| |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Lotemax |
| Other names | 11β,17α,Dihydroxy-21-oxa-21-chloromethylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione 17α-ethylcarbonate |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Routes of administration | Eye drops |
| Drug class | Corticosteroid; glucocorticoid |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | None |
| Protein binding | 95% |
| Metabolism | Ester hydrolysis |
| Metabolites | Δ-cortienic acid and its etabonate |
| Onset of action | ≤2 hrs (allergic conjunctivitis) |
| Elimination half-life | 2.8 hrs |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.167.120 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C24H31ClO7 |
| Molar mass | 466.96 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 220.5 to 223.5 °C (428.9 to 434.3 °F) |
| Solubility in water | 0.0005 mg/mL (20 °C) |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
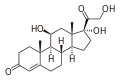
Loteprednol (synthesized as the ester loteprednol etabonate) is a topical corticosteroid used to treat inflammations of the eye. It is marketed by Bausch and Lomb as Lotemax and Loterex.
It was patented in 1980 and approved for medical use in 1998. It is available as a generic medication.
Medical uses
Applications for this drug include the reduction of inflammation after eye surgery, seasonal allergic conjunctivitis, uveitis, and chronic forms of keratitis - such as adenoviral, Thygeson's keratitis, vernal keratoconjunctivitis,pingueculitis, giant papillary conjunctivitis, and episcleritis.
Contraindications
Contraindications: As corticosteroids are immunosuppressive, loteprednol is contraindicated in patients with viral, fungal or mycobacterial infections of the eye.
Adverse effects
The most common adverse effects in patients being treated with the gel formulation are anterior chamber inflammation (in 5% of people), eye pain (2%), and foreign body sensation (2%).
Interactions
Because long term use (more than 10 days) can cause increased intraocular pressure, loteprednol may interfere with the treatment of glaucoma. Following ocular administration, the drug is very slowly absorbed into the blood, therefore the blood level is limited to an extremely small concentration, and interactions with drugs taken by mouth or through any route other than topical ophthalmic are very unlikely.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of action
Main article: Glucocorticoid § Mechanism of actionCorticosteroids mediate their anti-inflammatory effects mainly through the modulation of the cytosolic glucocorticoid receptor (GR) at the genomic level. Preclinical studies demonstrated that loteprednol etabonate is highly lipophilic and has strong binding affinity to glucocorticoid receptors. After it binds to the GR in the cytoplasm, the activated corticosteroid-GR complex migrates to the nucleus, where it upregulates the expression of anti-inflammatory proteins and represses the expression of proinflammatory proteins. Corticosteroids inhibit inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, adhesion molecules, and other inflammatory mediators. They also reduce synthesis of histamine, stabilize cell membranes, and inhibit degranulation of mast cells. Recent work suggests that the activated corticosteroid-GR complex also elicits nongenomic effects, particularly the inhibition of vasodilation, vascular permeability, and migration of leukocytes.
Pharmacokinetics
Neither loteprednol etabonate nor its inactive metabolites Δ-cortienic acid and Δ-cortienic acid etabonate are detectable in the bloodstream, even after oral administration. A study with patients receiving loteprednol eye drops over 42 days showed no adrenal suppression, which would be a sign of the drug reaching the bloodstream to a clinically relevant extent.
Steroid receptor affinity was 4.3 times that of dexamethasone in animal studies.
Retrometabolic drug design
Loteprednol etabonate was developed using retrometabolic drug design. It is a so-called soft drug, meaning its structure was designed so that it is predictably metabolised to inactive substances. These metabolites, Δ-cortienic acid and its etabonate, are derivatives of cortienic acid, itself an inactive metabolite of hydrocortisone.
-
 Cortisol, a naturally occurring corticosteroid, known as hydrocortisone when used as a drug
Cortisol, a naturally occurring corticosteroid, known as hydrocortisone when used as a drug
-
 Δ-Cortienic acid, inactive metabolite of loteprednol
Δ-Cortienic acid, inactive metabolite of loteprednol
-
 Cortienic acid, inactive metabolite of hydrocortisone
Cortienic acid, inactive metabolite of hydrocortisone
Chemistry
Loteprednol etabonate is an ester of loteprednol with etabonate (ethyl carbonate). The pure chemical compound has a melting point between 220.5 °C (428.9 °F) and 223.5 °C (434.3 °F). Its solubility in water is 1:2,000,000, therefore it is formulated for ophthalmic use as either an ointment, a gel, or a suspension.
Loteprednol is a corticosteroid. The ketone side chain of classical corticosteroids such as hydrocortisone is replaced by a cleavable ester, which accounts for the rapid inactivation. (This is not the same as the etabonate ester.)


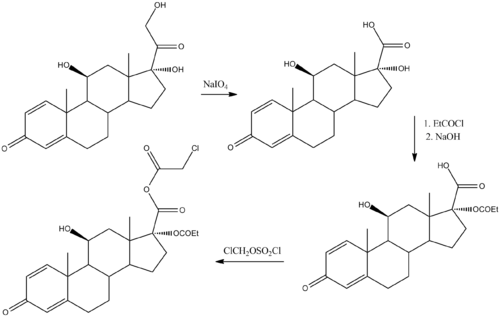
Chemical synthesis
| This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (June 2016) |
References
- "Prescription medicines: registration of new chemical entities in Australia, 2014". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 21 June 2022. Retrieved 10 April 2023.
- ^ Haberfeld H, ed. (2015). Austria-Codex (in German). Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag.
- Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 488. ISBN 9783527607495.
- "First Generic Drug Approvals 2023". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 30 May 2023. Archived from the original on 30 June 2023. Retrieved 30 June 2023.
- ^ Loteprednol Professional Drug Facts.
- Pavesio CE, Decory HH (April 2008). "Treatment of ocular inflammatory conditions with loteprednol etabonate". The British Journal of Ophthalmology. 92 (4): 455–459. doi:10.1136/bjo.2007.132621. PMID 18245274. S2CID 25873047.
- ^ Dinnendahl V, Fricke U (2008). Arzneistoff-Profile (in German). Vol. 6 (22 ed.). Eschborn, Germany: Govi Pharmazeutischer Verlag. ISBN 978-3-7741-9846-3.
- "Highlights of Prescribing Information: Lotemax" (PDF). 2012.
- Comstock TL, Decory HH (2012). "Advances in corticosteroid therapy for ocular inflammation: loteprednol etabonate". International Journal of Inflammation. 2012: 789623. doi:10.1155/2012/789623. PMC 3321285. PMID 22536546.
- Amon M, Busin M (October 2012). "Loteprednol etabonate ophthalmic suspension 0.5 %: efficacy and safety for postoperative anti-inflammatory use". International Ophthalmology. 32 (5): 507–517. doi:10.1007/s10792-012-9589-2. PMC 3459083. PMID 22707339.
- Sheppard JD, Comstock TL, Cavet ME (April 2016). "Impact of the Topical Ophthalmic Corticosteroid Loteprednol Etabonate on Intraocular Pressure". Advances in Therapy. 33 (4): 532–552. doi:10.1007/s12325-016-0315-8. PMC 4846687. PMID 26984315.
- Bodor N, Buchwald P (2002). "Design and development of a soft corticosteroid, loteprednol etabonate". In Schleimer RP, O'Byrne PM, Szefler SJ, Brattsand R (eds.). Inhaled Steroids in Asthma. Optimizing Effects in the Airways. Lung Biology in Health and Disease. Vol. 163. Marcel Dekker, New York. pp. 541–564.
- "Loteprednol (Professional Patient Advice)". Retrieved October 4, 2018.
- Pavesio CE, Decory HH (April 2008). "Treatment of ocular inflammatory conditions with loteprednol etabonate". The British Journal of Ophthalmology. 92 (4): 455–459. doi:10.1136/bjo.2007.132621. PMID 18245274. S2CID 25873047.
- Druzgala P, Hochhaus G, Bodor N (February 1991). "Soft drugs--10. Blanching activity and receptor binding affinity of a new type of glucocorticoid: loteprednol etabonate". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 38 (2): 149–154. doi:10.1016/0960-0760(91)90120-T. PMID 2004037. S2CID 27107845.
Further reading
- Stewart R, Horwitz B, Howes J, Novack GD, Hart K (November 1998). "Double-masked, placebo-controlled evaluation of loteprednol etabonate 0.5% for postoperative inflammation. Loteprednol Etabonate Post-operative Inflammation Study Group 1". Journal of Cataract and Refractive Surgery. 24 (11): 1480–1489. doi:10.1016/s0886-3350(98)80170-3. PMID 9818338. S2CID 24423725.
| Glucocorticoids and antiglucocorticoids (D07, H02) | |
|---|---|
| Glucocorticoids | |
| Antiglucocorticoids |
|
| Synthesis modifiers | |
| |