| Principality of LippeFürstentum Lippe (German) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1789–1918 | |||||||||
 Flag
Flag
 Coat of arms
Coat of arms
| |||||||||
 The Principality of Lippe within the German Empire The Principality of Lippe within the German Empire | |||||||||
 The Principality of Lippe in 1918 The Principality of Lippe in 1918 | |||||||||
| Status | State of the Holy Roman Empire (1789–1806) State of the Confederation of the Rhine (1806–1813) State of the German Confederation (1815–1866) State of the North German Confederation (1867–1871) Federated State of the German Empire (1871–1918) | ||||||||
| Capital | Detmold | ||||||||
| Common languages | West Low German | ||||||||
| Religion | Church of Lippe | ||||||||
| Government | Principality | ||||||||
| Prince | |||||||||
| • 1789–1802 | Leopold I (first) | ||||||||
| • 1905–1918 | Leopold IV (last) | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
| • Raised to Principality | 1789 | ||||||||
| • German Revolution | 12 November 1918 | ||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
| 1910 | 1,215 km (469 sq mi) | ||||||||
| Population | |||||||||
| • 1910 | 150,000+ | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Lippe (later Lippe-Detmold and then again Lippe) was a state in Germany, ruled by the House of Lippe. It was located between the Weser river and the southeast part of the Teutoburg Forest. It originated as a state during the Holy Roman Empire, and was promoted to the status of principality in 1789. During this period the ruling house split into a number of branches, with the main line residing at Detmold. During the Reformation, Lippe had converted to Lutheranism in 1538 and then to Calvinism in 1604.
From the demise of the empire in 1806, the principality was independent, but it joined the North German Confederation in 1866 and became one of the States of the German Empire in 1871. Over the course of the nineteenth century it gradually developed into a constitutional monarchy with moderate participation in government for the landed nobility. Its economy was overwhelmingly agrarian and among the weakest in the German Empire. After the last prince abdicated in 1918, it continued as a Free State of Germany until it was merged into North Rhine-Westphalia in 1947.
History
County of Lippe
Main article: County of LippeThe founder of what would become the County of Lippe (1528–1789), then the Principality of Lippe (1789–1918) was Bernhard I, who received a grant of territory from Lothair III in 1123. Bernhard I assumed the title of Edler Herr zu Lippe ("Noble Lord at Lippe"). The history of the dynasty and its further acquisitions of land really began with Bernard II. His territory was probably formed out of land he acquired on the destruction of the Duchy of Saxony following the demise of Henry the Lion in 1180. Simon V was the first ruler of Lippe to style himself as a count (Graf) in 1528.
Following the death of Simon VI in 1613, the county was partitioned between his three sons; Lippe-Detmold went to Simon VII, Lippe-Brake to Otto and Lippe-Alverdissen went to Philip I. The County of Lippe-Brake was reunited with the main Detmold line in 1709. A son of Simon VII, Jobst Herman, founded another branch of the family, the Lippe-Biesterfeld line; the Lippe-Weissenfeld branch later separated from the Lippe-Biesterfelds. Both Lippe-Biesterfeld and Lippe-Weissenfeld were paragiums (non-sovereign estates of a cadet-branch) within the County of Lippe, and both branches, owning only modest manor houses in the county, acquired property in other states by marriage and moved out of the county in the late 18th century, the Biesterfeld branch to the Rhineland and the Weissenfeld branch to Saxony.
Principality of Lippe

Leopold I (1767-1802) became the first Prince (Fürst) of Lippe in 1789. Following the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806 Lippe joined Napoleon's Confederation of the Rhine in 1807. After the Napoleonic Wars Lippe became a member of the German Confederation in 1815, then joined the North German Confederation in 1866 and the German Empire in 1871. On 20 July 1895, Prince Woldemar died childless. The title nominally passed to his brother Alexander who was incapable of governing due to mental illness. The regency initially passed to Adolf of Schaumburg-Lippe, in accordance with Woldemar's will.
Since the counts of Lippe-Biesterfled and Lippe-Weissenfeld also laid claim to the regency and the right to succeed Alexander, a succession dispute arose, which continued until 1905. The Schaumburg-Lippe claim was actively supported by Emperor Wilhelm II (whose sister was married to Prince Adolf). A ruling in the Reichsgericht in Leipzig in 1897 decided the matter in favour of Ernest, Count of Lippe-Biesterfeld, who then assumed the regency. However, at the instruction of Wilhelm II, the military forces stationed in Lippe refused to address him as "illustrious" and denied the other honours that he was entitled to. In response, Ernest sent a letter round to the other sovereign princes of the German Empire in which he complained about the emperor's behaviour - an unprecedented action, which brought German public opinion strongly in favour of Ernest's position.
After Ernest's death in 1904, his son Leopold assumed the regency. When Prince Alexander died the following year, the Reichsgericht finally recognised the right of the House Lippe-Biesterfeld to the succession and Leopold took the throne as Prince Leopold IV.
The Principality of Lippe came to an end on 12 November 1918 with the abdication of Leopold IV, becoming the Free State of Lippe. In 1947, Lippe merged into the state of North Rhine-Westphalia. The princely family still owns the estate and Fürstliches Residenzschloss [de] in Detmold.
Government
An 1819/20 attempt to establish a constitution failed and the first basic law was passed in 1836. It was liberalised in 1849, restored in 1853 and then steadily modernised in 1853, 1876, and 1912. The 1876 electoral law abolished an estates-based system and introduced the three-class franchise, which did not offer a general, equal, or democratic possibility of participation to the citizens. Lippe increasingly developed into a constitutional monarchy. In 1836, a Landtag [de] (parliament) was established, which gave moderate legislative power to the landed nobility. The highest national authority was the cabinet, headed by the State Minister, which oversaw the top-level administrative and legal authorities. The top-level administrative authority was German: Regierungsollegium (governing college). In 1868, the property of the princes and the property of the state were separated. The Princes retained a large personal estate, including palaces, land, forests, long-term leases, Bad Meinberg, and the salt deposits at Uflen, which mostly came under state control after the abdication of Leopold IV in 1918.
As a state of the German Empire, Lippe was represented on the Bundesrat (Federal Council). Lippe had a single representative, who was selected by the landed nobility. The Bundesrat was dominated by Prussia, which had 17 representatives, out of a total of 58, meaning that Lippe was practically irrelevant in the council. It was one of sixteen states with only one representative on the council.
Law
From 1817, Lippe fell under the Oberappellationsgericht [de] (upper appellate court) in Wolfenbüttel, along with the Duchy of Brunswick, and the principalities of Schaumberg-Lippe and Waldeck-Pyrmont. When the Wolfenbüttel court was abolished, an "interim upper appellate court" was established, which had oversight of the courts in Lippe. In 1857, Lippe placed itself under the Oberlandsgericht (supreme regional court) at Celle [de] in the Kingdom of Hanover. After the Prussian annexation of Hannover in 1866, this was subordinated to the Prussian appellate system, but then became an Oberlandsgericht once more in 1879. Its role as Lippe's Oberlandsgericht was regulated by a treaty of 4 January 1879. Most of Lippe fell within the Detmold court district [de], which contained the Amtsgerichte (district courts) of Blomberg, Detmold, Hohenhausen, Horn, Lage, Lemgo, Oerlinghausen, and Salzuflen. The exclaves of Lipperode and Cappel came under the Prussian district court in Lippstadt. Lippe belonged to Celle until 1944.
Administrative subdivisions
| Cities | 1871 populations |
|---|---|
| Barntrup | 01116 |
| Blomberg | 02203 |
| Detmold | 06469 |
| Horn | 01717 |
| Lage | 02514 |
| Lemgo | 04801 |
| Salzuflen | 02072 |
| Amt | 1871 Population |
| Blomberg | 03608 |
| Brake [de] | 07981 |
| Detmold | 08513 |
| Hohenhausen [de] | 06482 |
| Horn | 05800 |
| Lage | 13406 |
| Lipperode [de] | 00728 |
| Oerlinghausen | 08571 |
| Schieder | 03660 |
| Schötmar [de] | 10806 |
| Schwalenberg | 06225 |
| Sternberg-Barntrup | 09223 |
| Varenholz [de] | 05140 |
In 1879, the Principality was divided into five administrative subdivisions, called Ämter (singular Amt): Blomberg, Brake [de], Detmold, Schötmar [de] and Lipperode-Cappel. The cities of Barntrup, Blomberg, Detmold, Horn, Lage, Lemgo and Salzuflen, as well as the village of Schwalenberg were outside of the Amt-system (Schwalenberg received the status of city in 1906).
In 1910, the system was reformed. Lippe was divided into five Verwaltungsämter, containing thirteen Ämtern.
- Verwaltungsamt Blomberg (Ämter Blomberg, Schieder and Schwalenberg) with 45 districts and an area of 199.36 km (76.97 sq mi)
- Verwaltungsamt Brake (Ämter Brake, Hohenhausen, Sternberg-Barntrup and Varenholz) with 64 districts and an area of 364.60 km (140.77 sq mi)
- Verwaltungsamt Detmold (Ämter Detmold, Horn and Lage) with 64 districts and an area of 375.05 km (144.81 sq mi)
- Verwaltungsamt Lipperode-Cappel (Amt Lipperode-Cappel) with 3 districts and an area of 7.66 km (2.96 sq mi)
- Verwaltungsamt Schötmar (Ämter Oerlinghausen and Schötmar) with 34 districts and an area of 158.06 km (61.03 sq mi)
The eight cities remained outside the Amt-system.
Economy

On the whole, Lippe was always an agrarian state and, in economic terms, was one of the weakest states in the German Empire. The loess floodplains of the Werre and the Bega always enabled intensive agriculture. In the less fertile sandy soils of the Senne region, on the other hand, intensive agriculture was not possible. Instead, activity focussed on animal husbandry and the breeding of Senner horses at Jagdschloss Lopshorn [de].
Industry existed only on a limited scale and was mostly based on the direct extraction of the land's mineral and forest resources. This was partially a consequence of the power of the landed nobility and the unfriendly attitude of the monarchs towards economic undertakings at the beginning of the Industrial Revolution. The monarchy's economic interventions focussed mainly on securing their own economic power, which rested more on the direct income from the princes' own estates, forests, salt mines and health baths, than on taxes on independent production and trade.
The textile industry supported flax farming and linen production. The largest industrial concern was probably Hoffmann's Stärkefabriken. The Principality also had a significant sepiolite industry in Lemgo, salt evaporation ponds in Salzuflen (1878: 1,240,000 kg of salt) and a timber industry, which still exists today, with numerous sawmills processing material from Lippe's forests. As in neighbouring Prussia, the cigar industry also gained particular significance. Like the textile industry, it was partially organised in a proto-industrial fashion, through the putting-out system. There were also beer breweries (e.g. Strate [de] and Falkenkrug [de]), brickworks, a sugar factory in Lage, and oil mills. The spa towns of Bad Meinberg und Bad Salzuflen also gained economic significance.
For industry, the construction of the Lippe railway (1880) and the Lippische branch line [de] (1895) was important, since they connected the region to the Hamm–Minden railway.
Military

A Lippe battalion was formed on 5 May 1807, the 2nd battalion of the 5th infantry regiment of the Prince's Division of the Confederation of the Rhine. It also included a company from Schaumburg-Lippe. In 1867, Lippe concluded a military convention [de] with Prussia, becoming part of the catchment area for Prussia's 26th Infantry brigade of the 13th Division (VII Corps). Following the integration of Lippe into the Prussian Army, the Prince's Division was dissolved on 27 May 1867. The Lippe soldiers were mainly employed in the 55th (6th Westphalian) Infantry Regiment "Count Bülow von Dennewitz" [de]. The regiment's headquarters and its 3rd battalion were based in Detmold by 1918.
A white-blue-red uniform based on that of France was introduced for the Lippe soldiers in 1815. This uniform was also depicted on the Notgeld issued by the city of Detmold in the 1920s and bottles of Lipper Schütze schnapps were modelled on it, ensuring that it remained part of the popular imagination. By 1867, at the latest, Lippe soldiers had switched to using the Prussian uniform and could only be distinguished from other troops by the Lippe cockade in the national colours (yellow-red-yellow).
In reality, Lippe no longer had a military of its own after 1867 and even before that was in no position to maintain an independent force the size of a regiment. The song Lippe-Detmold, eine wunderschöne Stadt [de] ("Lippe-Detmold, a wonderful city") presents a caricature of this military weakness and became a kind of national song for Lippe. In the song, a Lippe soldier goes to war and is shot dead, forcing his general to abandon the campaign, because he had been the Lippe army's only soldier. The Lippe Notgeld of the 1920s was inspired by the song. Despite this, Lippe retained a certain military significance as the site of the Sennelager Training Area.
List of princes of Lippe
For the previous rulers of Lippe, see House of Lippe § Rulers of Lippe.| Princes of Lippe | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Portrait | Born | Reign | Death | Consort | Notes |
| Leopold I |  |
2 December 1767 | 1789–1802 | 4 April 1802 | Pauline Christine of Anhalt-Bernburg 2 January 1796 |
Count of Lippe-Detmold from 1782 |
| Regency of Pauline Christine of Anhalt-Bernburg (1802–1820) | ||||||
| Leopold II |  |
6 November 1796 | 1802–1851 | 1 January 1851 | Emilia Frederica of Schwarzburg-Sondershausen 23 April 1820 |
Succeeded while underage and assumed full powers in 1820. |
| Leopold III |  |
1 September 1821 | 1851–1875 | 8 December 1875 | Elisabeth of Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt 17 April 1852 |
Left no descendants. The principality fell to his brother. |
| Woldemar |  |
18 April 1824 | 1875–1895 | 20 March 1895 | Sophie of Baden 9 November 1858 |
Left no descendants. The principality fell to his brother. |
| Regencies of Ernest, Count of Lippe-Biesterfeld (1895–1904) and Leopold, Count of Lippe-Biesterfeld (1904–1905) | ||||||
| Alexander |  |
16 January 1831 | 1895–1905 | 13 January 1905 | Unmarried | Incapable of exercising office due to mental illness. |
| Leopold IV |  |
30 May 1871 | 1905–1918 | 30 December 1949 | Bertha of Hesse-Philippsthal-Barchfeld 16 August 1901 Anna of Ysenburg and Büdingen 16 April 1922 |
From the Lippe-Biesterfeld line, regent of Lippe from 1904. In 1918, he abdicated following the dissolution of the monarchy. |
List of state ministers
| Heads of government of Lippe | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Portrait | Birth–Death | Party affiliation |
Took office | Left office | ||
| Karl Friedrich Funk von Senftenau [de] | 
|
1748–1828 | N/A | 1810 | 1828 | ||
| Friedrich Wilhelm Helwing [de] | 
|
1758–1833 | N/A | 1829 | 1832 | ||
| Wilhelm Arnold Eschenburg [de] | 
|
1778–1861 | N/A | 1832 | 1848 | ||
| Friedrich Simon Leopold Petri [de] | 
|
1775–1850 | N/A | 1848 | 1850 | ||
| Christian Theodor von Meien [de] | 
|
1781–1857 | N/A | 1850 | 1853 | ||
| Laurenz Hannibal Fischer [de] | 
|
1784–1868 | N/A | 1853 | 1855 | ||
| Alexander von Oheimb [de] | 
|
1820–1903 | N/A | 1856 | 1868 | ||
| Carl Theodor Heldman [de] | 
|
1801–1872 | N/A | 1868 | 1872 | ||
| Adalbert von Flottwell [de] | 1829–1909 | DkP | 1872 | 1875 | |||
| August Eschenburg [de] | 
|
1823–1904 | N/A | 1876 | 1885 | ||
| Hugo Samuel von Richthofen [de] | 
|
1842–1904 | N/A | 1885 | 1889 | ||
| Friedrich Otto Hermann von Wolffgramm [de] | 
|
1836–1895 | N/A | 1889 | 1895 | ||
| Karl Friedrich von Oertzen [de] | 
|
1844–1914 | N/A | 1895 | 1897 | ||
| Karl Miesitschek von Wischkau [de] | 1859–1937 | N/A | 1897 | 1899 | |||
| Max von Gevekot [de] | 
|
1845–1916 | N/A | 1900 | 1912 | ||
| Karl Ludwig von Biedenweg [de] | 1864–1940 | N/A | 1913 | 1918 | |||
See also
Notes
- ^ Chisholm 1911, p. 740.
- Lippischer Erbfolgestreit on Wikisource
- G. Benecke, Society and Politics in Germany, 1500–1750, Routletge & Kegan Paul Ltd, 1974, p. 41.
- "Wo Deutschland fast noch eine Monarchie ist" by Andreas Fasel, Die Welt, 25 December 2015 (in German)
- Andreas Kunz (ed.): Lippe Detmold. (PDF; 37 kB) in eKompendium-hgisg.de
- "Der Freistaat Lippe im Überblick". www.gonschior.de.
- ^ "retro|bib - Seite aus Meyers Konversationslexikon: Lipnik - Lippe". www.retrobibliothek.de.
References
Attribution
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Lippe". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 16 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 740–741.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Lippe". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 16 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 740–741.
Further reading
- A. Falkmann, Beiträge zur Geschichte des Fürstenthums Lippe (Detmold, 1857–1892; 6 vols.)
- Schwanold, Das Fürstentum Lippe, das Land und seine Bewohner (Detmold, 1899)
- Piderit, Die lippischen Edelherrn im Mittelalter (Detmold, 1876)
- A. Falkmann and O. Preuss, Lippische Regenten (Detmold, 1860–1868)
- H. Triepel, Der Streit um die Thronfolge im Fürstentum Lippe (Leipzig, 1903)
- P. Laband, Die Thronfolge im Fürstentum Lippe (Freiburg, 1891)
- Schiedsspruch in dem Rechtstreit über die Thronfolge im Fürstentum Lippe vom 25 Okt. 1905 (Leipzig, 1906)
External links
- Ordinances and by-laws of the county of Lippe online (in German)
- Guidelines for the integration of the Land Lippe within the territory of the federal state North-Rhine-Westphalia of 17 January 1947 (in German)
| Prince-bishops |  | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prince-abbots | |||||||
| Secular | |||||||
| Counts / Lords |
| ||||||
| Cities | |||||||
| from 1648 until 1648 without seat in Imperial Diet status uncertain
Circles est. 1500: Bavarian, Swabian, Upper Rhenish, Lower Rhenish–Westphalian, Franconian, (Lower) Saxon
| |||||||
| States of the Confederation of the Rhine (1806–1813) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank elevated by Napoleon |
| 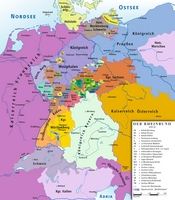 | ||||||
| States created |
| |||||||
| Pre-existing states |
| |||||||
| ||||||||
| States of the German Confederation (1815–1866) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Empires | 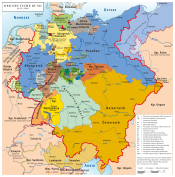 | ||||||||
| Kingdoms | |||||||||
| Electorates | |||||||||
| Grand duchies | |||||||||
| Duchies |
| ||||||||
| Principalities |
| ||||||||
| Free cities | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| States of the North German Confederation (1866–1871) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Kingdoms | 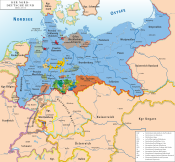 | |
| Grand Duchies | ||
| Duchies | ||
| Principalities | ||
| City-states | ||
| States of the German Empire (1871–1918) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Kingdoms |
|  |
| Grand Duchies | ||
| Duchies | ||
| Principalities | ||
| City-states | ||
| Imperial Territories | ||
| Other | ||
- Principality of Lippe
- States and territories disestablished in 1918
- States and territories established in 1123
- States of the Confederation of the Rhine
- States of the German Empire
- Lower Rhenish-Westphalian Circle
- Lists of princes
- Former principalities
- Principalities of the Holy Roman Empire
- 1120s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire
- 1123 establishments in Europe
- 1918 disestablishments in Germany
- Former states and territories of North Rhine-Westphalia
- States of the North German Confederation