| This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (September 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Selz | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Rhineland-Palatinate |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Donnersbergkreis |
| • elevation | 321 m (1,053 ft) |
| Mouth | |
| • location | Rhine at Ingelheim |
| • coordinates | 49°59′45″N 8°1′33″E / 49.99583°N 8.02583°E / 49.99583; 8.02583 |
| Length | 63 km (39 mi) |
| Basin size | 375 km (145 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| • average | 0.77 m/s (27 cu ft/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Progression | Rhine→ North Sea |
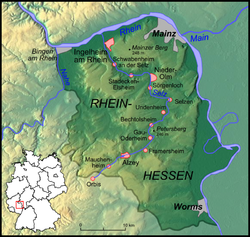
The Selz is a river in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, and a left hand tributary of the Rhine. It flows through the largest German wine region, Rheinhessen (Rhenish Hesse).
It rises near the village of Orbis in the county of Donnersbergkreis, crosses the border from the Palatinate into Rhenish Hesse and after about 8 kilometres (5 mi) the town of Alzey in the Alzey-Worms district. There the river passes a pond, and disappears underground, flowing through ditches under the town. On its way it passes through Gau-Odernheim, Nieder-Olm and Ingelheim, before finally discharging into the Rhine in Frei-Weinheim [de; eo], a district of Ingelheim.
The Selz has a catchment area of 375 square kilometres (145 sq mi) characterised by a warm, dry climate with an average annual precipitation of around 500 millimetres (20 in). Despite its low, and often irregular water flow, the Selz is regarded as the main river in the rather dry rolling countryside of Rhenish Hesse. During periods of low water, its waters consist of a significant amount of clean effluent from sewage farms.
Environmental restoration
For a number of decades of the 20th century there was a lot canalisation of rivers and streams in Germany. As a result of this river straightening process that was carried out between 1958 and 1963, the Selz stream was constricted between embankments and flows in a relatively meandering course through the plain between the famous rolling hills of Rhenish Hesse. In order to prevent river bed degradation and to improve both biodiversity and flood protection, the local nature conservation association (Selztalverband) and the district of Mainz-Bingen managed a revitalization of the Selz over a considerable length between Hahnheim, Undenheim and Sörgenloch.
The loss of the floodplain and shorter sections of river caused higher water levels and risk of flood than in the past. Some floods that nearly caused a disaster were the reason for a restoration concept. The concept includes flood protection, river bed stabilization and renaturization measures. The main objectives are:
- flood protection up to a 100-year flood
- improvement of the ecological situation
- stabilizing river bed/erosion control
- stabilizing groundwater level
Floodplains have been widened to between 50 and 100 metres (160 and 330 ft). Nature is allowed to develop undisturbed in biotopes, which protect and promote the biodiversity of the landscape with its meadows, ditches, bank slopes, marsh areas, wetland, Phragmites, willows, hedges and boundary ridges. During the past 25 years, the village of Hahnheim has planted 27,000 trees and hedges along the Selz within its boundaries.
Since the Selz renaturation project covers several miles of the Selz's riverbank, it has increased the overall length of the river.
Tributaries
Settlements



The following villages and towns are located on the Selz (from source to mouth):
- Orbis
- Morschheim
- Mauchenheim
- Alzey
- Alzey-Schafhausen [de]
- Framersheim (confluence of Weidas and Selz)
- Gau-Köngernheim [de]
- Gau-Odernheim
- Bechtolsheim
- Undenheim
- Friesenheim
- Köngernheim
- Selzen
- Hahnheim
- Sörgenloch
- Nieder-Olm, the reason for the foundation of Nieder-Olm is given by the passage of an old Roman road over the Selz river which led to the Roman camps around Mainz and the city itself.
- Stadecken-Elsheim
- Bubenheim
- Schwabenheim an der Selz
- Großwinternheim [de; eo]
- Ingelheim am Rhein
Cycle track

A signposted cycle track along the Selz, the Selztalradweg, does partially use two old railway tracks of the Amiche [de] and Zuckerlottche [de]. Both trackbeds now have a tarmac surface. Sometimes the cycle path along the river bed may be used in dry weather. Both routes are covered by tall trees, shading the cycleway from the hot sun.
See also
External links
- restoring Selz River Archived 2004-12-21 at the Wayback Machine
- "pathways along the Selz" (PDF). (3.37 MB)
| Baltic Sea | |
|---|---|
| Black Sea | |
| North Sea | |
| Maas | |
