| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Potassium sulfite | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.279 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
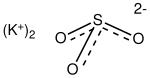
| Chemical formula | K2SO3 |
| Molar mass | 158.26 g/mol |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 2.49 g/cm |
| Solubility in water | Soluble |
| Acidity (pKa) | 8 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | −64.0·10 cm/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Potassium sulfate Potassium selenite |
| Other cations | Sodium sulfite |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Potassium sulfite is the inorganic compound with the formula K2SO3. It is the salt of potassium cation and sulfite anion. It is a white solid that is highly soluble in water. Potassium sulfite is used for preserving food and beverages.
History
Potassium sulfite was first obtained by Georg Ernst Stahl in the early 18th century, and was therefore known afterwards as Stahl's sulphureous salt. It became the first discovered sulfite and was first properly studied along with other sulfites by French chemists in the 1790s, and it was called sulphite of potash in the early 19th century. Gilles-François Boulduc also discovered the salt in water of Passy in the 1720s.
Production and reactions
Main article: Sulfite § Reactions See also: Wellman–Lord processPotassium sulfite is produced by the thermal decomposition of potassium metabisulfite at 190 °C:
- K2S2O5 → K2SO3 + SO2
Structure
The structure of solid K2SO3, as assessed by X-ray crystallography. The S-O distances are 1.515 Å, and the O-S-O angles are 105.2°
References
- ^ Andersen, Leif; Strömberg, Dan; Nevala, H.; Pohjola, S.; Niinistö, Lauri; Volden, Hans V.; Weidlein, Johann; Zingaro, Ralph A. (1986). "The Structure of Potassium Sulfite". Acta Chemica Scandinavica. 40a: 479–480. doi:10.3891/acta.chem.scand.40a-0479.
- "Potassium sulfite (225)". Codex Alimentarius. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
- Coleby, L. J. M. (1938). Studies in the chemical works of Stahl (Doctoral thesis). University of London. pp. 57–63, 181.
- Thomson, Thomas (1807). System of Chemistry.
- Chang, Ku-ming (Kevin) (2014). "Communications of Chemical Knowledge: Georg Ernst Stahl and the Chemists at the French Academy of Sciences in the First Half of the Eighteenth Century". Osiris. 29 (1): 135–157. doi:10.1086/678101. ISSN 0369-7827.
- Johnstone, H. F. (1946). "Sulfites and Pyrosulfites of the Alkali Metals". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 2. pp. 162–167. doi:10.1002/9780470132333.ch49. ISBN 9780470132333.
| Potassium compounds | |
|---|---|
| H, (pseudo)halogens | |
| chalcogens | |
| pnictogens | |
| B, C group | |
| transition metals | |
| organic | |
| Compounds containing the sulfite group (SO2−3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This inorganic compound–related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |