle in Figure 8 is right. Apply the Pythagorean theorem to obtain
Then use the tangent secant theorem (Euclid's Elements: Book 3, Proposition 36), which says that the square on the tangent through a point B outside the circle is equal to the product of the two lines segments (from B) created by any secant of the circle through B. In the present case: BH = BC·BP, or
Substituting into the previous equation gives the law of cosines:
Note that h is the power of the point B with respect to the circle. The use of the Pythagorean theorem and the tangent secant theorem can be replaced by a single application of the power of a point theorem.
Case of acute angle γ, where a < 2b cos γ. Drop the perpendicular from A onto a = BC, creating a line segment of length b cos γ. Duplicate the right triangle to form the isosceles triangle ACP. Construct the circle with center A and radius b, and a chord through B perpendicular to c = AB, half of which is h = BH. Apply the Pythagorean theorem to obtain
Now use the chord theorem (Euclid's Elements: Book 3, Proposition 35), which says that if two chords intersect, the product of the two line segments obtained on one chord is equal to the product of the two line segments obtained on the other chord. In the present case: BH = BC·BP, or
Substituting into the previous equation gives the law of cosines:
Note that the power of the point B with respect to the circle has the negative value −h.
Case of obtuse angle γ. This proof uses the power of a point theorem directly, without the auxiliary triangles obtained by constructing a tangent or a chord. Construct a circle with center B and radius a (see Figure 9), which intersects the secant through A and C in C and K. The power of the point A with respect to the circle is equal to both AB − BC and AC·AK. Therefore,
which is the law of cosines.
Using algebraic measures for line segments (allowing negative numbers as lengths of segments) the case of obtuse angle (CK > 0) and acute angle (CK < 0) can be treated simultaneously.
Using the law of sines
The law of cosines can be proven algebraically from the law of sines and a few standard trigonometric identities. To start, three angles of a triangle sum to a straight angle ( radians). Thus by the angle sum identities for sine and cosine,
Squaring the first of these identities, then substituting from the second, and finally replacing the Pythagorean trigonometric identity, we have:
The law of sines holds that
so to prove the law of cosines, we multiply both sides of our previous identity by
This concludes the proof.
Using vectors
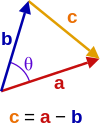
Denote
Therefore,
Taking the dot product of each side with itself:
Using the identity
leads to
The result follows.
Isosceles case
When a = b, i.e., when the triangle is isosceles with the two sides incident to the angle γ equal, the law of cosines simplifies significantly. Namely, because a + b = 2a = 2ab, the law of cosines becomes
or
Analogue for tetrahedra
Given an arbitrary tetrahedron whose four faces have areas A, B, C, and D, with dihedral angle between faces A and B, etc., a higher-dimensional analogue of the law of cosines is:
Version suited to small angles
When the angle, γ, is small and the adjacent sides, a and b, are of similar length, the right hand side of the standard form of the law of cosines is subject to catastrophic cancellation in numerical approximations. In situations where this is an important concern, a mathematically equivalent version of the law of cosines, similar to the haversine formula, can prove useful:
In the limit of an infinitesimal angle, the law of cosines degenerates into the circular arc length formula, c = a γ.
In spherical and hyperbolic geometry
Main articles: Spherical law of cosines and Hyperbolic law of cosines
Versions similar to the law of cosines for the Euclidean plane also hold on a unit sphere and in a hyperbolic plane. In spherical geometry, a triangle is defined by three points u, v, and w on the unit sphere, and the arcs of great circles connecting those points. If these great circles make angles A, B, and C with opposite sides a, b, c then the spherical law of cosines asserts that both of the following relationships hold:
In hyperbolic geometry, a pair of equations are collectively known as the hyperbolic law of cosines. The first is
where sinh and cosh are the hyperbolic sine and cosine, and the second is
As in Euclidean geometry, one can use the law of cosines to determine the angles A, B, C from the knowledge of the sides a, b, c. In contrast to Euclidean geometry, the reverse is also possible in both non-Euclidean models: the angles A, B, C determine the sides a, b, c.
Polyhedra
The Law of Cosines can be generalized to all polyhedra by considering any polyhedron with vector sides and invoking the Divergence Theorem.
See also
- Half-side formula
- Law of sines
- Law of tangents
- Law of cotangents
- List of trigonometric identities
- Mollweide's formula
Notes
- Given sides and angle can be found using the law of sines, leaving up to two possibilities for angle . Either choice determines because the three interior angles sum to a straight angle. Finally can be found from by another application of the law of sines.
References
- ^ Euclid. Thomas L. Heath (ed.). "Elements". Translated by Thomas L. Heath. Retrieved 24 January 2023.
- Heath, Thomas (1956) . "Introduction". The Thirteen Books of Euclid's Elements (2nd ed.).
- Kennedy, E.S.; Muruwwa, Ahmad (1958). "Bīrūnī on the Solar Equation". Journal of Near Eastern Studies. 17 (2): 112–121. doi:10.1086/371451. JSTOR 542617. Johannes de Muris credits an anonymous author for the relevant section of his work De Arte Mesurandi. See Van Brummelen, Glen (2009). The Mathematics of the Heavens and the Earth. Princeton University Press. pp. 240–241.
- Van Brummelen, Glen (2012). Heavenly mathematics: The forgotten art of spherical trigonometry. Princeton University Press. p. 98.
- Naṣīr al-Dīn al-Ṭūsī (1891). "Ch. 3.2: Sur la manière de calculer les côtés et les angles d'un triangle les uns par les autres". Traité du quadrilatère attribué a Nassiruddinel-Toussy (in French). Translated by Caratheodory, Alexandre Pacha. Typographie et Lithographie Osmanié. p. 69.
On donne deux côtés et un angle. Que si l'angle donné est compris entre les deux côtés donnés, comme l'angle A est compris entre les deux côtés AB AC, abaissez de B sur AC la perpendiculaire BE. Vous aurez ainsi le triangle rectangle dont nous connaissons le côté AB et l'angle A; on en tirera BE, EA, et l'on retombera ainsi dans un des cas précédents; c. à. d. dans le cas où BE, CE sont connus; on connaîtra dès lors BC et l'angle C, comme nous l'avons expliqué
[Given the angle A is included between the two sides AB AC, drop from B to AC the perpendicular BE. You will thus have the right triangle of which we know the side AB and the angle A; in that triangle compute BE, EA, and the problem is reduced to one of the preceding cases; that is, to the case where BE, CE are known; we will thus know BC and the angle C, as we have explained.] - Azarian, Mohammad K. (2000). "Meftab Al-Hesab: A Summary" (PDF). Missouri Journal of Mathematical Sciences. 12 (2): 75–95. doi:10.35834/2000/1202075.
- Aydin, Nuh; Hammoudi, Lakhdar; Bakbouk, Ghada (2020). Al-Kashi's Miftah al-Hisab, Volume II: Geometry. Birkhäuser. p. 31. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-61330-3. ISBN 978-3-030-61329-7.
- Pickover, Clifford A. (2009). The Math Book: From Pythagoras to the 57th Dimension. Sterling Publishing Company, Inc. p. 106. ISBN 9781402757969.
- Programme de mathématiques de première générale (in French). Ministère de l'Éducation nationale et de la Jeunesse. 2022. pp. 11, 12.
- For example in Carnot, Lazare (1803). Géométrie de position. J.B.M Duprat. p. 202.
- Java applet version by Prof. D E Joyce of Clark University.
- ^ Alexander Bogomolny credits this proof to teacher John Molokach (2011), but it may be older. Bogomolny, Alexander. "The Law of Cosines (Independent of the Pythagorean Theorem)". Cut the Knot. Retrieved 2024-01-09.
- Wylie, Clarence Raymond (1955). Plane Trigonometry. McGraw-Hill. §9.1 The Law of Cosines, pp. 195–198. LCCN 54-11278.
- Burton, L. J. (1949). "The Laws of Sines and Cosines". The American Mathematical Monthly. 56 (8): 550–551. doi:10.1080/00029890.1949.11999439. JSTOR 2305533.
- Casey, John (1889). A Treatise on Spherical Trigonometry: And Its Application to Geodesy and Astronomy with Numerous Examples. London: Longmans, Green, & Company. p. 133.
- Collins, L; Osler, T (2011). "Law of Cosines Generalised for any Polygon and any Polyhedron". The Mathematical Gazette. 95 (533): 240–243. doi:10.1017/S0025557200002953. JSTOR 23248682.
External links
- "Cosine theorem", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, EMS Press, 2001
- Several derivations of the Cosine Law, including Euclid's at cut-the-knot
- Interactive applet of Law of Cosines

 and
and  opposite respective angles
opposite respective angles 
 and
and  (see Fig. 1), the law of cosines states:
(see Fig. 1), the law of cosines states:

 and the law of cosines
and the law of cosines 






 and
and 



 is negative and
is negative and  is positive; historically sines and cosines were considered to be line segments with non-negative lengths.) By squaring both sides,
is positive; historically sines and cosines were considered to be line segments with non-negative lengths.) By squaring both sides,  we obtain the familiar law of cosines:
we obtain the familiar law of cosines:












 and subtracting the equations for
and subtracting the equations for  and
and 
















 radians). Thus by the angle sum identities for sine and cosine,
radians). Thus by the angle sum identities for sine and cosine,


 from the second, and finally replacing
from the second, and finally replacing 
 the
the 











 between faces A and B, etc., a higher-dimensional analogue of the law of cosines is:
between faces A and B, etc., a higher-dimensional analogue of the law of cosines is:





 and angle
and angle 
 can be found using the law of sines, leaving up to two possibilities for angle
can be found using the law of sines, leaving up to two possibilities for angle  . Either choice determines
. Either choice determines  because the three interior angles sum to a straight angle. Finally
because the three interior angles sum to a straight angle. Finally  can be found from
can be found from  by another application of the law of sines.
by another application of the law of sines.