| Albinism–deafness syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Woolf syndrome and Ziprkowski–Margolis syndrome |
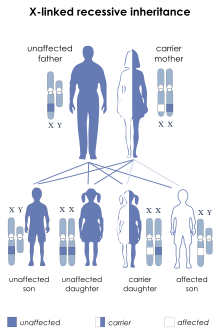 | |
| Albinism–deafness syndrome is inherited in an X-linked recessive manner | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
Albinism–deafness syndrome is a condition characterized by congenital neural deafness and a severe or extreme piebald-like phenotype with extensive areas of hypopigmentation.
A locus at Xq26.3-q27.I has been suggested.
It has been suggested that it is a form of Waardenburg syndrome type II.
See also
References
- Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. p. 928. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
- Shiloh Y, Litvak G, Ziv Y, et al. (July 1990). "Genetic mapping of X-linked albinism-deafness syndrome (ADFN) to Xq26.3-q27.I". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 47 (1): 20–7. PMC 1683749. PMID 2349949.
- Zlotogora J (November 1995). "X-linked albinism-deafness syndrome and Waardenburg syndrome type II: a hypothesis". Am. J. Med. Genet. 59 (3): 386–7. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320590321. PMID 8599367.
External links
| Classification | D |
|---|---|
| External resources |
| Pigmentation disorders/Dyschromia | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypo-/ leucism |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Hyper- |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Dyschromia | |||||||||||||||||||||
| See also | |||||||||||||||||||||
This Genodermatoses article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |