| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
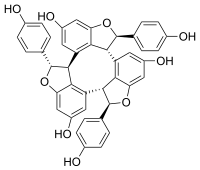
| Preferred IUPAC name (1R,5bR,6R,10bS,11S,15bR)-1,6,11-Tris(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,5b,6,10b,11,15b-hexahydrocyclononatris(benzofuran)-4,9,14-triol | |
| Other names α-Viniferin; (+)-α-Viniferin | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C42H30O9 |
| Molar mass | 678.693 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
α-Viniferin is a stilbene trimer. It can be isolated from Caragana chamlagu and from Caragana sinica and from the stem bark of Dryobalanops aromatica. It is also present in relation to resistance to Botrytis cinerea and Plasmopara viticola in Vitis vinifera and Vitis riparia. It has been shown to inhibit acetylcholinesterase.
References
- ^ Sung, Sang Hyun; Kang, So Young; Lee, Ki Yong; Park, Mi Jung; Kim, Jeong Hun; Park, Jong Hee; Kim, Young Chul; Kim, Jinwoong; Kim, Young Choong (2002). "(+)-α-Viniferin, a Stilbene Trimer from Caragana chamlague, Inhibits Acetylcholinesterase". Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 25 (1): 125–127. doi:10.1248/bpb.25.125. PMID 11824541.
- Shu, N; Zhou, H; Hu, C (2006). "Simultaneous determination of the contents of three stilbene oligomers in Caragana sinica collected in different seasons using an improved HPLC method". Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 29 (4): 608–12. doi:10.1248/bpb.29.608. PMID 16595888.
- Wibowo, A.; Ahmat, N.; Hamzah, A.S.; Sufian, A.S.; Ismail, N.H.; Ahmad, R.; Jaafar, F.M.; Takayama, H. (2011). "Malaysianol A, a new trimer resveratrol oligomer from the stem bark of Dryobalanops aromatica". Fitoterapia. 82 (4): 676–81. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2011.02.006. PMID 21338657.
- Disease resistance of Vitis spp. and the production of the stress metabolites resveratrol, epsilon -viniferin, alpha -viniferin and pterostilbene. Langcake P, Physiological Plant Pathology, 1981, Vol. 18, No. 2, pages 213-226 (abstract Archived 2014-12-10 at the Wayback Machine)
| Oligostilbenoids and their glycosides | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimers |
| ||||||||||||
| Trimers | |||||||||||||
| Tetramers: |
| ||||||||||||
| Higher polymers (five units or more) |
| ||||||||||||
| Oligomeric forms of resveratrol |
| ||||||||||||
| Glycosides or conjugates |
| ||||||||||||
This article about an aromatic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |