 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Depo-Medrol, Depo-Medrate, Depo-Medrone, others |
| Other names | Depot methylprednisolone acetate; Methylprednisolone 21-acetate; 6α-Methylprednisolone 21-acetate; NSC-48985 |
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection |
| Drug class | Corticosteroid; Glucocorticoid |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.157 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
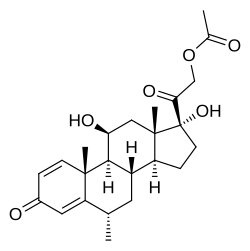
| Formula | C24H32O6 |
| Molar mass | 416.514 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Methylprednisolone acetate, sold under the brand names Depo-Medrol among others, is a synthetic glucocorticoid corticosteroid and a corticosteroid ester—specifically the C21 acetate ester of methylprednisolone—which is used in clinical and veterinary medicine. It has been formulated as an aqueous suspension for intramuscular, intra-articular, soft tissue, and intralesional injection alone and in combination with lidocaine, a local anesthetic. Methylprednisolone acetate was previously suspended with polyethylene glycol but is no longer formulated with this excipient due to concerns about possible toxicity. Depo methylprednisolone acetate is a depot injection and is absorbed slowly with a duration of weeks to months with a single intramuscular injection.
See also
References
- ^ "Depo-Medrol- methylprednisolone acetate injection, suspension". DailyMed. 18 January 2019. Retrieved 19 February 2020.
- Elks J (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 811–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. 2000. pp. 675–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- ^ Muller NF, Dessing RP, eds. (19 June 1998). European Drug Index: European Drug Registrations (Fourth ed.). CRC Press. pp. 337–. ISBN 978-3-7692-2114-5.
- ^ Plumb DC (21 February 2018). Plumb's Veterinary Drug Handbook: Pocket. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 1088–1091. ISBN 978-1-119-34649-4.
- ^ Lennard TA, Vivian DG, Walkowski, Singla AK (11 June 2011). Pain Procedures in Clinical Practice E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 8–. ISBN 978-1-4377-3774-5.
- Scott DW, Miller Jr WH (1 December 2010). Equine Dermatology - E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 122–. ISBN 978-1-4377-0921-6.
- Canale ST, Beaty JH (29 October 2012). Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 1906–. ISBN 978-0-323-08718-6.
| Glucocorticoids and antiglucocorticoids (D07, H02) | |
|---|---|
| Glucocorticoids | |
| Antiglucocorticoids |
|
| Synthesis modifiers | |
| |
This article about a steroid is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |