This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Flyer22 Frozen (talk | contribs) at 08:15, 22 May 2016 (WP:Dummy edit: Sex with children is child abuse, depending on how "child" is defined.). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 08:15, 22 May 2016 by Flyer22 Frozen (talk | contribs) (WP:Dummy edit: Sex with children is child abuse, depending on how "child" is defined.)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
Sex tourism is travel to engage in sexual activity, particularly with prostitutes. The World Tourism Organization, a specialized agency of the United Nations, defines sex tourism as "trips organized from within the tourism sector, or from outside this sector but using its structures and networks, with the primary purpose of effecting a commercial sexual relationship by the tourist with residents at the destination".
Some people regard sexual activity while traveling as a way of enhancing their travel experience. However, social problems arise when particular countries or cities acquire a reputation as a destination or become attractive for sex tourism. Attractions for sex tourists can include lower costs for sexual services in the destination country, more favorable local attitudes to prostitution, separation from person's normal social circle and physical environment, because prostitution is either legal or there is indifferent law enforcement, and access to child prostitution.
General
Overview
Generally, people who travel to engage in sexual activity with an adult prostitute are subject to prostitution laws of the destination country. When the sexual activity involves child prostitution, is non-consensual or involves sex trafficking, it is often illegal, both in the participating country and in the individual's home country.
Sex tourism may be domestic, which involves travel within the same country, or trans-national, which involves travel across national borders. Sex tourism is a multibillion-dollar industry that supports an international workforce estimated to number in the millions, that also benefits service industries such as the airline, taxi, restaurant and hotel industries.
Most sex tourism involves male tourists seeking female prostitutes and several countries have become preferred destinations for sex tourists. These include Brazil, Costa Rica, the Dominican Republic, the Netherlands (particularly Amsterdam), Kenya, Colombia, Thailand, the Philippines, Cambodia, Cuba, and Indonesia (particularly Bali).
A number of countries have become popular destinations for female sex tourism, including Southern Europe (mainly in Greece, Italy, Cyprus, Spain and Portugal); the Caribbean (led by Jamaica, Barbados and the Dominican Republic); Brazil, Egypt, Turkey, Southeast Asia, and Phuket in Thailand); and Gambia, Senegal and Kenya in Africa. Other popular destinations include Bulgaria, Tunisia, Lebanon, Morocco, Jordan, Azerbaijan, Fiji, Colombia and Costa Rica. Bali Indonesia is the only destination where females from Western Europe , Japan and Australia engages in sex tourism with male locals.
Motivations for sex tourism
According to The Ethics of Tourism: Critical and Applied Perspectives by Lovelock and Lovelock, romance (in general) and sexual encounters (more specifically) are a key factor in world travel. Tourist markets have exploited this motivation for travel through prostitution. This industry of sex work is extremely profitable, and the tourist market's role in sex tourism raises questions about its moral and legal standing. Key factors in the issue of sex tourism are child sex tourism and the trafficking of women and girls for use as prostitutes.
Sex tourism can be formally or informally arranged, and local sex workers in the tourist destination are often migrants. These migrants can be either voluntary migrants, or trafficked sex workers. The most common type of sex tourism is of men seeking women. Less common forms include female sex tourism (women seeking men), men seeking men, and adults seeking children.
Sex tourism is characterized by a disparity between the motivations of the tourist and the sex worker — the tourist has disposable capital which can be used to pay for sexual services as well as a number of other experiences associated with travel and tourism (leisure, recreation, sightseeing, etc.); conversely, the sex worker is usually living in poverty and providing sexual services because it is the only option available to them.
Demographics
Sex tourists generally come from developed nations in Europe as well as the United States. Asian countries, especially Thailand, the Philippines, Cambodia, and Nepal are common destinations for sex tourists, as well as countries in Central and South America.
A study conducted by ProCon (a nonprofit, nonpartisan public charity which provides different opinions on controversial issues) estimated the percentage of men who had paid for sex at least once in their lives, and found the highest rates in Cambodia (between 59 and 80% of men had paid for sex at least once) and Thailand (an estimated 75%), followed by Italy (16.7-45%), Spain (27-39%), Japan (37%), the Netherlands (13.5-21.6%), and the United States (15.0-20.0%). Studies indicate that the percentage of men engaging in commercial sex in the United States has declined significantly in recent decades: in 1964, an estimated 69-80% of men had paid for sex at least once. This indicates growing stigma against prostitution in the U.S. Nations with higher rates of prostitution clients, or “johns,” display much more positive attitudes towards commercial sex. In some countries, such as Cambodia and Thailand, sex with prostitutes is considered commonplace and men who do not engage in commercial sex may be considered unusual by their peers.
Cultural attitudes
According to Female Sex Trafficking in Asia: The Resilience of Patriarchy in a Changing World by Samarasinghe, cultural attitudes towards sex tourism in Asian countries are complex. Families in poor rural areas commonly sell their children to human traffickers, who take the children to large cities in order to perform sex work. The people in these communities are generally aware of what they are committing their children to, but consider the rewards of increased financial return to be greater than the consequence for their children. Additionally, this is a common practice among rural families, and children are often enticed by the prospect of moving to a large city.
Attitudes towards sex work in general is a complex issue. Samarasinghe states that many women in Asian countries such as Thailand support husbands visiting prostitutes. This is because prostitution is seen as an alternative to men taking on mistresses, whom they would be obligated to support financially, drawing funds away from the wife and children. Thus, opposition to prostitution does not gather a great deal of support within receiving countries of sex tourism.
The countries where tourists come from tend to have harsher attitudes towards prostitution. Men who travel seeking to pay for sex may do so because it is much harder to engage in sex work in their home countries. Conversely, in receiving countries such as Cambodia, commercial sex work is generally accepted as a common behavior for men, and sex with minors is often accepted as well. Law makers as well as law enforcement often do not place priority on policing prostitution and sex trafficking.
University of Leicester sociologists studied this subject as part of a research project for the Economic and Social Research Council and End Child Prostitution and Trafficking campaign. The study included interviews with over 250 Caribbean sex tourists. Amongst their findings were:
- Preconceptions about race and gender influenced the tourists' opinions.
- Economically underdeveloped tourist-receiving countries are considered culturally different so that (in the Western tourist's understanding) prostitution and traditional male domination of women have less stigma than similar practices might have in their home countries.
However, despite a great deal of interest in sexual tourism amongst theorists, methodologically thorough and detailed studies remain rare, despite the increasing accessibility of such groups for study in the past three decades.
Economic and policy implications
McPhee notes that one of the central challenges to addressing sex tourism is the differing laws and norms regarding normal sexual behavior in sending and receiving countries. Because sex tourism is a transnational issue, it must be addressed beyond the domestic level. Sex tourism also has economic implications for all nations involved. Sex tourism is encouraged by the tourist sector of destination countries, because it draws individuals from wealthier nations with greater amounts of disposable income into poorer nations. This stimulates the economy of these poorer nations. These economic reinforcements are part of the reason sex tourism continues to exist.
In an article published by the University of Chicago, Patil argues that tourism in general has changed with economic policies in recent decades. Patil states that the promotion of tourism caters to tourists in both Western and Eastern countries by emphasizing racial/ethnic and gender differences. In order to appeal to tourists from Western countries, travel agencies may emphasize a stereotypical, exoticized portrait of the people in the destination country. This, in turn, can reproduce colonial and traditional attitudes toward race and gender, reinforcing inequality between groups. According to Patil, the state plays a vital part in this interaction, meaning that governments create barriers to formation of new policy.
In an article for International Family Planning Perspectives, Mahler describes the economic conditions that lead to sexual exploitation of children. Young girls and adolescent women are sold into slavery or transported across national borders to work in the commercial sex industry. Mahler states that the rate of child prostitution is higher in countries where girls marry at very young ages. Additionally, prostitution of children is highest in countries where young girls are expected to carry some of the family’s financial burden, such as in Thailand. 80% of prostitutes in Thailand send money home to their families. Sex work yields higher wages than work in the formal sector, and remittances from a relative in the sex industry allows poor families (especially in rural areas) to achieve a much higher quality of life.
Sex tourism is also encouraged by cultural attitudes. In Thailand, for example, prostitution is very common, and is socially reinforced by the high value placed on sexual experience for men combined with the high value placed on sexual purity for women. The social restrictions placed on women create high demand for commercial sex workers, and this ensures a consistent supply of prostitutes. The high number of prostitutes and widespread cultural acceptance of prostitutes in Thailand is one of the factors that promotes sex tourism to this country.
Child sex tourism
Main article: Child sex tourismSome people travel to engage in sex with child prostitutes in a practice called child sex tourism. While it is criminal in most countries, this multibillion-dollar industry is believed to involve as many as 2 million children around the world.
"Child sex tourists may not have a specific preference for children as sexual partners but take advantage of a situation in which children are made available to them for sexual exploitation. It is often the case that these people have travelled from a wealthier country (or a richer town or region within a country) to a less-developed destination, where poorer economic conditions, favourable exchange rates for the traveller and relative anonymity are key factors conditioning their behaviour and sex tourism."
In an effort to eradicate the practice, many countries have enacted laws to allow prosecution of their citizens for child abuse that occurs outside their home country, even if it is not against the law in the country where the child abuse took place, for example, the United States Protect Act. The Code of Conduct for the Sexual Exploitation of Children in Travel and Tourism is an international organization composed of members of the tourism industry and children's rights experts with the purpose to eradicate the practice of child sex tourism.
Thailand, Cambodia, Brazil, Colombia and Mexico have been identified as countries where child sexual exploitation is prevalent. Child sex tourism has been closely linked to poverty.
In Thailand, though the exact numbers are not known, it has been estimated that children make up to 9% of prostitutes in the country. Brazil is considered to have the worst child sex trafficking record, after Thailand.
UNICEF notes that sexual activity is often seen as a private matter, making communities reluctant to act and intervene in cases of sexual exploitation. These attitudes make children far more vulnerable to sexual exploitation. Most exploitation of children takes place as a result of their absorption into the adult sex trade where they are exploited by local people and sex tourists. The Internet provides an efficient global networking tool for individuals to share information on destinations and procurement.
In cases involving children, the USA has relatively strict domestic laws that hold accountable any American citizen or permanent resident of the U.S. who travels abroad for the purpose of engaging in illicit conduct with a minor. As of 2009, sex tourism and human trafficking remained fast-growing industries.
Opposition to sex tourism
One of the primary sources of opposition to sex tourism is with regard to child sex tourism, internationally defined as travel to have sex with a person under 18 years of age. This occurs when tourists from countries such as America take advantage of legal prostitution, lower consent ages, and the lack of extradition laws in order to engage in sex with minors in foreign countries. Nations such as the United States provide a steady stream of tourists who feed the sex tourism industry as they attempt to subvert laws in their home country. Human rights organizations and governments argue that this pattern creates an incentive for trafficking of children and violation of children’s human rights.
Oppositions to sex tourism also stem from concerns around the trafficking of women. The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime targets the trafficking of women and children as a central concern in their approach to transnational crime. The United Nations Global Report on Trafficking in Persons states that women “comprise the vast majority” of human trafficking victims for sexual exploitation across the world. They also note that women make up a relatively large portion of human trafficking offenders — about 30% of convicted human traffickers are women. Samarasinghe argues that women who become involved in human trafficking were once victims of sex trafficking and sexual exploitation themselves. The only way for these women to gain economic security and freedom is therefore to participate in the trafficking system as well. These factors all contribute to the debate on human rights and their relations with sex tourism. In The Prostitution of Sexuality, Berry argues that the growing sex tourism industry reflects a global increase in sexual exploitation, and a lack of concern for the rights and dignity of sex workers. Berry states that sex tourism, as well as the growing international porn industry, indicate a normalization of prostitution and an increase in the exploitation of women. Additionally, Berry argues that sex tourism and prostitution directly contribute to gender inequality, and that general feminist political action should be expanded to include active opposition to prostitution.
Sex tourism is also problematic in its violation of several central human capabilities. Nussbaum’s Capability approach argues that every human being has ten central human capabilities. The men, women, and children involved in prostitution and forced sex work are often considered to be lacking one or more of these capabilities. This is because their placement in these occupations are often driven by poverty and lack of economic opportunity, and by engaging in sex work they lose the right to dictate matters of their own sexuality and sexual health. This specifically is considered to violate the capability of bodily integrity.
Prostitution laws across the globe
Prostitution legal and regulated Prostitution (the exchange of sex for money) legal, but organized activities such as brothels and pimping are illegal; prostitution is not regulated Illegal to buy sex or to organize it. Selling sex is no criminal offence. Prostitution illegal No data-
 Prostitution in North America
Prostitution in North America
-
 Prostitution in South America
Prostitution in South America
-
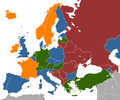 Prostitution in Europe
Prostitution in Europe
-
Prostitution in Asia
-
Prostitution in Africa
-
 Prostitution in Australia
Prostitution in Australia
Prostitution is also legal and regulated in New Zealand (map not shown). Prostitution is illegal in India. Prostitutes are highly punished if known under the Law.
The picture shows that in Taiwan prostitution is legal, but it is in fact illegal.
See also
- Sex Trafficking
- Cuban jineterismo
- Prostitution by country
- Prostitution in Germany
- Prostitution in the United Kingdom
- Prostitution law
- Zoophilia and the law
References
- Marina Diotallevi, ed. (17–22 October 1995). WTO Statement On The Prevention Of Organized Sex Tourism. Cairo (Egypt): World Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 14 August 2003. Retrieved 24 December 2014.
Adopted by the General Assembly of the World Tourism Organization at its eleventh session - Cairo (Egypt), 17–22 October 1995 (Resolution A/RES/338 (XI))
{{cite conference}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - Hannum, Ann Barger (2002). "Sex Tourism in Latin America". ReVista: Harvard Review of Latin America (Winter). Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA: Harvard University. Retrieved 6 October 2011.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|month=(help) - "La explotación sexual de menores en Kenia alcanza una dimensión horrible" (PDF) (in French). Spain: Unicef España. 17 January 2007. Retrieved 6 October 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - "Brazil". The Protection Project. Archived from the original on 20 December 2006. Retrieved 20 December 2006.
Brazil is a major sex tourism destination. Foreigners come from Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Spain, Latin America, and North America ...
{{cite web}}:|archive-date=/|archive-url=timestamp mismatch; 28 September 2007 suggested (help) - Gentile, Carmen J. (2 February 2006). "Brazil cracks down on child prostitution". San Francisco Chronicle. Chronicle foreign service.
... young prostitutes strut in front of middle-aged American and European tourists ...
- Kovaleski, Serge F. (2 January 2000). "Child Sex Trade Rises In Central America". Washington Post foreign service. Washington Post foreign service. Retrieved 20 December 2006.
... "an accelerated increase in child prostitution" in the country ... blamed largely on the unofficial promotion of sex tourism in Costa Rica over the Internet.
{{cite news}}: Check|archiveurl=value (help) - "Costa Rica" (PDF). The Protection Project. Retrieved 20 December 2006.
- Zúñiga, Jesús. "Cuba: The Thailand of the Caribbean". The New West Indian. Retrieved 20 December 2006.
- "Dominican Republic". The Protection Project. Archived from the original on 20 December 2006. Retrieved 20 December 2006.
The Dominican Republic is one of the most popular sex tourism destinations in the world, and it is advertised on the Internet as a "single man's paradise."
{{cite web}}:|archive-date=/|archive-url=timestamp mismatch; 28 September 2007 suggested (help) - Menon, Mandovi. "MensXP, Top 5 Sex Tourism Destinations". MensXP. Retrieved 8 December 2013.
- Scheeres, Julia (7 July 2001). "The Web, Where 'Pimps' Roam Free". Wired News. CondéNet. Retrieved 20 December 2006.
- Hughes, Dana. "Sun, Safaris and Sex Tourism in Kenya". Travel. ABC News. Retrieved 25 October 2008.
Tourists Gone Wild: 'They Come Here They Think "I Can Be Whatever I Want to Be" and That's How They Behave'
- Cruey, Greg. "Thailand's Sex Industry". About: Asia For Visitors. About (the New York Times Co.). Retrieved 20 December 2006.
Nowhere else is it so open and prevalent. Individual cities or regions have acquired a reputation as sex tourist destinations. Many of these have notable red-light districts, including de Wallen in Amsterdam, the Netherlands, Zona Norte in Tijuana, Mexico, Boy's Town in Nuevo Laredo, Mexico, Fortaleza and Rio de Janeiro in Brazil, Bangkok, Pattaya and Phuket in Thailand,
- Taylor, Jacqueline. "Child Prostitution and Sex Tourism CUBA" (PDF). Department of Sociology, University of Leicester, UK. ECPAT International. Retrieved September 1995.
In Cuba, the link between tourism and prostitution is perhaps more direct than in any other country which hosts sex tourists
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - Sex and Drug Parties in Bali?
- Bali's 'Gigolos,' Carefree Sex Industry Lead to HIV Crisis
- Clarke, Jeremy (25 November 2007). "Older white women join Kenya's sex tourists". Reuters. Retrieved 30 November 2007.
- Women going on sex tours look for big bamboos and Marlboro men, Pravda.Ru
- Bali Beach Gigolos Under Fire. Asia Sentinel, 4 May 2010
- ^ Lovelock, Brent; Lovelock, Kirsten M. (2013). The Ethics of Tourism: Critical and Applied Perspectives. Routledge.
- ^ United Nations Convention Against Transnational Organized Crime and the Protocols Thereto. Vienna: United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. 2004.
- ^ Global Report on Trafficking in Persons. Vienna: The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. 2014.
- ^ "Percentage of Men (by Country) Who Paid for Sex at Least Once: The Johns Chart". ProCon.org. ProCon. Retrieved 29 March 2015.
- ^ Samarasinghe, Vidyamali (2008). Female Sex Trafficking in Asia: The Resilience of Patriarchy in a Changing World. New York and London: Routledge.
- ^ McPhee, Duncan. Sex Offending and Sex Tourism: Problems, Policy, and Challenges. Palgrave Studies in Risk, Crime and Society.
- Taylor, Jacqueline Sánchez (May 2000). "Chapter 3: Tourism and 'embodied' commodities: sex tourism in the Caribbean". In Clift, Stephen; Carter, Simon (eds.). Tourism and Sex: Culture, Commerce and Coercion. Tourism, Leisure and Recreation. Continuum International Publishing Group. pp. 41–53. ISBN 1-85567-549-8.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - Bender, Kimberly. "The Implications of Sex Tourism on Men's Social, Psychological, and Physical Health" (PDF).
- "BangkokPod Interviews Kaewmala of Thai Sex Talk". Retrieved 11 December 2012.
- "OPEN-ENDED PROSTITUTION AS A SKILLFUL GAME OF LUCK: OPPORTUNITY, RISK AND SECURITY AMONG TOURIST-ORIENTED PROSTITUTES IN BANGKOK". Erik Cohen Department of Sociology and Social-Anthropology Hebrew University of Jerusalem.
- ^ Patil, Vrushali (2011). "Reproducing-Resisting Race and Gender Difference: Examining India's Online Tourism Campaign from a Transnational Feminist Perspective". Signs. 37 (1): 185–210. doi:10.1086/660181.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ Mahler, Karen (1997). "Global Concern for Children's Rights: The World Congress Against Sexual Exploitation". International Family Planning Perspectives. 23 (2): 79–84. doi:10.2307/2950828.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - "Report of the Special Rapporteur on the sale of children, child prostitution and child pornography, Najat Maalla M'jid" (PDF). United Nations General Assembly. 24 December 2012. Retrieved 4 September 2014.: "commercial sexual exploitation of children (CSEC) ... It is estimated that CSEC is worth 20 billion USD a year, according to ECPAT. Child abuse images were estimated being worth $3 billion annually in 2006. In 2009, they were estimated to be worth around $20 billion, showing thus a very worrying escalation."
- Janet Bagnall (2007). "Sex trade blights the lives of 2 million children; Canada is not doing enough to fight the international scourge of sex tourism". Montreal Gazette.
- "Child Sex Tourism". ECPAT International. Retrieved 3 July 2013.
- Chaninat & Leeds (3 September 2009). "US Sex Laws Abroad: The Long Arm of Uncle Sam". Sex Laws in Thailand, Part 1. Thailand Law Forum. Retrieved 7 October 2011.
- "The Crisis of Child Sexual Exploitation in Brazil: Between 250,000 and 2 million children forced into prostitution in Brazil". Libertad Latina. Retrieved 7 October 2011.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|month=(help) - ^ Guzder, Deena (30 August 2009). "Local Thai NGOs discuss efforts to end commercial sexual exploitation". Pulitzer Center on Crisis Reporting. Retrieved 6 October 2011.
- ^ Bang, Brandy; Baker, Paige L.; Carpinteri, Alexis; Van Hasselt, Vincent B. (2014). Commercial Sexual Exploitation of Children. Springer.
- ^ Berry, Kathleen (1994). The Prostitution of Sexuality. New York: NYU Press.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ Nussbaum, Martha C. (2011). Creating Capabilities: The Human Development Approach (1st ed.). Belknap Press.
External links
- Franck Michel, « Vers un tourisme sexuel de masse ? », "Mass-marketing sex tourism", "Sex tourism example"
Categories: